The students pick two elements from the periodic table which belongs to different groups. The student decided to choose barium (Ba) and phosphorus (P). Determine their charges:
Ba: ____ charge
P: ____ charge
Barium: +2 charge
Phosphorus: -3 charge
The following diagram shows the transfer of electrons to form what ionic compound? (Please provide the chemical name/formula)
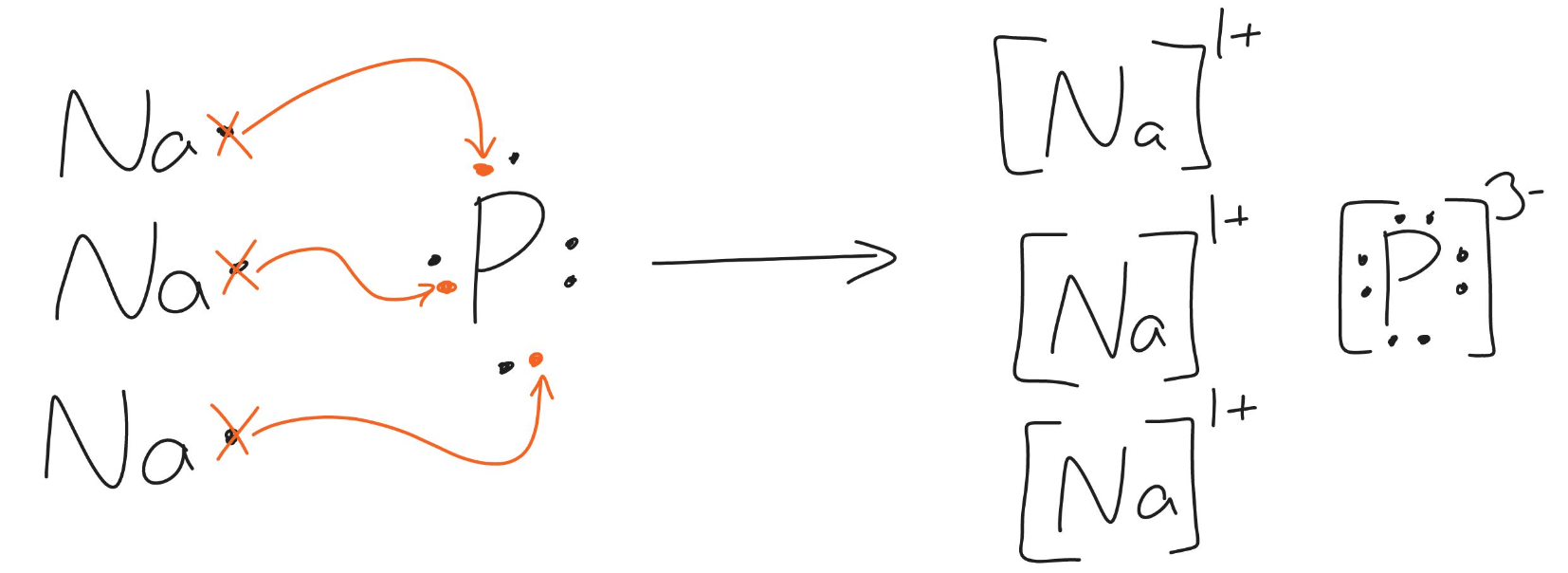
Na3P
Name this compound:
N2O4
Dinitrogen Tetroxide
A given molecule (formaldehyde) shown below has a unique geometrical shape. According to the VSEPR Theory, what is the primary reason why such shape is possible?
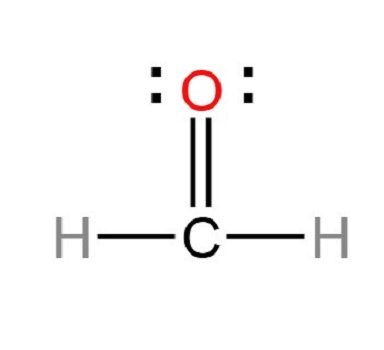
Repulsion of valence electrons
1. In this picture, determine the type of attraction the dash lines indicate:
2. Determine if this is considered intermolecular/intramolecular force:
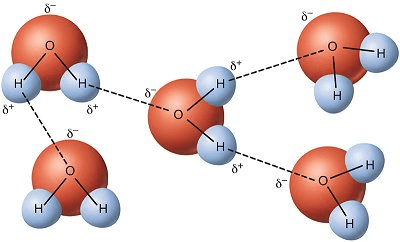
1. Hydrogen Bonds
2. Intermolecular Force (between molecules)
If two elements belong in the same group (column), what do they usually have in common?
The two elements have the same charge.
Determine the formula of the ionic compound that is based on the given Lewis Dot Structures:
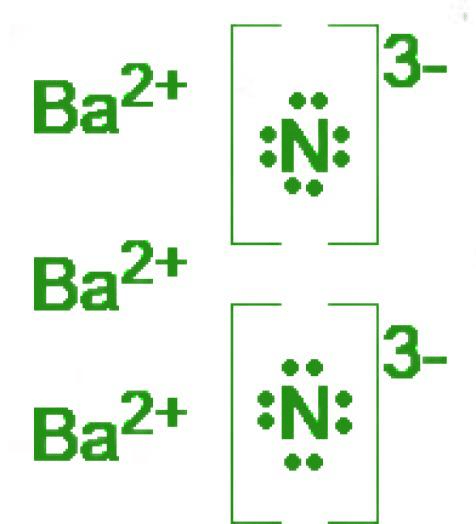
Ba3N2
Name this compound:
NO
Nitrogen Monoxide
Draw the Lewis structure for water and determine its shape:
1. 
2. bent shape (2 lone pairs)
List the properties of water, and determine the main reason why water demonstrate these properties
1. High Surface Tension
2. Low Vapor Pressure
3. Ice (solid) is less than dense than water (liquid)
Primary Reason: Hydrogen Bonding
Fill in the correct words for the following statement:
When forming ions, metals tend to _____ electrons, while nonmetals tend to _____ electrons.
1. gain
2. lose
Draw the Lewis dots structure for CaCl2
This is an ionic compound, therefore, you will need to include brackets on the drawing.
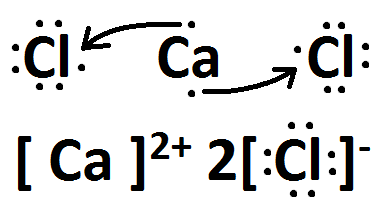
PO33- has a tetrahedral geometry as shown below. Determine the number of valence electrons this structure has:
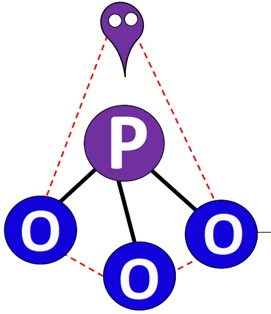
26 valence electrons
Determine the geometry of the center atom circled in red:
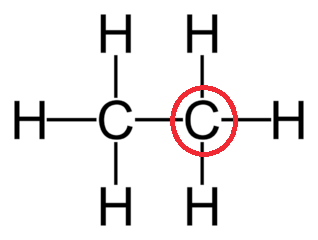
Tetrahedral Structure
Attach is a picture of a water molecule. Explain why this molecule is considered to be polar covalent:

Water is held together by covalent bonds (intramolecular force)
Hydrogens are partially positive while the oxygen is partially negative (2 lone pairs)
When forming ions, Calcium loses two electrons while Fluoride atoms gain 1 each in order to be considered "stable." What is the rule that demonstrate this idea?
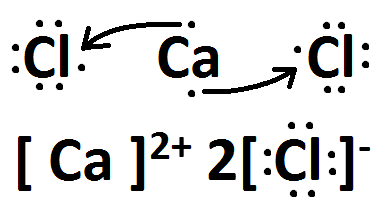
Octet Rule
1. Use the criss-cross reduce method to write the chemical formula for cobalt (II) phosphate.
2. Determine the overall charge of the compound:
1. Co3(PO4)2
2.Net Charge: 0
Explain the difference of a covalent and an ionic compound:
Covalent Compound: two or more nonmetallic atoms that share electrons to form a bond
Ionic Compound: two or more atoms (metal/nonmetals) transfers electrons to form a bond
Determine the geometry of the center atom circled in green:
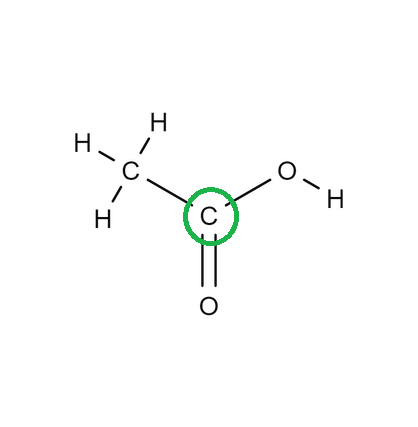
Trigonal Planar
Which of the following molecules have the same empirical formula:
CCl4 and C2Cl6
CH and C6H6
C2O6H5 and C4O8H12
H2O and H6O3
CH and C6H6
H2O and H6O3
Determine which elements violate the Octet Rule? Why?
Hydrogen and Helium
These two elements only needs two electrons to become "stable."
Draw the Lewis dots structure for MgF2
This is an ionic compound, therefore, you will need to include brackets on the drawing.
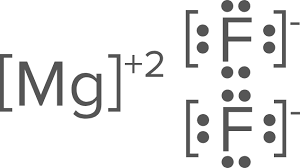
1. Determine if the picture below demonstrates intermolecular/intramolecular forces.
2. Identify which one of the following is "harder" to break. 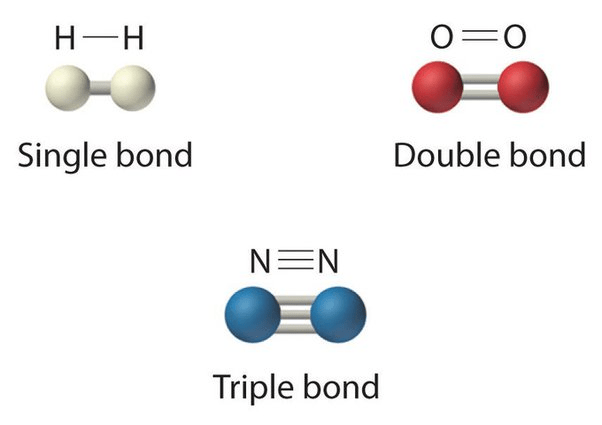
1. Intramolecular ("within")
2. Triple Bonds
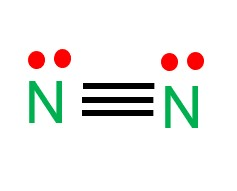
Draw the Lewis structure for a nitrogen molecule (N2) and determine its shape
Linear
Calculate the percent composition of water given that the molar mass of water is 18.02 g/mol:
% of Hydrogen: _______
% of Oxygen: ________
% of Hydrogen: 11.21%
% of Oxygen: 88.79%