The 1st stage of cellular respiration
What is glycolysis?
The O2 released during photosynthesis comes from
(A) CO2
(B) H2O
(C) NADPH
(D) RuBP (RuDP)
What is H2O?
The process in which molecules move from high to low concentration with the help of a protein channel.
What is facilitated diffusion?
Plants have multiple pigments that absorb different wavelengths of light. This pigment is the main one involved in photosynthesis.(Be specific)
What is chlorophyll a
What are the products of photosynthesis?
What are oxygen and glucose?
In this stage of cellular respiration, a three-carbon compound is converted into a two-carbon molecule, producing both NADH and CO₂.
What is Pyruvate Oxidation
Definition of reduction
What is the gaining of electrons and energy?
When large molecules are expelled from the cell through vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane, this is called:
What is exocytosis?
Redox is an abbreviation for what processes?
What is reduction and oxidation?
During respiration, most ATP is formed as a direct result of the net movement of
(A.) potassium against a concentration gradient
(B.) protons down a concentration gradient
(C.) electrons against a concentration gradient
(D.) electrons through a channel
(E.) sodium ions into the cell
What is "B"
Which stage of aerobic respiration produces the most ATP?
What oxidative phosphorylation/ETC?
Daily Double: Why are photosynthesis and cellular respiration considered complementary?
What is because photosynthesis produces oxygen and glucose, which are used in cellular respiration, and cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide and water, which are used in photosynthesis?
This part of the cell membrane is hydrophobic and prevents most ions and polar molecules from entering directly.
What are the lipid tails (or fatty acid tails)?
The movement of these ions through ATP synthase is the most immediate source of ATP production in cells.
What are protons (H+)?
These disc-shaped structures in chloroplasts are stacked into grana, serving as sites for the light-dependent reactions
What are thylakoids?
What are the reactants of the process that occurs in Figure I.
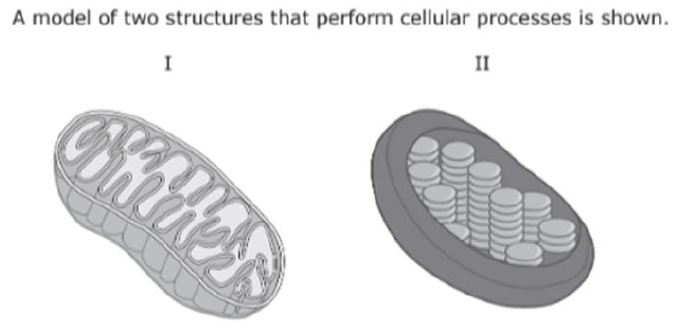
What are Glucose and Oxygen?
The chemical equation for photosynthesis shows which cell structure as the site of this process?
What is the chloroplast?
The figure is illustrating what type of transport?
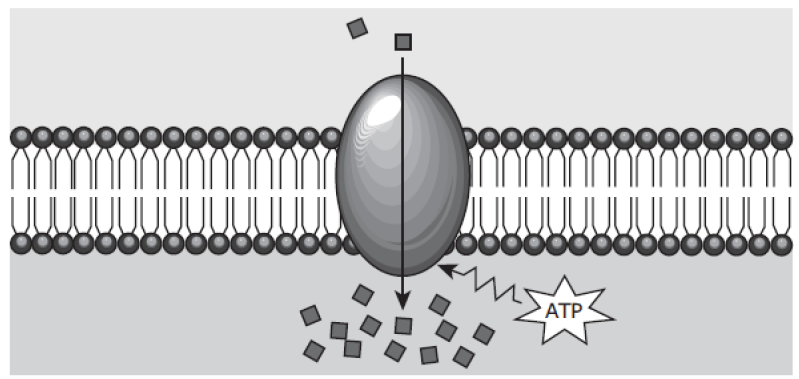
What is active transport?
This process that occurs specifically in the stroma uses CO₂ to produce glucose.
What is the Calvin Cycle?
These two electron carriers transport high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain, helping to generate a proton gradient and produce ATP.
What are NADH and FADH2?
In cellular respiration, this molecule acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
What is oxygen?
What is produced at position "e"
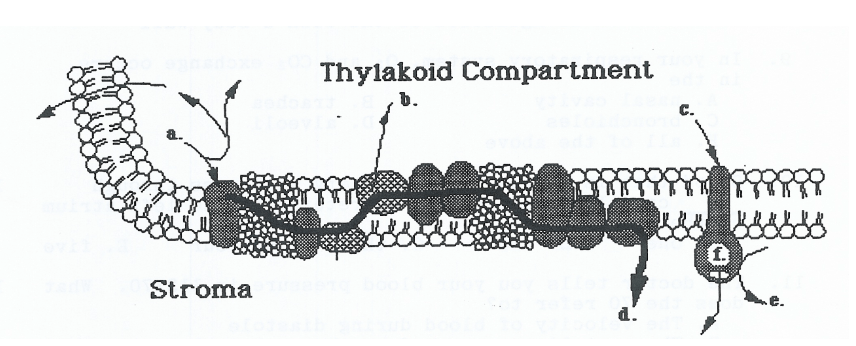
What is ATP?
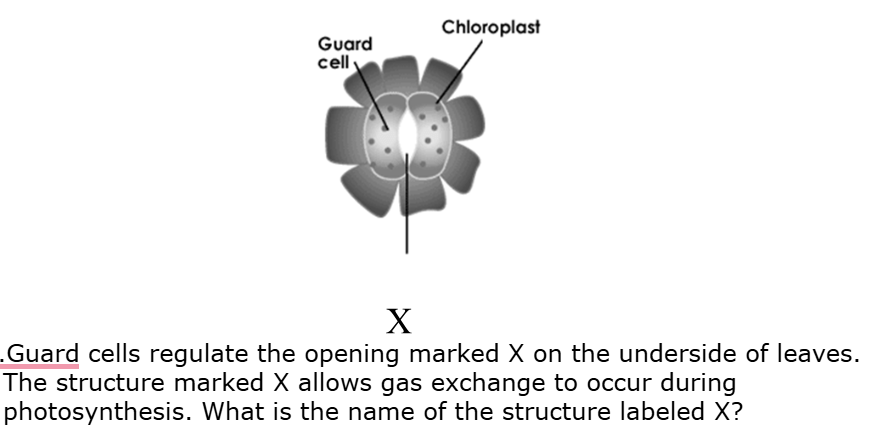
What is stomata?
This waste gas produced in the Krebs Cycle is released during cellular respiration
What is Carbon Dioxide?
Daily Double: Write out the equation for photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+Energy (ATP)
Photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O+Light Energy→C6H12O6+6O2