what type of molecule are enzymes
proteins
the monomer of carbohydrates
BONUS
monosaccharides
what are the 3 kinds of lipids
fats, oils, waxes
the monomer of proteins
amino acids
the monomer of nucleic acids
Name each part of this diagram
substrate, active site, products, enzyme
What is the function of enzymes
by increasing the rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy
what do humans store carbohydrates in
BONUS
glycogen
what is saturated fat like at room temperature? give one example.
solid
name two functions of proteins
BONUS
enzymes control rate of reactions
build + repair muscles
contract muscles
defend the body against pathogens
transport substances around the body
what is the function of nucleic acids
to store and pass on genetic information
what is the ending of proteins and sugars [2 different answers]
proteins: -ase
sugars: -ose
explain the 4 steps of enzyme action
1. enzyme and substrate are near each other
2. the enzyme grabs onto the substrate with its active site to for the enzyme-substrate complex
3. the substrate changes [breaks down or joins together]
4.the products are released and the enzyme is ready to receive another substrate
name 3 examples of complex carbohydrates
what type of fat is this?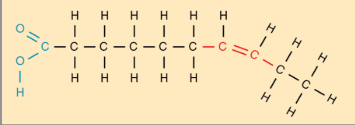
unsaturated fat
 Which part of amino acids makes them unique [20 different kinds!]
Which part of amino acids makes them unique [20 different kinds!]
the side chain
what elements make up nucleic acids
BONUS
CHONP
how many covalent bonds can carbon make with other atoms
BONUS
4 covalent
explain what a competitive inhibitor is and what it does to reaction rate
BONUS
binds to the active site getting in the way of the substrate that is supposed to bind there making it so the enzyme cannot work
what is deoxyribose an example of
sugar
what is the function of lipids
long term energy storage
what is the polymer of proteins
polypeptides
what foods would you find nucleic acids in?
anything that is or was living [needs to have DNA!]

nucleotide
acidity/heat and the protein becomes unable to function
what is the purpose of polysaccharides in the body and then why do we need to break them down into monosaccharides?
polysaccharides help us store glucose for later use. we break them down because our cells can only utilize sugars in their monosaccharide form
what 4 parts make up a triglyceride
glycerol and three fatty acids
how do you get from monomer to polymer of a protein [3 steps]
amino acids --> polypeptide chain --> protein
what are the three parts of a nucleotide?
1. phosphate
2. nitrogenous base
3. 5 carbon sugar
what gives polyunsaturated fats their structure?
