These are the two main stages of the cell cycle.
What are interphase and the mitotic phase?
This phase is characterized by the alignment of duplicated chromosomes along an imaginary plane equidistant from the cell’s poles, setting the stage for their separation.
What is metaphase?
A critical control point where stop and go-ahead signals can regulate the cell cycle
This type of neoplasm remains localized and lacks the invasive properties necessary for spreading to distant tissues.
What is a benign tumor?
The contractile ring composed of actin and myosin filaments forms during this process, leading to the physical separation of the cytoplasm in animal cells.
What is cytokinesis?
This phase of the cell cycle is when DNA replication occurs.
What is the S phase?
During this phase, the cohesin proteins binding sister chromatids are cleaved, enabling their migration to opposite poles of the cell
What is anaphase?
The stage of the cell cycle that this cell is in 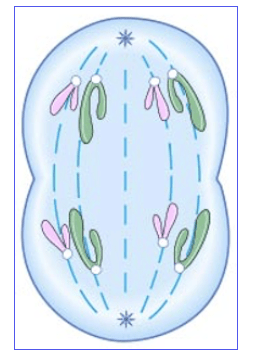
What is anaphase?
The dissemination of cancerous cells through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, resulting in the establishment of secondary tumors, is known by this term.
What is metastasis?
These identical copies of a chromosome, generated during the S phase of the cell cycle, remain connected at a specific region until they are separated during mitosis.
What are sister chromatids?
The mitotic spindles arise from this cell structure.
What is the centrosome?
This initial phase of mitosis involves the condensation of chromatin into visible chromosomes and the emergence of a microtubule-based structure from centrosomes
What is prophase?
This checkpoint checks to see if the cell has enough proteins, organelles, and nutrients in order to proceed to the next step of DNA replication
What is the G1 checkpoint?
The only stage of the cell cycle when you would see chromosomes
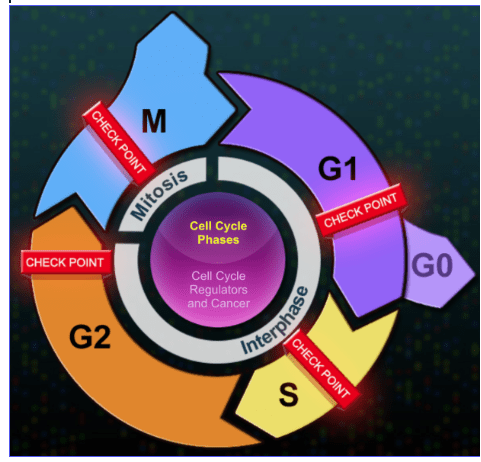
What is the M phase?
This less condensed form of DNA, prevalent during interphase, allows for the transcriptional activity necessary for cellular function and growth.
What is chromatin?
This process divides the cytoplasm to form two daughter cells.
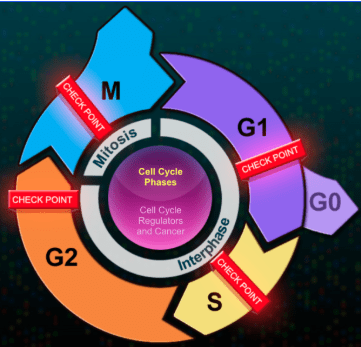
What is cytokinesis?
DAILY DOUBLE: Label the Diagram
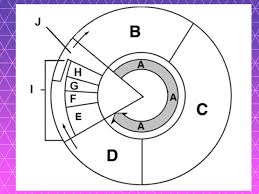
A: Interphase E. Prophase I. Mitosis (M phase)
B: G1 F. Metaphase J. Cytokinesis
C: S G. Anaphase
D: G2 H. Telophase
DAILY DOUBLE - Which of the following events does not occur during some stages of interphase?
a. DNA replication
b. organelle duplication
c. separation of sister chromatids
d. increase in cell size
separation of sister chromatids
These environmental agents induce changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, potentially resulting in the disruption of genes involved in cell cycle regulation.
What are carcinogens?
These cells exhibit uncontrolled proliferation, characterized by their insensitivity to regulatory signals such as anchorage dependence or density-dependent inhibition.
What are cancer cells?
This structure holds sister chromatids together.
What is the centromere?
Label these stages/phases occurring in the picture 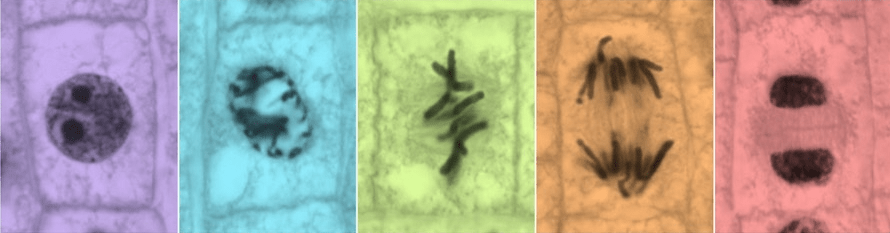
Interphase - no chromosomes visible
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
This specific checkpoint mechanism verifies the fidelity of DNA replication, ensuring that damaged or incomplete genetic material does not proceed to mitosis.
What is the G2 checkpoint?
The difference between Stage 1 and Stage 4 cancer.
What is a localized confined small tumor vs. spread to distant organs?
Uncontrolled cell division caused by mutations in these types of genes can lead to cancer.
What are oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes?