What is the difference between a complete fracture and an incomplete fracture?
Complete: the bone is broken all the way through
Incomplete: the bone is not broken all the way through
What is the function of yellow bone marrow and where is it found?
It is found in the medullary cavity and stores fats/nutrients. In severe situations, it can also produce blood cells
Periosteum
List the 3 types of structural joints
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
Levels of ___________ must be maintained in the blood
calicum
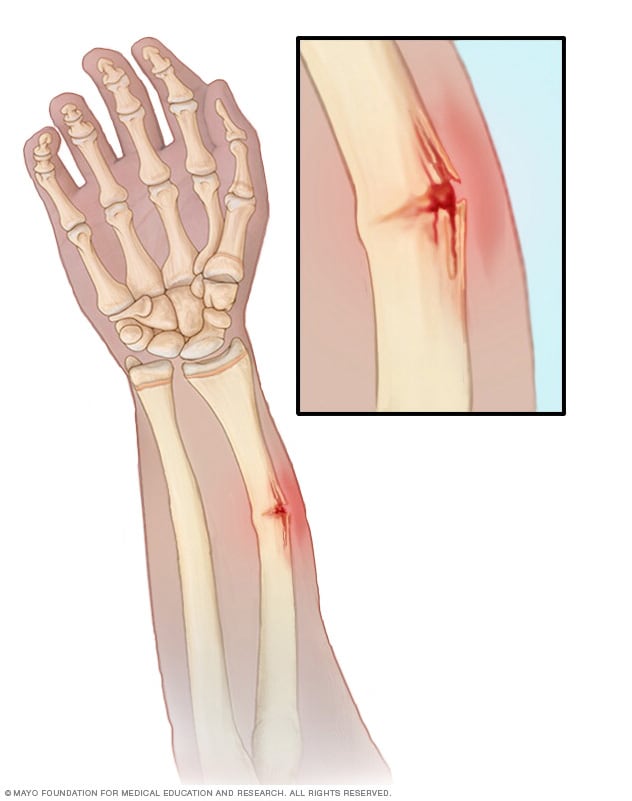 What kind of fracture is seen here? Is it complete or incomplete?
What kind of fracture is seen here? Is it complete or incomplete?
Greenstick fracture
Incomplete
The process of incorporating calcium and minerals into cartilage to become bone is _____________________.
Ossification
What structure attaches bone to bone? Muscle to bone?
Ligaments attach bone to bone
Tendons attach muscle to bone
Give an example of a fibrous joint
Sutures of skull
What is the difference between the axial and appendicular skeletons?
Axial: central axis of body (ribs, skull, sternum, vertebrae)
Appendicular: Pectoral & pelvic girdles (arms, legs, pelvis, shoulders)
Why are splints/casts used when on patients with a broken bone?
To ensure that the bone does not become displaced during the repair process
What is a hematoma?
Pooling of blood that forms when a broken bone is being repaired
What are trabeculae and where are they found?
Spaces filled with marrow or blood vessels in spongy bone
Which type of joint is the elbow/knee?
Hinge joint
What is the difference between osteoclasts and osteoblasts?
Osteoclasts break down bone & osteoblasts produce new bone
Draw a comminuted fracture

What is the function of the epiphyseal plate?
This is where the growth of the bone takes place
To connect all bone cells and allow them to receive nutrients and remove wastes
Which types of joints are immovable or only slightly movable?
Fibrous & cartilaginous
What is an embyro's skeleton made of?
Cartilage
List the steps of bone repair in order
-Hematoma forms
-Callus forms
-Callus ossifies
-Compact bone forms
Describe how bones maintain homeostasis in the body
If Calcium is too high- thyroid produces calcitonin, calcium from blood is absorbed into bones, and calcium levels decrease
If Calcium is too low- parathyroid produces PTH, osteoclasts break down bone to release calcium, calcium levels rise
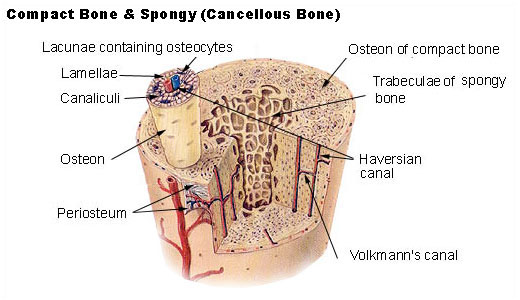
Draw a diagram of compact bone, making sure to label these structures: central canal, osteon, perforating canal, lamellae
Where is articular cartilage found? What is the function?
List the functions of the skeletal system
Movement
Manufacturing
Support
Storage
Protection