Maintaining the same intensity of 70-85% max HR for at least 20 minutes to improve aerobic power
What is continuous Training?
Tailoring a program and sessions to the specific needs of an athlete's sport, position and other physiological requirements
What is specificity?
Data that is derived from feelings, experiences, opinions and thoughts.
What is subjective data?
What is a warm-up?
The best training method for improving muscular strength and hypertrophy
What is resistance training?
Random intervals of work and rest to improve aerobic power.
What is fartlek training?
Measured using % of HR Max, % or VO2 Max, RPE or % of 1-Rep Max.
What is instensity?
Physical factors that affect training performance such as sleep, hydration, soreness, sleep and nutrition
What are physiological considerations?
The final phase of a RAMP warm-up, where sport specific exercises are incorporated
What is potentiate/prepare?
What is an eccentric contraction?
What is short interval training?
The characteristics that distinguish one performer from another, such as training status and genetic predisposition.
What is individuality?
What are psychological considerations?
A type of stretching, ususually completed in a cool down, which aims at increasing range of motion by holding a stretch for a specific amount of time
The energy system targeted from short interval training
What is ATP-PC?
Completing a series of different exercises to target multiple fitness components.
What is circuit training?
The effects that occur when training ceases, or when training load is less that required.
What is de-training?
Any device that measures physiological changes such as HR, Brain activity or body tempreture.
What are physiological sensors?
The phase of a session where work is done to target specific energy systems and fitness components
What is conditioining phase?
Can be implemented by changing intensity, frequency, or duration.
What is progression?
A type of flexibility training where a muscle is stretched through its full range of motion, then contracted isometrically against an immovable resistance.
What is PNF (Proprioceotive neuromuscular facilitation) stretching?
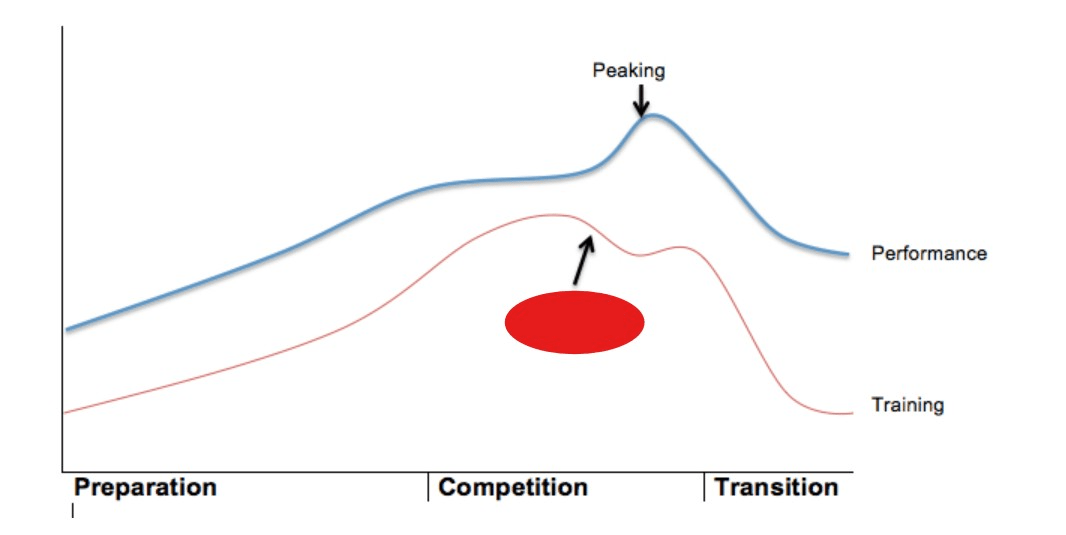
What is tapering?
Data that is delivered at the same time as it collected
What is real-time data?
A type of soreness which can be felt 12-24 hours after unaccustomed strenous exercise.
What is DOMS (Delayed onset muscle soreness)
A high-explosive training method suited towards muscular power
What is plyometric training?