The ability to do work.
What is energy?
A bucket of water is pulled up at constant speed. Is the bucket's PE increasing or decreasing?
Increasing
Heat must travel in which direction?
Hot to cold
Electric fields are pointed toward [positively/negatively] charged particles.
Negatively
An Object that allows charge to flow freely
What is a conductor?
KE or PE? Electric current in a smart phone.
An elevator moves from the 15th floor to the 10th floor at a constant speed. What is happening to the elevator's PE and KE?
PE decreasing. KE constant
"Energy is conserved."
What is the first law of Thermodynamics?
As the distance increases, the strength of an electric field appears to [increase/decrease]
Decrease
A material that offers very little resistance.
What is a superconductor?
KE or PE? Flames from a burner on a stove.
Kinetic Energy
Select the point with least PE.
Point C
T/F. Internal Potential Energy lies between the bonds of an object's atoms.
True
Device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
What is an electric motor?
T/F. All objects are able to conduct electricity. It's just a matter of how much or under what conditions.
True
KE or PE? Energy in a chromebook's battery
Potential energy
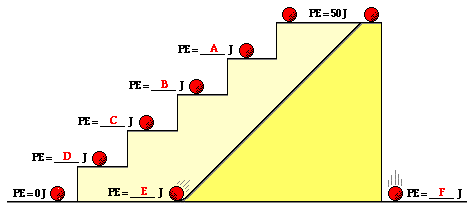
What is the PE of the ball at point B?
30 J
Thermodynamic law that helps us better understand the passage of time.
Second law of Thermodynamics (entropy)
Light acts as a [wave/particle].
Wave AND a particle
T/F. When you rub a balloon and hold it near an aluminum can, there is an observable electrostatic interaction since the can will move away from the balloon. Since balloons are made of insulative material the can has to be the object that is charged.
False.
KE or PE? Paint on a luminous watch dial.
Potential energy
What does it mean for energy to be dissipated?
Energy is transferred out of the system
Why is the Absolute Zero (0 Kelvin) a theoretical value?
0th & 1st - heat needs to go somewhere
2nd - entropy should always increase
Picture a particle in an electric field. At it's initial position, it feels an electric force strength of 16 N/mC. If the particle doubles it's distance away from the electric field source, what will the new electric force strength be at this final position?
4 N/mC.
Silicon is an example of a/an...
Insulator