What are intermolecular forces?
Attractions between molecules.
In an experiment, the amount of sunlight exposure, was systematically changed to investigate its effect on plant growth rate.
What is the independent variable?
How would you define polar versus nonpolar molecules?
polar- unequal sharing of electrons, difference in atom electronegativity
nonpolar-equal sharing of electrons
How do you determine what type of IMF a molecule has?
You need to determine if the molecular is polar or nonpolar and distinguish which atoms are in the molecule.
Is C12H22O11 have ionic or covalent bonds as the intramolecular force?
Covalent Bond (C, H, and O are all nonmetals)
What are intramolecular forces?
Attractions within molecules.
In a chemistry experiment, the concentration of the reactant was varied in a series of reactions to observe its effect on the rate of the product formation. What is the dependent variable?
rate of the product formed.
Is a Na-Cl bond polar, nonpolar, or neither?
Neither! It is ionic
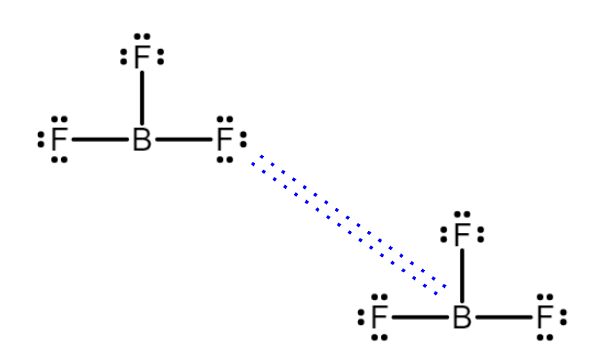
Identify and draw the IMF between BF3
LDF
What does the length of the plateau (horizontal line) in this cooling curve indicate?
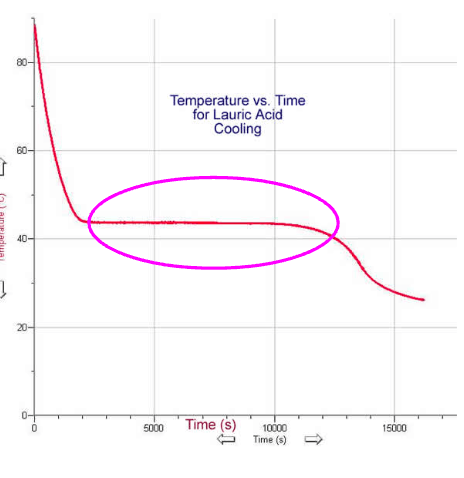
The plateau represents the phase change. The longer the plateau, the more time/energy needed for the phase change to occur.
Describe Covalent bonding and where you would find covalent bonds.
Sharing of electrons
Between non-metals (or atoms with similar electronegativity)
Other than room or table conditions what is a constant that was important to keep in the penny lab?
drop size (same type of dropper)
height from which drop falls
penny cleanliness.
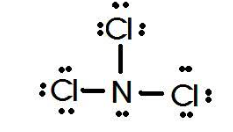
Draw the lewis structure for NCl3 and determine its polarity
Polar
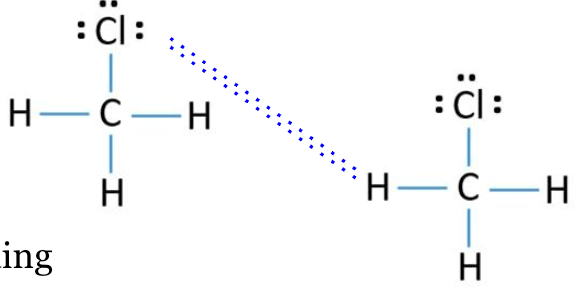
Identify and draw the IMF between CH3Cl
Dipole-Dipole
Describe what is happening during a phase change?
The intermolecular forces are being broken (the attraction BETWEEN molecules)
*No bonds are broken!
Describe an ionic bond.
between a metal and a non metal
the non-metal gains electrons from the metal
If the acetone was taken out of the fridge right before the evaporation experiment, while the water was out at room temperature, how would the data be affected?
The acetone would evaporate more slowly than it should (making it seem like the IMFs were stronger.)
Draw the lewis structure for CO2 and determine its polarity
Nonpolar
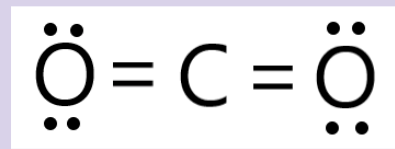
Which liquid would result in more drops on our penny: water or acetone? Explain WHY.
Water has hydrogen bonding which is a stronger IMF than dipole-dipole (acetone). A stronger IMF means stronger surface tension. It is harder to break the attraction between the molecules which would result in more liquid drops on our penny.
Which molecule will change its phase first: methanol or ethanol? Explain WHY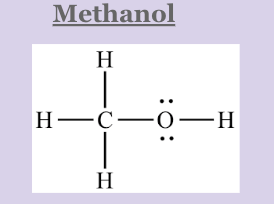
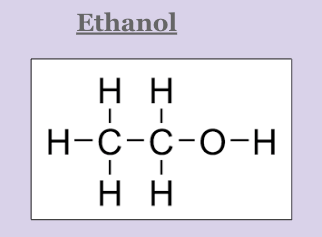
Methanol will change its phase first because even though they both exhibit hydrogen bonding (strong IMF), ethanol is a larger molecule. It will take more energy to break the IMF of the larger molecule (Ethanol)
If an experiment is done to see whether chicken eggs will hatch more quickly as temperature increases, what type of graph would be made? Why?
line
Independent variable is continuous (numerical)
If we were to measure how many drops of water fit on various coins, what type of graph would we make? Why?
What VSEPR shapes will always be polar?
Explain WHY any shape with lone pairs (on the central atom) will result in a polar molecule
The lone pairs create a pyramidal repulsion. The net dipole from the polarity of each bond would NOT cancel out! Bent and Trigonal Pyramidal will always be polar.
Why is hydrogen bonding the strongest IMF?
H-F, H-O, H-N bonds are very polar (very large electronegativity differences)
When did Stevenson High School open?
1965