What is the difference between a Specialist and Generalist?
Specialist have a narrower ecological niche that makes them more prone to extinction while generalist have a broader niche.
What is carrying capacity?
The max. Number of individuals in a pop. that an ecosystem can support (based on limiting resources)
What is biotic potential and logistic growth?
Biotic potential = exponential growth
Logistic growth = initial rapid growth, then limiting factors limit pop. to K
What was the Malthusian theory?
Humans will reach a carrying capacity limited by food
What are the four stages of demographic transition?
Stage 1 = Pre industrial
Stage 2 = transitional
Stage 3 = industrial
Stage 4 = post industrial
How many Offspring do K-selected have?
Very Few
Name a 3 limiting resources.
Name a density independent factor.
Natural disasters (flood, hurricane, tornado, fire)
How do you calculate doubling time?
70 / % of Growth rate
What stage has Rapid growth, due to high CBR and declining CDR?
Stage 2 - Transitional
Which type are more likely to be invasive? R or K selected?
R-Selected
Which survivorship curve represents humans?
Type 1
Name 3 density dependent factors.
Food, competition for habitat, water, light, even disease
Solve this problem: A country has a CDR of 13 and a CBR of 15.
Calculate the annual growth rate, and the doubling time.
(15-13)/10 = 2/10 = 0.2% growth rate
70/0.2% = 350 years to double
What stage has the highest contraceptive use rates?
Stage 4 = Post industrial
Which type, generalist or specialist are more able to adapt to environmental conditions?
Generalist
What is overshoot and die off, and a consequence of each?
Overshoot: when a population briefly exceeds carrying capacity
Consequence: resource depletion
Die off: sharp decrease in pop. size when resource depletion (overshoot) leads to many individuals dying
Consequence: decrease pop size
What growth does an extreme pyramid shape show?
Rapid growth
What are two factors that affect TFR?
- Development (Affluence)
- Gov. Policy
What stage is TFR the highest?
Stage 1 = Preindustrial
What is an example of an r-selected and K-selected species?
R-Selected - Mammals, Birds
K-Selected - Insects, Fish, Plants
Explain type 1, 2 and 3 survivorship curves and give an example of each.
Type I (mostly K-selected)
High survivorship early in life due to high parental care
High survivorship in mid life due to large size & defensive behavior
Rapid decrease in survivorship in late life as old age sets in
Ex: most mammals
Type II (in between r & K)
Steadily decreasing survivorship throughout life
Ex: Squirrels
Type III (mostly r-selected)
High mortality (low survivorship) early in life due to little to no parental care
Few make it to midlife; slow, steady decline in survivorship in mid life
Even fewer make it to adulthood; slow decline in survivorship in old age
Ex: insects, fish, plants
What shape is the US's age structure diagram? Expanding rapidly, slowly, declining or stable.
Expanding slowly
Calculate the percent change in the population density of zebra mussels from 2009 to 2015, when population in 2009 is 2,000 and population in 2015 is 2,500.
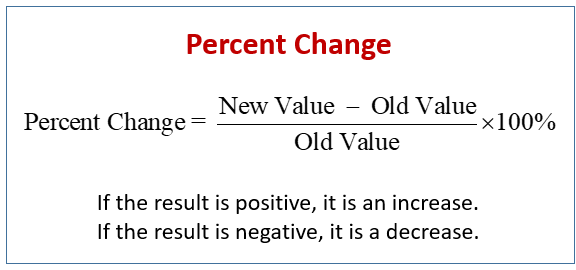
(2,500 - 2,000) / 2,000 = 0.25 * 100 = 25%
25% increase in population density
At what stage does birth rate decrease? At what stage does death rate decrease?
Death Rate - Decrease in stage 2
Birth Rate - Decrease in stage 3