The London (dispersion) forces are weakest for which of the following gases under the same conditions of temperature and pressure?
A. H2
B. O2
C. Xe
D. F2
A. H2
London dispersion forces strength is primarily determined by the size and polarizability of the molecule. The larger the molecule and the more electrons it has, the stronger the dispersion forces.
A sample of a hard, solid binary compound at room temperature did not conduct electricity as a pure solid but became highly conductive when dissolved in water. Which of the following types of interactions is most likely found between the particles in the substance?
A. Ionic Bonds
B. Metallic Bonds
C. Covalent Bonds
D. Hydrogen Bonds
A. Ionic Bonds
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in their solid state because the ions are held in a fixed, rigid crystal lattice structure and cannot move freely to carry an electrical current.
- When dissolved in water, the strong electrostatic forces of the ionic bonds are overcome by interactions with the polar water molecules, allowing the ions to dissociate and move freely in the solution.
- This mobility of ions in the aqueous solution enables the substance to become highly conductive of electricity.
Of the following, the best explanation for the fact that most gases are easily compressed is that the molecules in a gas...
A. are in constant motion
B. are relatively far apart
C. have relatively small masses
D. have a real, nonzero volume
B. are relatively far apart
Gases are easily compressed because there are large amounts of empty space between their molecules. When pressure is applied, this empty space allows the molecules to be forced closer together, significantly reducing the volume of the gas.
At standard temperature and pressure, a 0.50 mol sample of H2 gas and a separate 1.0 mol sample of O2 gas have the same...
A. average molecular kinetic energy
B. average molecular speed
C. volume
D. density
A. average molecular kinetic energy
Since both gas samples (H₂ and O₂) are at standard temperature and pressure (STP), they have the same temperature. Therefore, despite having different molar masses and different numbers of moles, their average molecular kinetic energy must be the same.
If 50.mL of 1.0M NaOH is diluted with distilled water to a volume of 2.0L, the concentration of the resulting solution is...
A. 0.025 M
B. 0.050 M
C. 0.10 M
D. 0.50 M
A. 0.025 M
M1V1 = M2V2
M2 = (M1V1)/V2
Which of the following questions about the components in a mixture could be investigated with a paper chromatography experiment?
A. Do the components have different densities?
B. Do the components have different molecular masses?
C. Do the components have different molecular polarities?
D. Do the components have different average molecular speeds?
C. Do the components have different molecular polarities?
Paper chromatography is a technique for separating components of a mixture based on differences in their attraction to the stationary phase and to the moving solvent phase (which has a different polarity from the stationary phase). The separations rely on the relative attraction between the components of the mixture and the stationary and mobile phases. Components that are more attracted to the stationary phase move more slowly, and components that have a polarity more similar to the mobile phase move more quickly.
In an experiment, a photon with a frequency of 7 x 1014 s-1 was absorbed by a sample. What is the approximate energy of this photon?
A. 5 x 10-19 J
B. 1 x 10-15 J
C. 2 x 106 J
D. 1 x 1048 J
A. 5 x 10-19 J
E = hv
O2, H2O, C3H8, CF4
Of the substances listed above, which has the highest boiling point and why?
A. O2, because its molecules have a double bond between the oxygen atoms.
B. H2O, because hydrogen bonds form between its molecules.
C. C3H8, because multiple hydrogen bonds can form between its molecules.
D. CF4, because its molecules have the largest dipole moment, since C-F bonds are highly polar.
B. H2O, because hydrogen bonds form between its molecules.
The substance with the highest boiling is the substance with the strongest intermolecular forces. Hydrogen bonding is the strongest intermolecular force for small molecules, and H2O is the only substance listed that exhibits hydrogen bonding; therefore, H2O has the highest boiling point.
At room temperature I2(s) is a molecular solid. Which of the following provides a characteristic of I2(s) with a correct explanation?
A. It has a high melting point because it has weak intermolecular forces.
B. It is hard because it forms a three-dimensional covalent network.
C. It is not a good conductor of electricity because its valence electrons are localized in bonding and nonbonding pairs.
D. It is very soluble in water because its molecules are polar.
C. It is not a good conductor of electricity because its valence electrons are localized in bonding and nonbonding pairs.
Iodine (I2) is a molecular solid, meaning it consists of discrete, nonpolar I2 molecules held together by relatively weak London dispersion forces.
- Electrical Conductivity: In solid iodine, the valence electrons are localized within the covalent bonds of each I2 molecule and in nonbonding pairs (lone pairs). There are no free-moving ions or delocalized electrons throughout the solid structure that could carry an electrical current, making it a poor conductor (an insulator).
When a sample of oxygen in a closed container of constant volume is heated until its absolute temperature is doubled, which of the following is also doubled?
A. The pressure of the gas
B. The average velocity of the gas molecules
C. The number of molecules per cm3
D. The potential energy of the molecules
A. The pressure of the gas
According to Gay-Lussac's Law and the ideal gas law (PV=nRT), for a fixed amount of gas in a closed container of constant volume, the pressure (P) is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (T) (in Kelvin).
This relationship is expressed as:
P1/T1 = P2/T2
If the absolute temperature (T) is doubled from T1 to T2 = 2T1, the pressure must also double to P2 = 2P1 to maintain the constant ratio.
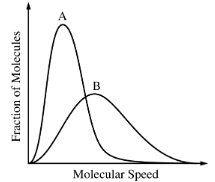 The Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions of molecular speeds in samples of two different gases at the same temperature are shown above. Which gas has the greater molar mass?
The Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions of molecular speeds in samples of two different gases at the same temperature are shown above. Which gas has the greater molar mass?
A. Gas A
B. Gas B
C. Both gases have the same molar mass
D. It cannot be determined unless the pressures of each sample is known
A. Gas A
The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve shows the fraction of molecules at various molecular speeds. The peak of the curve represents the most probable speed of the gas molecules at a given temperature. The question states both gases are at the same temperature.
At a constant temperature, all gas molecules have the same average kinetic energy. The kinetic energy (KE) of a molecule is given by the formula KE = 1/2 mv2, where m is the mass and v is the velocity.
For different gases at the same temperature, their average kinetic energies are equal. Therefore, heavier gas molecules (higher molar mass, M) will have lower average speeds, while lighter gas molecules will have higher average speeds.
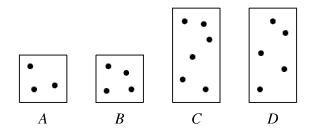 The diagrams above represent aqueous solutions of compound X at various molarities. Each dot represents one mole of the solute, and the volume of the solution in the large boxes is twice the volume in the small boxes. Which solution has the highest molarity?
The diagrams above represent aqueous solutions of compound X at various molarities. Each dot represents one mole of the solute, and the volume of the solution in the large boxes is twice the volume in the small boxes. Which solution has the highest molarity?
B
Molarity of solution is box A: 3/V
Molarity of solution is box B: 4/V
Molarity of solution is box C: 6/2V = 3/V
Molarity of solution is box D: 5/2V = 2.5/V
Of the following organic compounds, which is LEAST soluble in water at 298K?
A. CH3CH2CH2OH, 1-propanol
B. C6H14, hexane
C. C6H12O6, glucose
D. CH3COOH, ethanoic (acetic) acid
B. C6H14, hexane
"Like dissolves like" - water is a polar solvent and dissolves polar substances the best. You are looking for the opposite.
Hexane (C₆H₁₄) is a nonpolar hydrocarbon. It lacks polar functional groups (like -OH or -COOH) and cannot form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Its nonpolar nature makes it immiscible (or very poorly soluble) in the polar water solvent, making it the least soluble among the options provided.
Humans are warned to shield their eyes from ultraviolet radiation with wavelengths shorter than 300nm but not from infrared radiation with wavelengths of about 900nm. Which of the following explains the reason for this based on what happens at the molecular level with exposure to these types of radiation?
A. 900nm radiation has triple the energy of 300nm radiation, so infrared radiation is more likely to promote electrons or break covalent bonds.
B. 900nm radiation has one-third the energy of 300nm radiation, so infrared radiation is more likely to cause molecular rotation to occur.
C. 300nm radiation has triple the energy of 900nm radiation, so ultraviolet radiation is more likely to promote electrons or break covalent bonds.
D. 300nm radiation has one-third the energy of 900nm radiation, so ultraviolet radiation is more likely to cause molecular vibration to occur.
C. 300nm radiation has triple the energy of 900nm radiation, so ultraviolet radiation is more likely to promote electrons or break covalent bonds.
E = hv and c = νλ, so E = hc/λ. Radiation with a wavelength of 300nm therefore has three times as much energy as radiation with a wavelength of 900nm. Ultraviolet/visible radiation is associated with transitions in electronic energy levels and breaking covalent bonds.
At 298K and 1 atm, Br2 is a liquid and I2 is a crystalline solid. Which of the following statements best explains the different physical states of Br2 and I2 at 298K and 1 atm?
A. The London dispersion forces among I2 molecules are stronger than those among Br2 molecules.
B. The London dispersion forces among Br2 molecules are stronger than those among I2 molecules.
C. The Br-Br bond is stronger than the I-I bond.
D. The I-I bond is stronger than the Br-Br bond.
A. The London dispersion forces among I2 molecules are stronger than those among Br2 molecules.
Both Br2 and I2 experience only London dispersion forces. There are greater London dispersion forces between I2 molecules than between Br2 molecules because I2 molecules have larger, more polarizable electron clouds. This results in I2 being a solid while Br2 is a liquid.
Which statement best helps to explain the observation that NH3(l) boils at -28oC, whereas PH3(l) boils at -126oC?
A. The dispersion forces in NH3 are weaker than the dispersion forces in PH3.
B. The dispersion forces in NH3 are stronger than the dipole-dipole forces in PH3.
C. NH3 has hydrogen bonding that is stronger than the dipole-dipole forces in PH3.
D. NH3 has hydrogen bonding that is weaker than the dipole-dipole forces in PH3.
C. NH3 has hydrogen bonding that is stronger than the dipole-dipole forces in PH3.
It is the hydrogen bonding between molecules of NH3 that results in its boiling point being higher than the boiling point of PH3. The presence of strong hydrogen bonds in NH₃ means more energy is required to transition from a liquid to a gas phase compared to the weaker forces in PH₃. This results in NH₃ having a much higher boiling point (-28°C) than PH₃ (-126°C).
When 4.0L of He(g), 6.0L of N2(g), and 10.L of Ar(g), all at 0oC and 1.0atm, are pumped into an evacuated 8.0L rigid container, the final pressure in the container at 0oC is...
A. 0.5 atm
B. 1.0 atm
C. 2.5 atm
D. 4.0 atm
C. 2.5 atm
Step 1: Calculate the partial pressure of each gas. Use Boyle's Law P1V1 = P2V2. P2=(P1V1)/V2. P1 = 1.0atm for all 3. V2 = 8.0L for all 3. V1 = given value from problem.
Step 2: Sum partial pressures to find total pressure. Use Dalton's Law of partial pressures: Ptotal = P2,He + P2,N2 + P2,Ar
To flexible containers for gases are at the same temperature and pressure. One holds 0.50 gram of hydrogen and the other holds 8.0 grams of oxygen. Which of the following statements regarding these gas samples is FALSE?
A. The volume of the hydrogen container is the same as the volume of the oxygen container.
B. The number of molecules in the hydrogen container is the same as the number of molecules in the oxygen container.
C. The average kinetic energy of the hydrogen molecules is the same as the average kinetic energy of the oxygen molecules.
D. The average speed of the hydrogen molecules is the same as the average speed of the oxygen molecules.
D. The average speed of the hydrogen molecules is the same as the average speed of the oxygen molecules.
- The problem states that both gases are at the same temperature and pressure.
- Average kinetic energy of gas molecules depends only on the absolute temperature. Since the temperatures are the same, the average kinetic energy for both gases is the same, making statement C true.
- The number of moles of each gas can be calculated using their molar masses (Hydrogen H₂ ≈ 2 g/mol; Oxygen O₂ ≈ 32 g/mol):
- Moles of H₂ = 0.50 g / 2 g/mol = 0.25 moles.
- Moles of O₂ = 8.0 g / 32 g/mol = 0.25 moles.
- According to Avogadro's law, equal moles of gases at the same temperature and pressure occupy equal volumes and contain the same number of molecules. This makes statements A and B true.
- The average speed of gas molecules (root mean square speed) is inversely proportional to the square root of their molar mass (vrms∝(1/mM)1/2). Since oxygen has a much larger molar mass than hydrogen, hydrogen molecules will move at a higher average speed. Therefore, the statement that their average speeds are the same is false.
How many moles of Na+ ions are in 100. mL of 0.100 M Na3PO4(aq)?
A. 0.300 mol
B. 0.100 mol
C. 0.0300 mol
D. 0.0100 mol
C. 0.0300 mol
Step 1: convert mL to L
Step 2: calculate moles of sodium phosphate using n = M x V
Step 3: determine moles of sodium ions. Na3PO4 --> 3Na+ + PO43-
This equation shows that 1 mole of produces 3 moles of Na+ ions. Use this stoichiometric ratio to find the moles of Na+ ions.
nNa+ = (Step 2 Answer) x (3 mol Na+ / 1 mol Na3PO4)
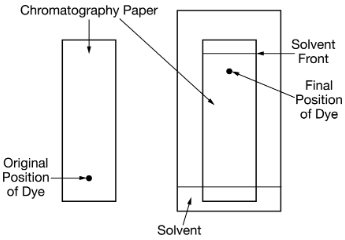 Based on the results of the paper chromatography experiment shown above, which of the following can be concluded about the dye?
Based on the results of the paper chromatography experiment shown above, which of the following can be concluded about the dye?
A. It has a small molar mass.
B. It has weak intermolecular forces.
C. It has a weaker attraction for the stationary phase that it has for the mobile phase.
D. It has a stronger attraction for the stationary phase than it has for the mobile phase.
C. It has a weaker attraction for the stationary phase that it has for the mobile phase.
- Components that travel further up the paper have a stronger affinity (attraction) for the mobile phase and a weaker attraction for the stationary phase. They move more quickly with the flowing solvent.
- Components that travel a shorter distance have a stronger attraction for the stationary phase and a weaker attraction for the mobile phase. They are "slowed down" by adhering to the paper.
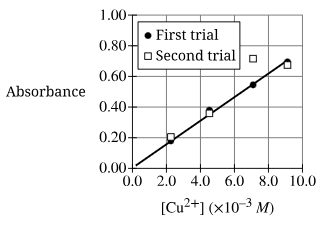 A student prepared four solutions of known [Cu2+] and measured the absorbance of each solution using the same cuvette. The graph shows the data for two absorbance measurements done for each solution. Which of the following identifies the most likely error that affected the absorbance recorded for the solution with [Cu2+] ≈ 7 x 10-3 M in the second trial?
A student prepared four solutions of known [Cu2+] and measured the absorbance of each solution using the same cuvette. The graph shows the data for two absorbance measurements done for each solution. Which of the following identifies the most likely error that affected the absorbance recorded for the solution with [Cu2+] ≈ 7 x 10-3 M in the second trial?
A. The cuvette was rinsed with water between measurements.
B. A fingerprint was left on the side of the cuvette facing the detector.
C. The absorbance was measured at a wavelength where Cu2+ has a lower molar absorptivity.
D. The cuvette was not filled with the same volume of solution.
B. A fingerprint was left on the side of the cuvette facing the detector.
The data show that the absorbance for the second trial at 7 x 10-3 M is too high relative to the remainder of the results. A fingerprint on the cuvette would result in an absorbance that is too high.
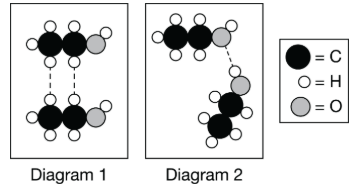 Which particle diagram shown above best represents the strongest intermolecular force between two ethanol, C2H6O, molecules?
Which particle diagram shown above best represents the strongest intermolecular force between two ethanol, C2H6O, molecules?
A. Diagram 1, because it shows hydrogen bonds forming between hydrogen atoms from different ethanol molecules.
B. Diagram 1, because it shows strong, directional dipole-dipole forces between two polar ethanol molecules.
C. Diagram 2, because it shows the formation of a hydrogen bond between an H atom bonded to an O atom with an O atom from another molecule.
D. Diagram 2, because it shows the dipole from an ethanol molecule inducing a dipole in another ethanol molecule.
C. Diagram 2, because it shows the formation of a hydrogen bond between an H atom bonded to an O atom with an O atom from another molecule.
Hydrogen bonding is the strongest attractive force between ethanol molecules. It requires an atom to be bonded to a small atom with a high electronegativity, like F, O, or N. The hydrogen bond forms between atoms with partial positive and partial negative charges. In the O-H bond, the H atom has a partial positive charge, and the O atom has a partial negative charge. The hydrogen bond is formed between O-H -- O-H bonds from different molecules, as shown.
A 0.10M aqueous solutions of sodium sulfate, Na2SO4, is a better conductor of electricity than a 0.10M aqueous solution of sodium chloride, NaCl. Which of the following best explains this observation?
A. Na2SO4 is more soluble in water than NaCl is.
B. Na2SO4 has a higher molar mass than NaCl has.
C. More moles of ions are present in a given volume of 0.10M Na2SO4 than in the same volume of 0.10M NaCl.
D. The degree of dissociation of Na2SO4 in solution is significantly greater than that of NaCl.
C. More moles of ions are present in a given volume of 0.10M Na2SO4 than in the same volume of 0.10M NaCl.
Electrical conductivity in an aqueous solution depends on the concentration of mobile ions. Both sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and sodium chloride (NaCl) are strong electrolytes and dissociate completely in water. NaCl dissociates into 1 Na+ and 1 Cl-; 0.10M NaCl solution contains 0.10M Na+ and 0.10M Cl- (total ion concentration of 0.20M). Na2SO4 dissociated into 2 Na+ and 1 SO42-; 0.10M Na2SO4 solution contains 0.20M Na+ and 0.10M SO42- (total ion concentration of 0.30M).
Since the 0.10 M Na2SO4 solution contains a higher concentration of ions (0.30 M) than the 0.10 M NaCl solution (0.20 M), it is a better conductor of electricity.
A gas mixture at 0oC and 1atm contains 0.010 mol of H2, 0.015 mol of O2, and 0.025 mol of N2. Assuming ideal behavior, what is the partial pressure of hydrogen gas (H2) in the mixture?
A. About 0.010atm, because there is 0.010 mol of H2 in the sample.
B. About 0.050atm, because there is 0.050 mol of gases at 0oC and 1atm.
C. About 0.20atm, because H2 comprises 20% of the total number of moles of gas.
D. About 0.40atm, because the mole ratio of H2 : O2 : N2 is 0.4 : 0.6 : 1
C. About 0.20atm, because H2 comprises 20% of the total number of moles of gas.
Step 1: Calculate Total Moles. ntotal = nH2 + nO2 + nN2N
Step 2: Calculate Mole Fraction of Hydrogen. XH2 = nH2 / ntotal
Step 3: Calculate Partial Pressure of Hydrogen. Use Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure to find the partial pressure of hydrogen gas (PH2): PH2 = XH2 x Ptotal
The partial pressure of hydrogen gas is 0.20 atm, which corresponds to the reasoning in option C: H2 comprises 20% of the total number of moles of gas.
CCl4(g) deviates more from ideal gas behavior than CH4(g) does. Which of the following statements best explains this observations?
A. The mass of the CCl4 molecule is greater than that of the CH4 molecule.
B. The bond energy of the C-Cl bond is greater than that of the C-H bond.
C. The dipole-dipole forces between CCl4 molecules are greater than those between CH4 molecules.
D. The London dispersion forces between CCl4 molecules are stronger than those between CH4 molecules.
D. The London dispersion forces between CCl4 molecules are stronger than those between CH4 molecules.
In the ideal gas model, intermolecular attractions are nonexistent. Real gases deviate from ideal behavior to a greater degree as their intermolecular forces increase. The electron cloud of CCl4 is much larger and more polarizable than the electron cloud of CH4; therefore, the London dispersion forces among CCl4 molecules are much stronger than those among CH4 molecules. Thus, CCl4 deviates more from ideal behavior than CH4 does.
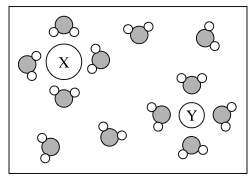 The diagram above represents a solution of ions in water. Which of the following are the most likely identities of ions X and Y?
The diagram above represents a solution of ions in water. Which of the following are the most likely identities of ions X and Y?
A. Ion X is Na+ and Ion Y is K+
B. Ion X is Na+ and Ion Y is F-
C. Ion X is Cl- and Ion Y is K+
D. Ion X is Cl- and Ion Y is F-
C. Ion X is Cl- and Ion Y is K+
The O atom is at the negative end of the water molecule, and the H atoms are at the positive end. The orientation of the water molecules around the two ions suggests that the X ion is negative (attracting the positive end of the water dipoles) and the Y ion is positive (attracting the negative end of the water dipoles). Option (C) shows X as a negative ion and Y as a positive ion.
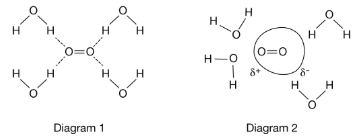 The survival of aquatic organisms depends on the small amount of O2 that dissolves in H2O. The diagram above represents possible models to explain this phenomenon. Which diagram provides the better particle representation for the solubility of O2 in H2O, and why?
The survival of aquatic organisms depends on the small amount of O2 that dissolves in H2O. The diagram above represents possible models to explain this phenomenon. Which diagram provides the better particle representation for the solubility of O2 in H2O, and why?
A. Diagram 1, because O2 molecules can form hydrogen bonds with the H2O molecules.
B. Diagram 1, because O2 and H2O are polar molecules that can interact through dipole-dipole forces.
C. Diagram 2, because the polar H2O molecules can induce temporary dipoles on the electron clouds of O2 molecules.
D. Diagram 2, because the nonpolar O2 molecules can induce temporary dipoles on the electron clouds of H2O molecules.
C. Diagram 2, because the polar H2O molecules can induce temporary dipoles on the electron clouds of O2 molecules.
The relatively small solubility of O2 in water is due to dipole-induced dipole forces between the polar H2O molecules and the nonpolar O2 molecules. The permanent dipole moment of the H2O molecules induces temporary dipole moments on the electron clouds of the nonpolar O2 molecules.
2 NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g)
dark brown colorless
The dimerization of NO2(g), an exothermic process, is represented by the equation above.
Which of the following experimental techniques will allow the most accurate determination of the concentration of NO2(g) at equilibrium?
A. Paper chromatography
B. Gravimetric analysis
C. Titration
D. Spectrophotometry
D. Spectrophotometry
- Spectrophotometry is the most accurate experimental technique because NO2 is a dark brown gas, while N2O4 is colorless.
- The concentration of the colored NO2 gas can be directly measured by its ability to absorb light (specifically in the visible spectrum) using a spectrophotometer and applying the Beer-Lambert law. The intensity of the brown color is directly proportional to the concentration of NO2.
- This method allows for continuous and non-invasive monitoring of the concentration at equilibrium without disturbing the system.