If you use money as a store of value, you would be
A: Buying a new watch
B: Lending money to a friend
C: Paying for gas on your credit card
D: Putting money into a savings account
D, putting money into a savings account
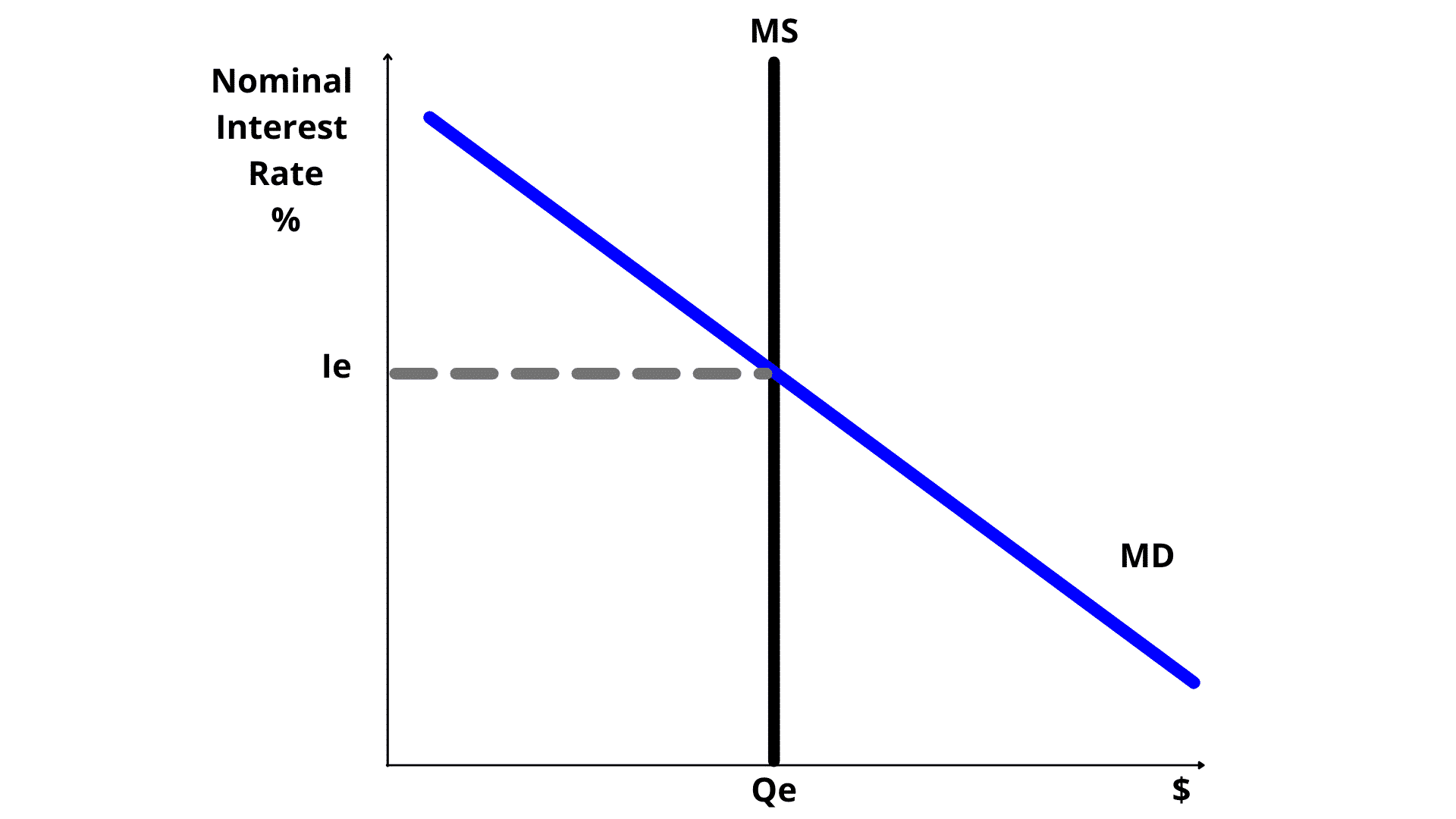
Draw out base Money Market Graph. Include labeled x and y axis, equilibrium, and lines.
Y-axis- labeled Nominal Intrest Rate
X-axis- labeled Quantity of Money
Need MS and MD, NIRe and Qe
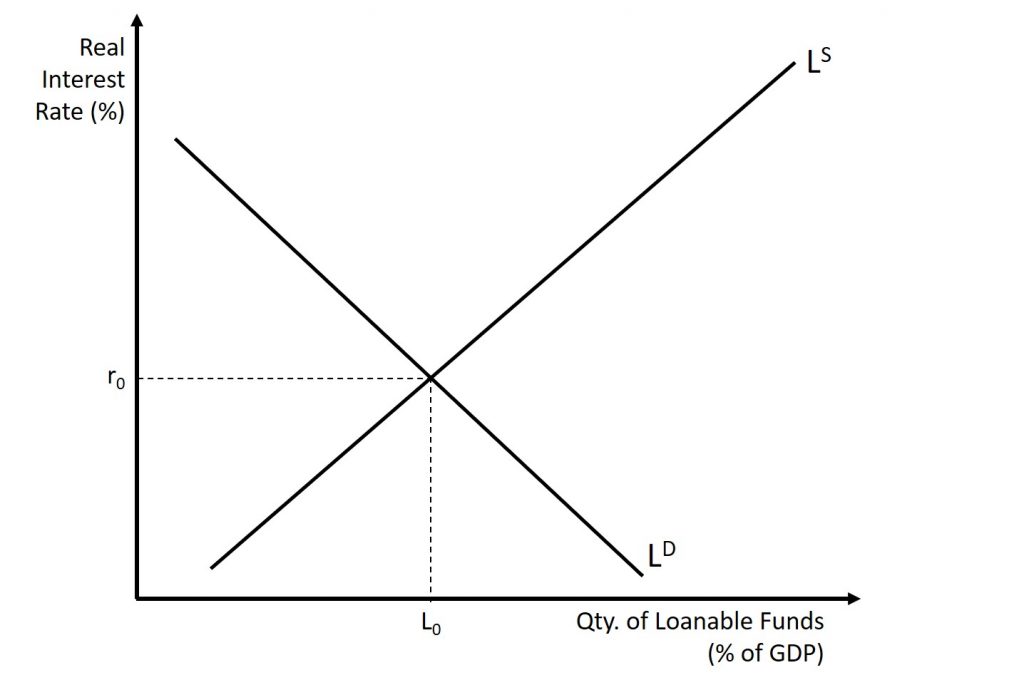
What does the Loanable Funds Market measure? (4.7)
What is the difference between nominal and real interest rates? (4.2)
Nominal: not adjusted for inflation
Real: adjusted for inflation
What does market equilibrium mean for the loanable funds market? (4.7)
the amount of borrowing equals the amount of saving (supply of loanable funds=demand of loanable funds)
Which of the following is true for the money market graph?
A: The demand for money is vertical because of autonomous spending
B: There is an inverse relationship between the nominal interest rate and the quantity of money demanded
C: The supply of money is downward sloping
B: there is an inverse relationship between the nominal interest rate and the quantity of money demanded
Draw out base Loanable Funds Graph. Include X-axis and Y-axis, equilibrium, and lines (all labeled)
Y-axis- labeled Real Intrest Rate
X-axis- labeled Quantity of Loanable funds
has RIRe, Qe, D, and S
If you are out shopping for school supplies and clothes, what is the easiest and most convenient for you to spend: M1 or M2? Explain. (4.3)
M1, since it's more liquid and easier to spend.
What is the difference between required reserves and excess reserves in banks? (4.4)
Required Reserves: what the bank has to keep in stock
Excess reserves: the money that the bank is able to loan out
Interest rates and supply of loanable funds have a(n) ______ relationship.
(4.7)
direct
Fractional Reserve Banking means that banks are required to...
A: charge the same interest rate on all their loans
B: expand the money supply when requested by the central bank
C: Insure their deposits against losses and bank runs
D: Keep part of their demand deposits as reserves
D: keep part of their demand deposits as reserves
MONEY MARKET GRAPH SHIFTERS
Supply of Money: Need one (vertical line)
Demand of Money: Need at least one (downward slopping)
Supply: Fed Reserve, reserve requirement, open market operation, discount rate
Demand: Price level, income, technology, transaction costs
The price of bonds and interest rates have a(n) ___ relationship. (4.1)
inverse
What is the formula for the money multiplier? (4.4)
1/reserve requirement
What are the determinants that shift the Money Demand (MD) curve in a graph of the Money Market? (4.5)
Price Level
Income
Technology
(PIT)
When an economy is at full employment, expansionary monetary policy will lead to...
A: lower interest rates and more investment
B: lower interest rates and less investment
C: Higher interest rates and lower prices
D: Higher interest rates and higher prices
A: lower interest rates and more investment
Reserve Market Graph- Base graph
*Hint DIOR fancy graph*
True or False
CAP is the discount rate Interest on reserves floor
True-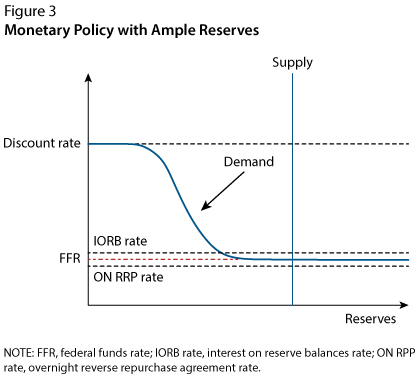
(4.6) In a limited economy, expansionary monetary policies cause:
Money Supply: Increase or Decrease
Interest Rate: Increase or Decrease
Borrowing: Increase or Decrease
Saving: Increase or Decrease
AD: Increase or Decrease
Money Supply Increase
Interest Rate Decrease
Borrowing Increase
Saving Decrease
AD Increase
What is the difference between money and wealth? (4.1)
Money: Medium of exchange used for transactions (cash/credit/debit)
Wealth: Broader Concept, assets (houses/cars/investments)
How is monetary policy different than fiscal policy? How are they similar? (4.6)
Different: They use different tools, they are performed by different administrative bodies
Similar: Both can achieve similar goals, both shift AD
If the Federal Reserve conducts an open market purchase of bonds, we can expect which of the following to occur in the short run?
A: The short-run Phillips curve will shift to the right
B: The short-run Phillips curve will shift to the left
C: There will be movement to the left along the short-run Phillips curve
D: There will be movement to the right along the short-run Phillips curve
C: there will be movement to the left along the short run Phillips curve
Loanable Funds Market
Shifters of Demand: F.A.D.E.
Shifters of Supply: S.E.L.F.
Foreign demand for domestic currency, All borrowing, lending, and credit, Deficit spending, Expectations for the future
Saving rate, Expectations for the future, Lending at the discount window, Foreign purchases of domestic assets
Assume that the current reserve requirement is 5%. If a bank receives a deposit of 9,000, what is the maximum possible increase in the money supply? (4.4)
$171,000
Required Reserve: 450
Money Multiplier: 20
8550(20)=171,000
List and describe the 3 functions of money (4.3)
Medium of Exchange: facilitates transactions between buyers/sellers (eliminates bartering)
Store of Value: saves purchasing power for future use
Unit of Account: provides a universal price tag for goods/services
Identify the 3 monetary policy "tools" typically used in an economy with limited reserves and explain how they would be used to increase the money supply (4.6)
Discount Rate: Decrease discount rate
Reserve Ratio: Decrease reserve ratio
Open-Market Operations: Buy bonds