Describe the difference between ionic and covalent bonds (in terms of electrons).
Ionic bonds transfer/donate/accept electrons while covalent bonds share electrons.
Describe the difference between homogenous and heterogenous mixtures?
A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components that make up the mixture are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture.
A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components of the mixture are not uniform or have localized regions with different properties.
What does VSEPR theory stand for?
____________ Shell __________ Pair _______
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
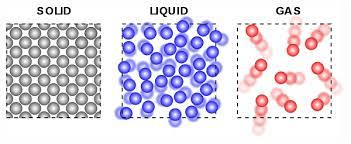
Draw a particle diagram that represents the three states of matter. (Solid, Liquid, and Gas)

Which substance is MOST soluble at 0 ºC?
KI
What types of elements makeup ionic bonds? What about Covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds are made up of metals and nonmetals.
Covalent bonds are made up two or more nonmetals.
Provide examples of a homogenous mixture & a heterogenous mixture.
Ex: Chocolate milk vs cereal
Ice tea vs pizza etc etc.
What is the axe formula of CH4?
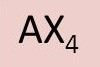
The phase change from water vapor to liquid water is known as...
a. evaporation
b. precipitation
c. condensation
d. sublimation
c. Condensation

Which of these solutes does not increase in solubility as temperature rises?
NaCl
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure of Magnesium Oxide. Use the bracket notation you learned to represent the ion.
A pure substance can be either an element or a ______________.
a. Single substance
b. Hot mess
c. Complex
d. Compound
Compound
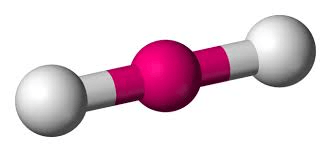
What is the molecular shape of this molecule?
What is the bond angle?
Linear
180 degrees
What is sublimation?
a. phase change between solid and liquid
b. phase change from gas to solid
c. phase change from solid to gas
d. phase change from solid to solid
c. Phase change from solid to gas

When 50 grams of KCl is dissolved in 100 grams of water at 50 ºC, the solution can be correctly described as:
(Unsaturated/Saturated/Supersaturated)
Saturated
100 point bonus: Why is is not supersaturated?
Fill in all lone electron & electron pairs missing from the LDS.
How many electrons in total does nitrogen share with its three chlorine atoms?
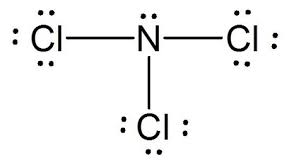
3 electrons
What differentiates a homogeneous mixture from a pure substance?
a. A pure substance can be separated into elements by physical means.
b. Pure substances are composed of a single element or compound while homogeneous mixtures are composed of multiple different elements or compounds.
c. A mixture has a defined composition.
d. A homogeneous mixture is uniform throughout.
b. Pure substances are composed of a single element or compound while homogeneous mixtures are composed of multiple different elements or compounds.
What is the molecular shape of this compound?
Trigonal Planar
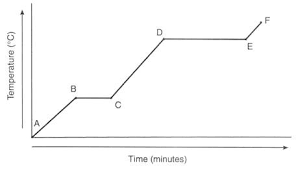
At what point(s) is a phase change occurring?
B-C, D-E

When 12 grams of potassium chloride, is dissolved in 100 grams of water at 50 ºC, the solution can be correctly described as:
Unsaturated
Give the name of the following covalent compounds:
- N2O4
- SCl6
Dinitrogen Tetroxide
Sulfur Hexachloride
When salt is mixed into water it becomes a _______.
- element
- compound
- mixture
- solute
Mixture
Determine the molecular shape of Carbon Tetrachloride. What is the bond angle?
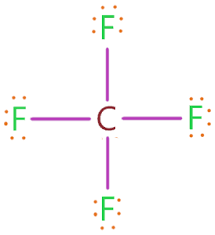
Tetrahedral
109.4 degree
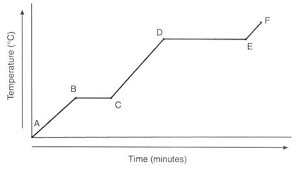
At which point is this substance a solid?
At which point is this substance a liquid?
At which point is this substance a gas?
Solid from A-B
Liquid from C-D
Gas from E-F

At what temperature can you fully dissolve 140g of NaNO3?
87-90 degrees