What are 2 specific examples of things that can cause weathering of rock?
Physical examples = wind, rain, freezing
Biological examples = tree roots crack rocks
Chemical examples = acid rain, breakdown from moss/lichen (pioneer species)
Fill in the blank with the correct answer choice:
Warm air ________ (rises / sinks) and warm air hold ___________ (less / more) moisture compared to cold air.
Warm air rises and warm air holds more moisture.
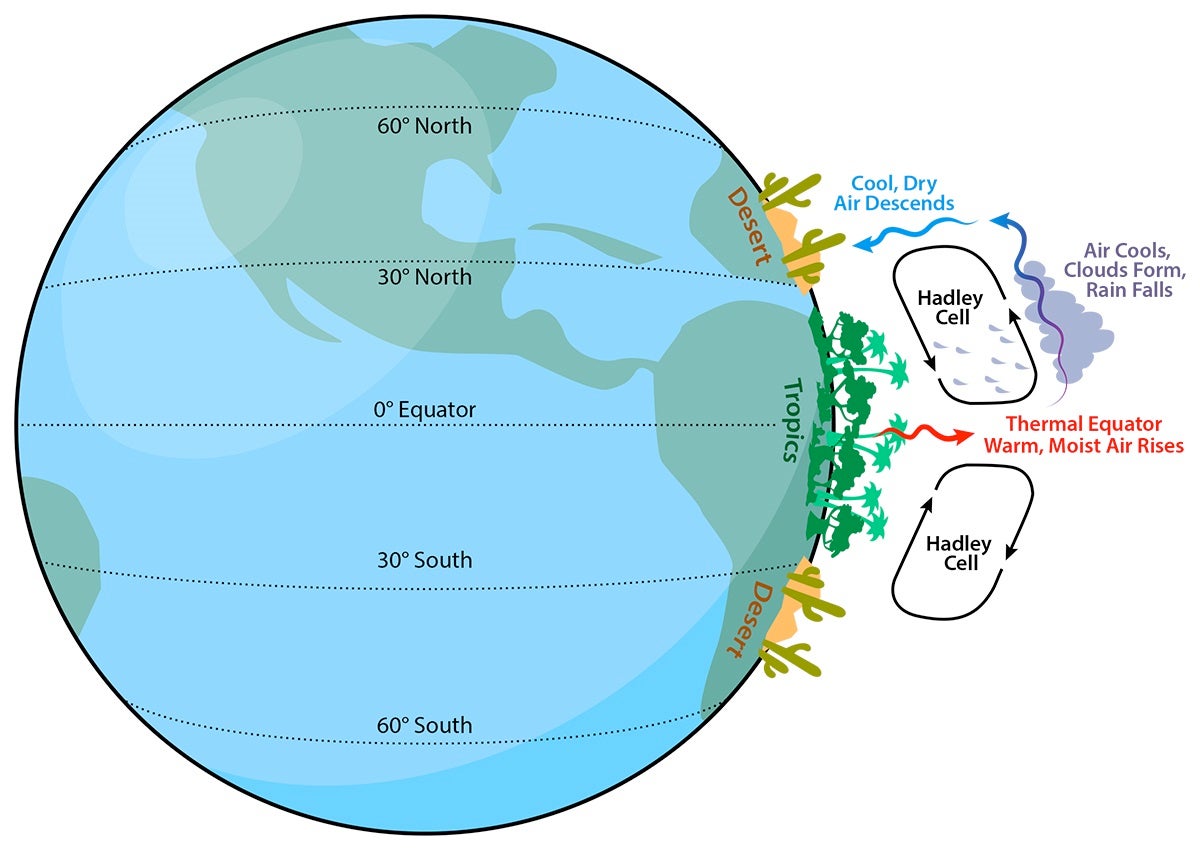
This is the reason tropical rain forests are found near the equator and deserts are found near 30 degrees north and south = Hadley cell.

This is the layer of the atmosphere in which the vast majority of ozone (O3) is found.
Stratosphere
Define albedo.
The proportion of light that is reflect by a surface
Surfaces with higher albedo reflect more light and absorb less such as ice and snow

What makes up the lithosphere? (earth layer)
Crust & thin upper mantle
Lithosphere is what makes up the plates in plate tectonics

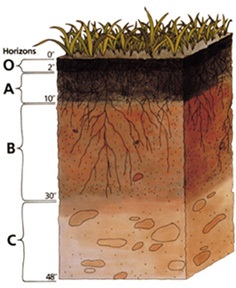
Which 2 soil horizons will have the most organic material such as plant roots and humus (decomposed material)?
O and A Horizon
What is the term for an area having little rainfall because it is sheltered from prevailing rain-bearing winds by a range of hills?
Rain shadow

The layer of Earth's atmosphere with the highest pressure; weather occurs here; and has the highest concentration of water vapor.
Troposphere
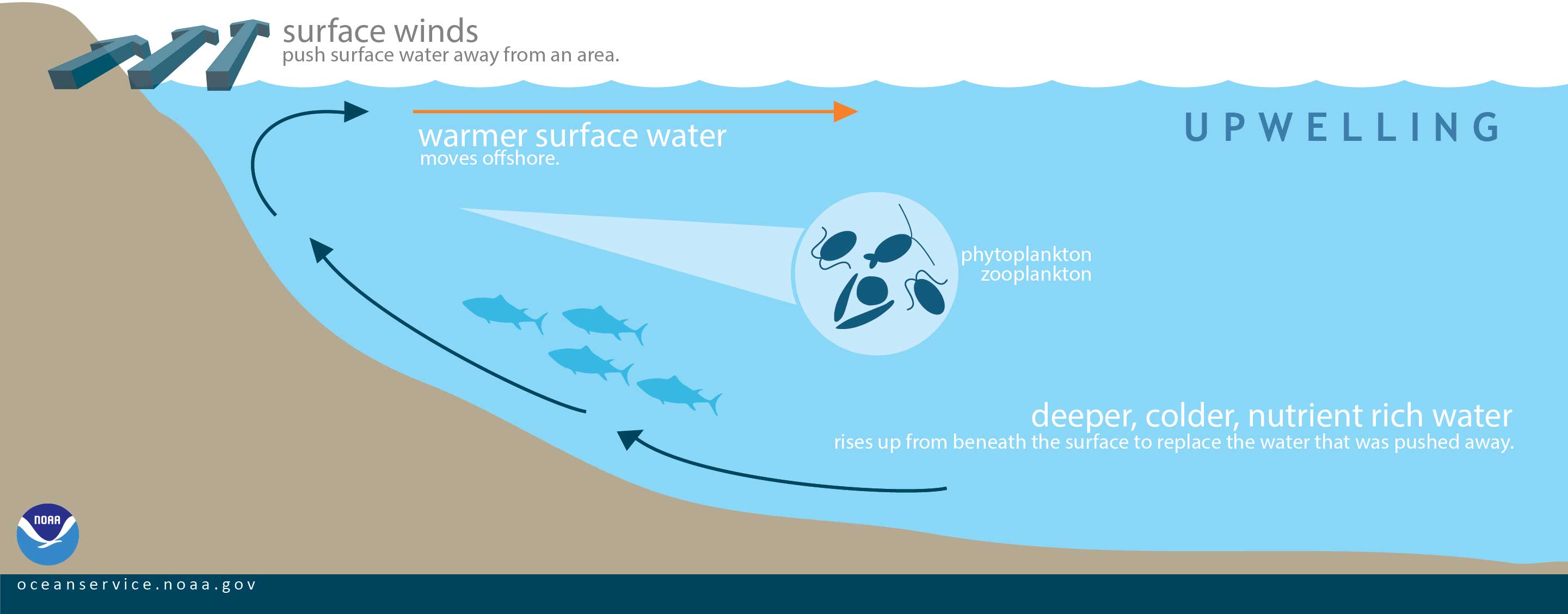
How will reduced upwelling during El Nino impact the anchovy fishing industry off the coast of Peru?
Decrease the fishing industry negatively impacting the fishermen because no upwelling means no nutrients for the anchovy thus decreasing the population

This type of boundary exists at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and increases the amount of Earth's crust through sea-floor spreading.
Divergent Boundary
Which soil texture (sand, silt, clay) will have the lowest water holding capacity?
Sand because it is more porous and has a higher porosity so the water will move right through it and not stay in place.
What is the Coriolis Effect?
The deflection of objects traveling through the atmosphere due to the spin of earth
Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), Argon (0.93%), Carbon Dioxide (0.04%)
Water Vapor could be 0-4% depending on region (think biomes)
An irregularly occurring and complex series of climatic changes affecting the equatorial Pacific region and beyond; characterized by the appearance of unusually warm, nutrient-poor water off northern Peru and Ecuador, typically in late December.
El Nino
Which letter represents the area that would receive nearly 24 hours of darkness on December 21st?

Letter A
Letter E would then have nearly 24 hours of sunlight on 12/21
Define soil degradation and provide 1 example of what could cause it.
Soil Degradation = the loss of the ability of soil to support plant growth
Examples: Tiling (loss of topsoil), Compaction (humans, livestock, agriculture machines), Nutrient depletion (monoculture - growing the same crop repeatedly)
Which direction do the trade winds blow? (these are found between the latitudes 0-30 degrees north and south)
East to West
<-------------------

What does the tilt of the Earths axis cause variation in?
Angle in solar insolation
Length of day
Season
What are upwelling zones in the ocean?
Areas where wind blows warm surface water away from a land mass, drawing up colder, deeper, nutrient rich water to replace it
Describe 1 human impact that would negatively impact a watershed, such as the Chesapeake Bay watershed.
Nutrient pollution (sewage, animal waste, synthetic fertilizers) leading to eutrophication
Urban development leading to more runoff of urban pollution
Deforestation leading to more runoff and weathering (soil erosion)
Identify 2 factors that can increase a soils water holding capacity and thus increase soil fertility.
Biological activity (insects, microbes), compost/humus, clay content, and root structures
What is solar insolation? How does it impact regional climates on earth?
Solar insolation is the intensity of sunlight and how the rays strike the earths surface - measure of solar energy
The equator gets more concentrated direct rays = warmer
30 and 60 degrees latitude get less concentrated rays because it is spread over more space

What happens to the trade winds during an el nino and a la nina?
Trade winds are weaker in an el nino and trade winds are stronger in a la nina.
What is the Thermohaline Circulation in the ocean?
It is an ocean current that connects all of the worlds oceans, mixing salt, nutrients, and temperature
thermo = temperature
haline = salt
What is the reason why rainforests are near the equator but deserts are at 30 degrees above and below it?

Dry air descends from the Hadley cells at around 30 degrees