Label the Graph Below
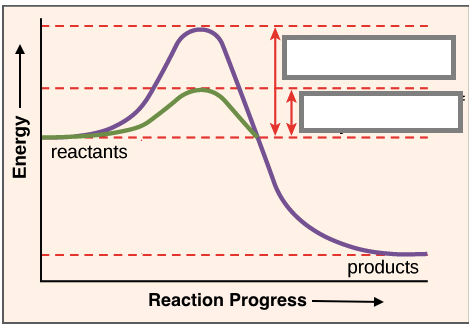
Green Line (Activation energy with a catalyst)
The enzyme lowers the activation energy (energy required to start a reaction).
This cycle releases CO₂ and builds NADH and FADH₂ while finishing glucose breakdown.
What is the Krebs Cycle/Citric acid cycle?
This molecule accepts electrons at the end of the ETC to become water.
What is Oxygen?
This gas is consumed by plants but produced by animals during cellular respiration.
What is CO₂?
This process that occurs specifically in the stroma uses CO₂ to produce glucose.
What is the Calvin Cycle?
The region of an enzyme that binds specifically to a substrate.
What is the active site?
This type of chemical reaction dominates Krebs by removing electrons from carbon-based molecules and transferring them to carriers.
What is oxidation Oxidation (redox)?
The intermembrane space becomes positively charged because of this particle in aerobic mitochondria.
What is Proton (H⁺)?
This pigment absorbs light and reflects green wavelengths.
What is Chlorophyll?
Why are photosynthesis and cellular respiration considered complementary?
What is because photosynthesis produces oxygen and glucose, which are used in cellular respiration, and cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide and water, which are used in photosynthesis?
When heat or pH breaks an enzyme’s 3D structure, this occurs.
What is Denaturation?
In the citric acid cycle, most harvested energy is temporarily stored in these high-energy electron carriers, not ATP itself.
What are NADH & FADH₂?
From one molecule of glucose, the total NADH formed in the Krebs cycle.
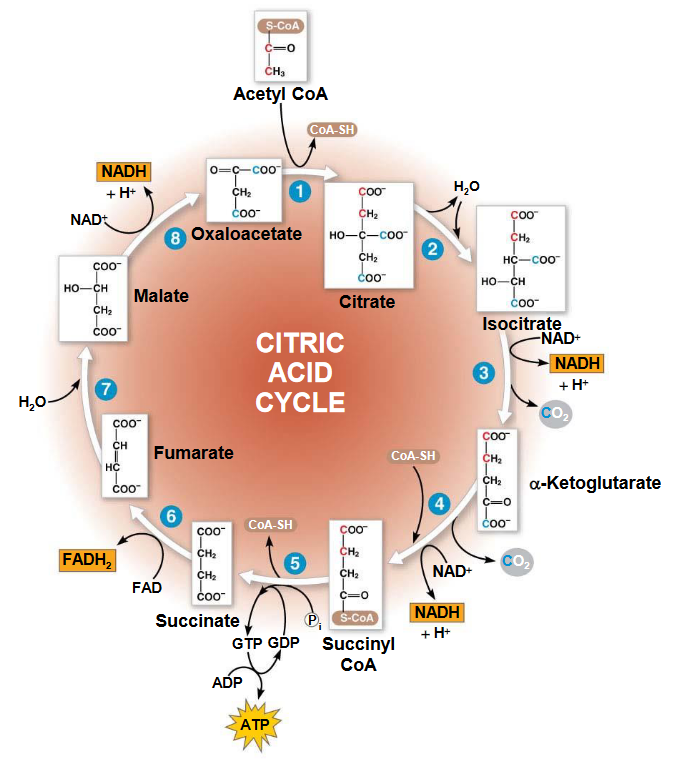
What are 6 NADH?
The site inside the chloroplast where the Calvin Cycle occurs.
What is the Stroma?
The 1st stage of cellular respiration
What is glycolysis?
This inhibition type blocks substrates by binding to the active site.
What is competitive inhibition?
Krebs alone yields only 2 ATP per glucose, but remains essential because it generates molecules that power this later ATP-producing process.
What is Oxidative phosphorylation?
Enzyme that uses the proton gradient to phosphorylate ADP into ATP.
What is ATP Synthase?
This type of metabolism occurs without oxygen.
What is anaerobic respiration (fermentation)?
Which stage of aerobic respiration produces the most ATP?
What oxidative phosphorylation/ETC?
Enzyme regulation method where end products shut down earlier pathway steps.
What is feedback inhibition?
Daily Double: Even though intermediate molecules change, this 2-carbon compound must form to connect glycolysis to mitochondrial energy harvest.
What is Acetyl CoA?
Daily Double: The carbon molecule that enters Krebs after acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate.

What is Citrate?
Daily Double: These complexes use light to “boost” electrons during the light reactions phase.
What are Photosystem I and Phostosystem II?
Write out the equation for photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+Energy (ATP)
Photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O+Light Energy→C6H12O6+6O2