Two species with the same niche cannot coexist in the same habitat for long without one either becoming extinct, or being driven out due to competition.
What is competitive exclusion principle? (Gause's Law)
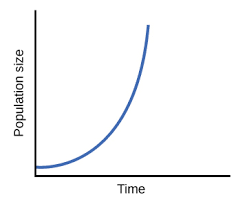
The type of population growth that is shown above.
What is exponential growth?
Relationship where members of one species consume members of another species.
What is predation?
The amount of energy or biomass that is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
What is the 10% rule?
Relationship where both organisms benefit.
What is mutualism?
Limiting factors that are typically abiotic.
What is density independent limiting factors?
Members of the same species trying to obtain the same resources.
What is intraspecific competition?

The type of population growth that is shown above.
What is logistic growth?
Why do predators have to consume other members of other species?
Energy & biomass (can't produce themselves)
What is sunlight?
Relationship where one organism benefits while the other is neither helped or harmed.
What is commensalism?
Limiting factors that are typically biotic.
What are density dependent limiting factors?
Members of different species trying to obtain the same resources.
What is interspecific competition?

The graph above is representing this relationship.
What is competition?
Things that help predators catch prey.
What are structural adaptations?
If your producer has 13000 kcals of energy, the amount available to your tertiary consumer.
What is 13 kcals?
Relationship where one organism benefits while the other is harmed.
What is parasitism?
The maximum number of organisms an ecosystem can support.
What is carrying capacity?

The type of competition being represented in the picture.
What is interspecific competition?

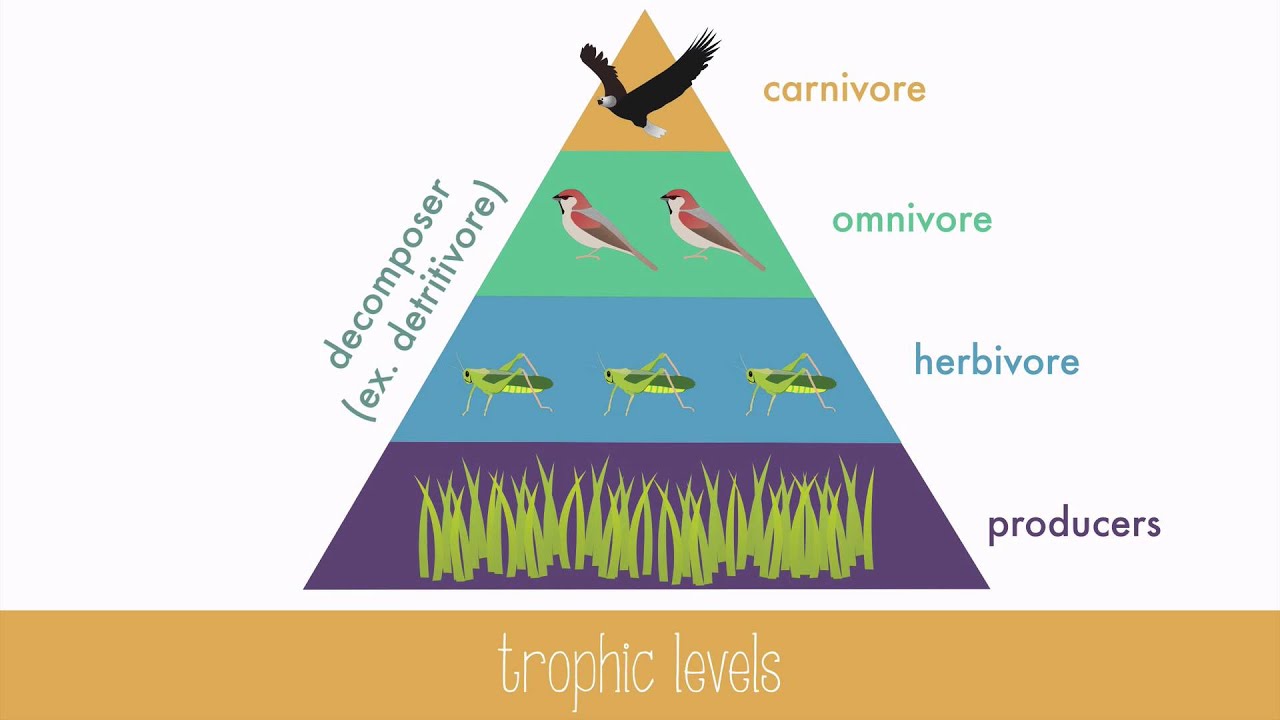
Draw a trophic level pyramid and place these organisms into their correct trophic levels.
Producers: carrots, grasses, grains
Primary consumers: rabbits, mice, grasshoppers
Secondary consumers: birds, owls
Tertiary consumers: foxes
Why are there significantly less predators than there are prey?
10% rule, not as much energy and biomass available at the top of the pyramid.
The grasshopper has 101 kg of biomass. Fill in the rest of the pyramid (top to bottom).
Grass (producer): 1010 kg
Grasshopper (pc): 101 kg
Bird (sc): 10.1 kg
Eagle (tc): 1.01 kg
1st - Primary
2nd - Secondary

This is representing this type of limiting factor.
What is a density independent limiting factor?

The type of competition being represented in this picture.
What is intraspecific competition?
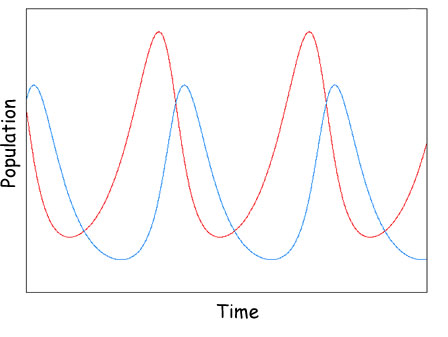
The graph above is representing this type of relationship.
What is predator/prey?
Why do predators increase after prey decreases?
Predators increase due to a lag of prey population decreasing.
Your secondary consumer has 45 kcals of energy available to them. Fill in the rest of the levels from producer to quaternary consumer.
Producer: 4500 kcals
Primary Consumer: 450 kcals
Secondary Consumer: 45 kcals
Tertiary Consumer: 4.5 kcals
Quaternary Consumer: 0.45 kcals

The type of succession being shown.
What is secondary succession?

This is representing this type of limiting factor.
What is a density dependent limiting factor?