The ion form of Hydrogen
H+
This type of model draws an atom with it's electrons separated by energy.
Bohr Model
I determine what type of atom I am.
Protons / Atomic Number
A 3 dimensional region around a nucleus in which it is likely to find an electron.
What is an orbital?
Do electrons ever change their shell?
Yes
How many valence electrons do elements in group 15 have and what kind of ion will they typically form?
5, anions
These rings represent what part(s) of an atom?
Electron Orbitals
The ion form of Cl
Cl-1
Each electron enters the lowest energy orbital available first
Aufbau Principle
using their location on the periodic table, determine the rank from least to greatest with the elements: Cl, Mg,Ca,N, and O
Ca,Mg,N,Cl and O
Define atomic radius
Is a measure of the size of its atom or the distance from the valence shell to the atom its self
Does the trend for ionization energy across the periodic table increase or decrease? and why?
Increase - smaller radius, electron is closer to the nucleus which makes it more difficult to pull
Why does it take more energy to remove the second electron from an ion than it did the first?
The effective charge of the nucleus increases, holding remaining electrons more tightly
What part of the periodic table describes how many energy levels this model should have?
Period / Row
Which trends in the periodic table increase across and decrease downwards?
electron affinity, electronegativity, ionization energy
I am an alkali earth metal with 3 energy levels.
Magnesium / Mg
How many sub-orbitals does a d-orbital have?
5
Predict which of the following elements has the largest En and state why? Na and Rb
sodium is higher because sodium is higher then Rb in the periodic table.
DAILY DOUBLE
When atomic radius trends across does it increase or decrease and why?
Decreases - has the same # of orbitals, more protons and elections therefore greater attraction and pull towards the nucleus
Top of the Halogens and Bottom of the Alkali metals
Draw a Bohr Model of a Boron Atom
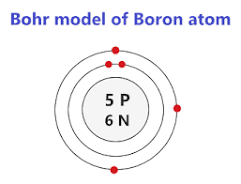
Which trends in the periodic table increase downwards and decrease across?
Atomic radius, reactivity
I am the heaviest noble gas
Oganesson
The electron configuration of copper?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9
How does the trend go for Electronegativity and explain why
Trend down - the larger atom will pull less strongly on the electron pair since they are further to its nucleus Trend across - the smallest atom will pull more strongly on the election pair since they are closer to its nucleus
Using their location on the periodic table, rank the size of follwoing sets of elements in order of increasing atomic size. Mg, S, Cl,Li, Cs and K
Cl, S, Mg, K, Cs
In an ionization energy, when the trend goes down, what happens? and why?
the trend decrease - more orbitals, electron further from nucleus and it is easier to remove an electron
In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: the atomic radius ________; the electronegativity _________; and the first ionization energy ________.
decreases, increases, increases
DAILY DOUBLE
Draw a Bohr model of an Argon Atom
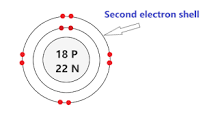
Who invented the periodic table
Dmitri Mendeleev
I am not a metal nor non-metal and have 5 valence electrons
Antimony / Sb
Arsenic / As
DAILY DOUBLE
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p5
What element is this?
Iodine
The shorthand notation for Uranium
[Rn]7s25f4