Life
True or False:
Chemical reactions typically occur faster at higher temperatures.
True
The following rate law has what overall order?
rate=k[A][B]
2
*(order A) 1 + (order B) 1=2
A certain first-order reaction has a rate constant of 0.00840 1/min at 300 K. What is the half-life (in minutes) of this reaction?
82.5 minutes
*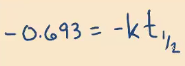
True or False
An intermediate is produced in early step of a reaction but consumed in later step
True!
For the following reaction:
2A + B → 2 C
The rate law is determined to be:
rate = 0.4357 [A][B]
What will be the initial rate (in M/s) if initial concentrations are: [A] = 0.500 M, [B] = 1.26 [M]
0.274 M/s
*plug concentrations into rate law equation
*reactants
What are the units for this rate law:
rate = k [A]
1/s
*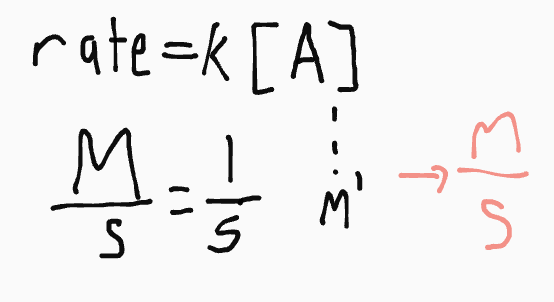
How many half-lives are required for the concentration of reactant to decrease to 6.25% of its original value?
4
*Take 100 and divide in half until you get to 6.25
Identify what the overall reaction is:
i. CH4 + Cl → CH3 + HCl (slow)
ii. CH3 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + Cl (fast)
CH4 + Cl2 →HCl +CH3Cl
Which of the following statements is not true?
-For a reaction to occur, the collision must be energetic enough for there to be mutual penetration of the valence shells of the reacting species
-For a collision to result in a reaction, molecules can collide in any orientation
-The more frequently collisions occur, the faster the reaction rate will be
-For a collision to result in a reaction, molecules can collide in any orientation
*This is false because not all collision angles are the same.
True or False
A catalyst can slow down the rate of a reaction.
False
*catalysts speed up a reaction. An inhibitor slows down the rate.
True or False:
Rates usually increase when the concentration of one or more of the reactants decreases.
False
*if the reactant increases, the rate will increase as well
Assume that the following first order reaction 2 FClO2 → FClO + O2 has a rate
constant k = 0.0143/min. Given initial FClO2 conc. = 0.73 M, what will be the
FClO2 concentration after 16 min?
0.58
*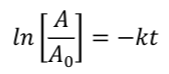
What is the catalyst in the reaction mechanism shown below?
AB + B3 → AB2 + B2
B + AB2 → AB + B2
AB
*catalyst is the species consumed in early step and regenerate in later
Which of the following must be true for a reaction mechanism to be valid. Select all correct answers
-The mechanism predicts the experimentally observed rate law
-All steps are bimolecular
-The first step is the rate-limiting step
-The steps sum to the overall reaction
The mechanism predicts the experimentally observed rate law
and
The steps sum to the overall reaction
--
*steps can be different than bimolecular
* The 1st step isn't always the rate-limiting though it is common
True or False:
Large pieces of iron react more slowly with acids than finely divided iron powder reacts with acids.
True
* smaller pieces are able to react quicker because of the increase in contact points compared to large pieces
Consider the following initial rate data for the reaction:
3 C + 4 D → 4 E
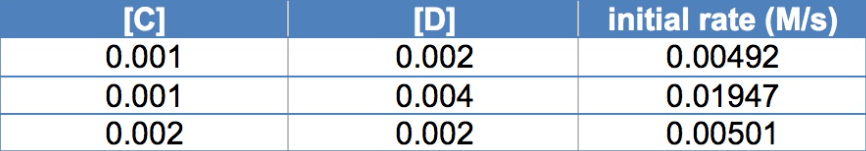
Based on this data, what is the order of the reaction with respect to D?
Order of D= 2
What is the intermediate in the reaction mechanism shown below?
A + B3 → AB + B2
AB + C → A + BC
AB
*produced early, consumed later
For the first order process:
A → B
The half-life of A is 62.1 seconds. If a sample of A initially has 250.0 g, what mass (in g) of A will remain after 173.1 seconds?
36.23 g
*1st calculate k from half-life equation
*then use1st order integrated rate law