results from the buildup of electrons on an object.
static electricity
always flow from the negative end of a power source to the positive end
electrons
a property of a circuit that hinders the motion of electric charge and converts electrical energy into other forms (usually heat)
Resistance
observed that a magnetic compass needle would turn when placed near a wire while carrying an electric current; the stronger the current, the stronger the deflection.
Hans Christian Oersted
used to increase the voltage of electricity as it travels through transmission lines
Step up transformers
Unlike charges attract
Like charges repel
Charged objects attract uncharged (neutral) objects
Law of Charges
electrons are able to travel down a path uninterrupted. This allows electrical devices to receive power.
Closed circuit
Formula for calculating amount of resistance
ohm's law: R=V/I
can be constructed by coiling a wire circuit around a soft iron core
records the total amount of electric energy (Joules) supplied to devices that are operating in your house
Power meter
Prevent and allow charges to move freely through them
the switch that turns devices on or off (completes or disrupts the flow of e-)
Control
The total amount of resistance in a series circuit
Rtotal=R1+R2+R3
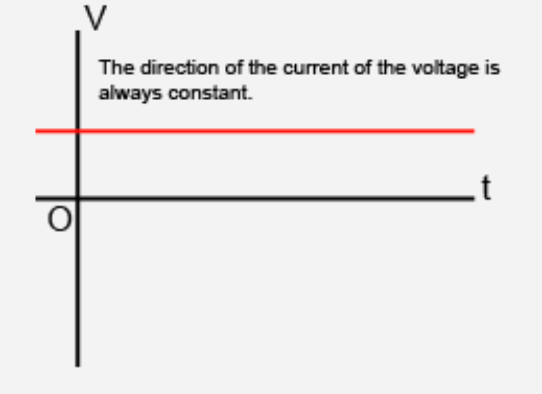
Direct current
acts as a safety switch that can cut off all power coming into the house if the current exceeds a certain level.
Circuit breaker
materials that are subjected to extremely low temperatures
Usually made of metal alloys or ceramics
Used in electric generators, high-voltage power lines, and supercomputers.
Superconductors
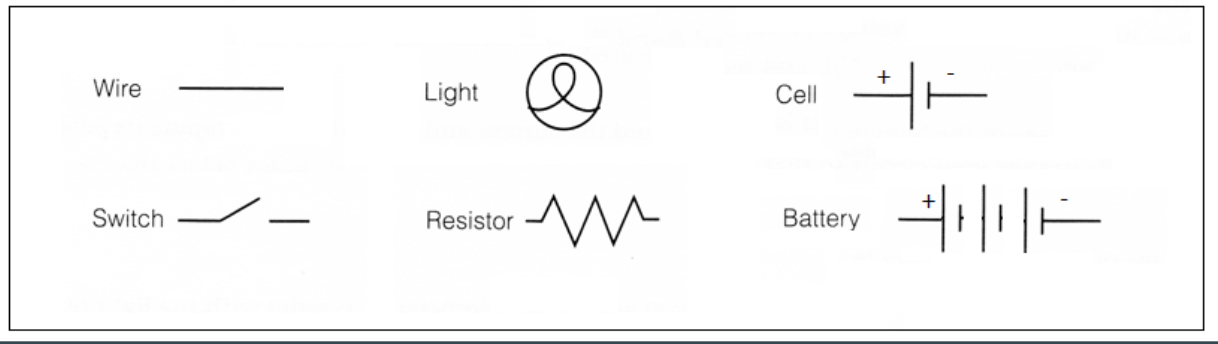
circuit symbols
The energy of charged particles, released
when they travel from place to place
electrical energy
rotated by magnetic forces between the permanent magnets and the armature, which acts as an electromagnet.
DC motor
P=E/t, P=IV
A type of static electricity in nature
lightning
multiple devices can be controlled seperately on this type of circuit
parallel circuit
The energy that results from motion
mechanical energy
The only viable form of electrical grid to efficiently use renewable energy
Micro-grid
release harmful by-products into the atmosphere, and are non-renewable.
fuels/coal/natural gas