a series of chemical reactions that convert the energy in food molecules into a usable form of energy called ATP
Cellular respiration
List the 3 REACTANTS in Photosynthesis.
CO2, H2O, Light energy
List the 2 REACTANTS in Cellular Respiration.
O2, glucose (sugar)
How does energy move through the environment?
It flows in one direction (not cycled)
What do water, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen have in common?
They are all cycled through the environment.
This process is part of the hydrologic cycle
evaporation, condensation, precipitation, or transpiration
Which direction does the arrow flow in a food web?
What is toward the thing that is eating.
DAILY DOUBLE
the process of a liquid changing to a gas at the surface of the liquid.
Evaporation
List the 2 PRODUCTS in Photosynthesis.
O2 and glucose (sugar)
List the 3 PRODUCTS in Cellular Respiration.
CO2, H2O, ATP (energy)
What do energy pyramids show?
the amount of energy available in each link of a food chain
How does matter move through the environment?
It is constantly cycled.
Carbon in the atmosphere (CO2) is transformed into glucose through this process
photosynthesis
An organism that gets its energy from the sun through photosynthesis
autotroph / producer
all the living things and nonliving things in a given area.
Ecosystem
Where specifically does photosynthesis occur?
Chloroplasts (in plant cells)
Where specifically does cellular respiration occur?
Mitochondria (in plant cells)
DAILY DOUBLE
How does available energy change as it moves through organisms in a food chain?
Decreases
How do animals acquire nitrogen atoms?
By eating plants (soil)
During this process, carbon in glucose is converted into carbon dioxide, which is released back into the atmosphere
cellular respiration
An organism that eats only autotrophs
Primary Consumer / Herbivore
a model of energy transfer that can show how the feeding relationships in a community are interconnected.
Food web
What kind(s) of organisms use photosynthesis for energy? Give me two.
plants, some protists (algea), some bacteria
Name 2 kinds of organisms that use cellular respiration for energy.
animals, plants, fungi, and algae
What is the difference in carnivores and omnivores?
Carnivores eat only meat and omnivores eat meat and plants.
What are the 2 ways nitrogen fixation occurs?
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and lightning
This organism converts atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, then into nitrate
bacteria
If an organisms eats a both an autotroph and a primary consumer, what would you call them..
What is a primary and secondary consumer?
The feeding level of an organism
Trophic Level
Explain the importance of phytoplankton.
They supply 50% of the world's oxygen.
What is the usable form of energy that plants and animals use to survive?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Draw a trophic pyramid with a quaternary consumer. If the sun provided 10,000 J of energy show how much energy remains at each level
1 quaternary consumers
10 tertiary consumers
100 secondary consumers
1,000 primary consumers
10,000 producers
Why is nitrogen essential to living things?
Nitrogen is a core component of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. As well as DNA
DAILY DOUBLE
These organisms use nitrates to produce amino acids, which are used by living things to make proteins
plants and algae
Why is it necessary for autotrophs to be the largest group of organisms in any given ecosystem?
What is the reduction of energy by 1/10 up the food web, the need of higher end consumers to eat a greater number of organisms, and to maintain/ achieve higher carrying capacities.
The accrual of toxic chemicals in the tissue of an organism over time
bioaccumulation
DAILY DOUBLE
Write out the full equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight (energy) --> 6O2 + C6H12O6
Write the full equation for cellular respiration
6O2 + C6H12O6 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (energy)
Explain the difference in a food chain and a food web.
A food chain models energy flow through feeding relationships and food webs show how food chains are interconnected.
Why does biomagnification occur?
Higher trophic levels must eat more biomass than lower trophic levels. This means they consume more of toxic chemicals stuck in the cells than lower trophic levels
Which cycle of matter does not utilize the atmosphere as a sink/source?
Phosphorus
List all the organisms (in order) in a food chain ending in a quaternary consumer.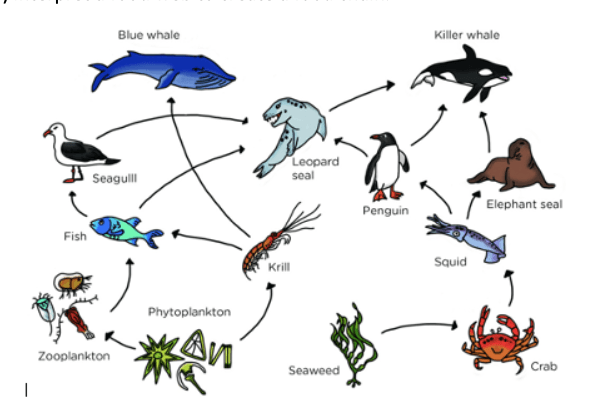
seaweed --> crab --> squid --> penguin -->killer whale
or
seaweed --> crab --> squid --> elephant seal -->killer whale
or
phytoplankton -->zooplankton->fish->leopard seal->killer whale
or
phytoplankton -->zooplankton->fish->seagull->leopard seal
Explain how Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration together form a cycle. Include the role of both plants and animals.
Plants take in CO2 and H2O to form sugar and oxygen during photosynthesis. Animals use the sugar and oxygen to do cellular respiration and produce H2O and CO2 as wastes.