demand for all goods and services in an economy
The amount of an additional $1 that is saved or spent
What is the marginal propensity to save and the marginal propensity to consume (MPC /MPS)
land labor and capital`
what are factors of production (that are sticky)
in the long run these are easily flexible
What is short run equilibrium?
a decrease in SRAS it will bring ESR up and to the left, increasing PL but decreasing Aggregate Output.
what is cost-push inflation
correcting a recession or expansion without government intervention
what is long run self adjustment
government spending
taxes
transfers
What are tools of fiscal policy
policies that are already in place from previously passed legislation that kick in immediately as the economy is in flux.
What are automatic stabilizers
symbol for income on the x axis
The value that illustrates that a change in taxes will cause a change in disposable income
what are sticky input costs
the time it takes for all of those sticky costs to catch up with the change in Price Level.
What is the long run
Where LRAS, SRAS, and AD intersect
What is long run equilibrium
Inflation (PL rising) due to an AD rightward shift is called
What is demand pull inflation
do not move during self adjustment (2)
1/1-MPC
OR
1/MPS
what is the spending multiplier formula
unemployment benefits, temporary assistance etc.
what are transfer payments
represents aggregate output on the AD model
What is GDP (real)
The value that illustrates the ripple effect of spending because one person's spending is another person's income
What is the spending multiplier
Change to SRAS when Wages fall by 3.7%
What is a rightward shift of SRAS
increase in quality and quantity of resources
technological processes
Why the LRAS curve shifts to the right
When the price level is too low we raise the price level to fix
What is a shortage
Combination of inflation (rising PL) and stagnating or falling aggregate output.
what is stag-flation
The only curve to move in long run self adjustment
- (MPC/MPS)
OR
- (MPC / 1-MPC)
What is the tax multiplier formula
Unemployment benefits increase
Temporary assistance increases
what are recessionary automatic stabilizers
When a change in the price level leads to a change in consumer spending (why AD slopes down and to the right)
what is the real wealth effect
The value of the spending multiplier if the MPC is .75
What is 1/.25 = 4
Change in SRAS when Workers are on strike
What is a leftward shift to SRAS
Location on X axis for LRAS
when the price level is too high we lower the price to fix
what is a surplus
it's location can change due to a positive or negative demand or supply shock
What is (Short Run) Equilibrium
If there is an inflationary gap, what will SRAS do to correct it? What happens to PL?
SRAS shifts left, PL rises
+ MPC/MPS
OR
+ MPC / 1-MPC
what is the transfer multiplier formula
Income taxes (brackets)
Corporate taxes (brackets)
Unemployment benefits decrease
what are inflationary automatic stabilizers
how changes in the interest rate impact overall economic activity, particularly influencing consumer spending and investment (why AD slopes down and to the right)
what is the interest rate effect
The value of the tax multiplier if the MPS .25.
What is - (.75/.25) = -3
Caused If PL rising is expected...
What is a decrease in SRAS
What is the relationship between unemployment and inflation
Disequilibrium modeled: (What is this)
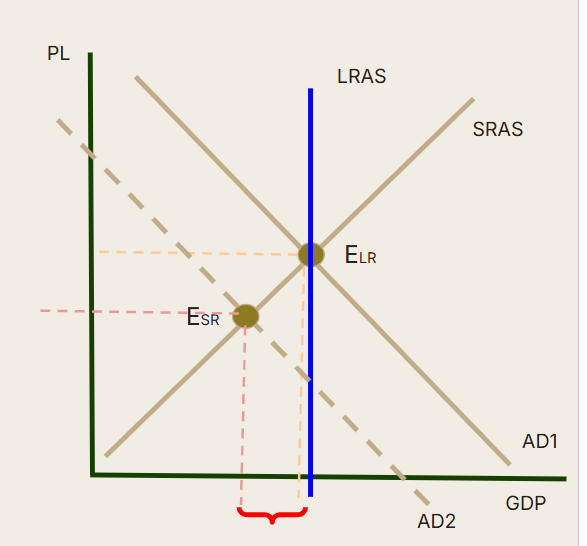
What is a recessionary gap
Disequilibrium modeled: (What is this)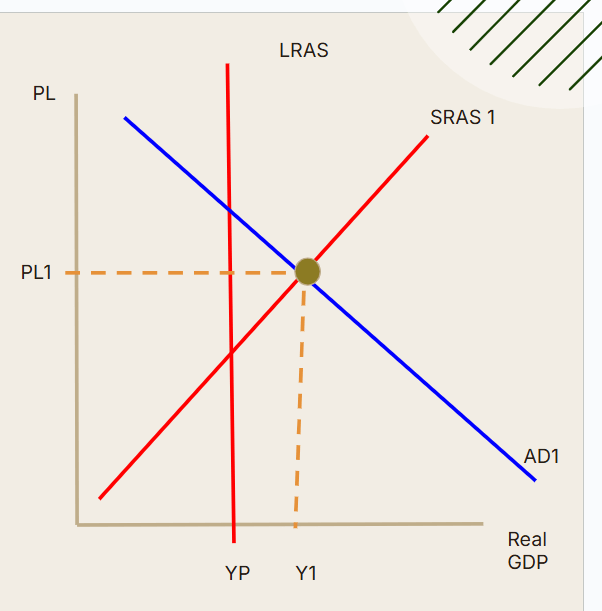
What is an inflationary gap
In the long run Workers will want higher wages and firms will want higher prices so the SRAS will shift leftward correcting this disequilibrium.
What is an inflationary gap
The total change in AD if the government increases spending by $1,000 and the MPC is .8
What is $5000
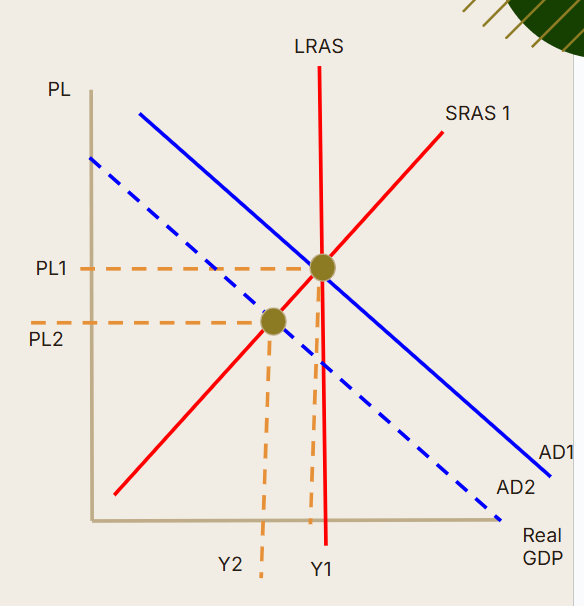
What must have happened to unemployment and transfer payments?
Unemployment rates rise, individuals will apply for additional unemployment benefits so transfer payments will increase