These pores allow water entry into the sponge.
What are ostia?
Sponges are categorized in this phylum.
What is Porifera?
This is the kind of symmetry that all cnidarians have.
What is radial symmetry?
What is the general term for the group of photosynthetic dinoflagellates that reside in coral tissues?
What are zooxanthellae?
This abiotic stressor is the cause of coral bleaching.
What is thermal stress / ocean warming?
These "feeding cells" are found in a sponge's choanoderm.
What are choanocytes?
This is the asexual process in which a sponge piece breaks off and grows into a new sponge.
What is fragmentation?
This cnidarian body plan is typically sessile.
What is a polyp?
These are two benefits for algae living in coral tissues.
What is a stable intracellular environment, habitat with optimal light exposure, and protection from UV rays and grazers?
Ocean acidification severely limits this coral process.
What is coral skeleton formation?
This is the outer protective layer of cells on a sponge.
What is the pinacoderm?
These food sources are what sponges eat.
What are bacteria, plankton, and small organic particles?
These are the stinging cells that are characteristic of all cnidarians.
What are cnidocytes?
This is the term for the nutritional strategy that accounts for up to 90% of coral's fixed carbon needs.
Hint: strategy/mode, not the actual process!
What is autotrophy?
This human activity, which involves an underwater excavation of the bottom of a waterway, causes major sedimentation that can smother corals.
What is dredging?
These provide structure and support for sponges.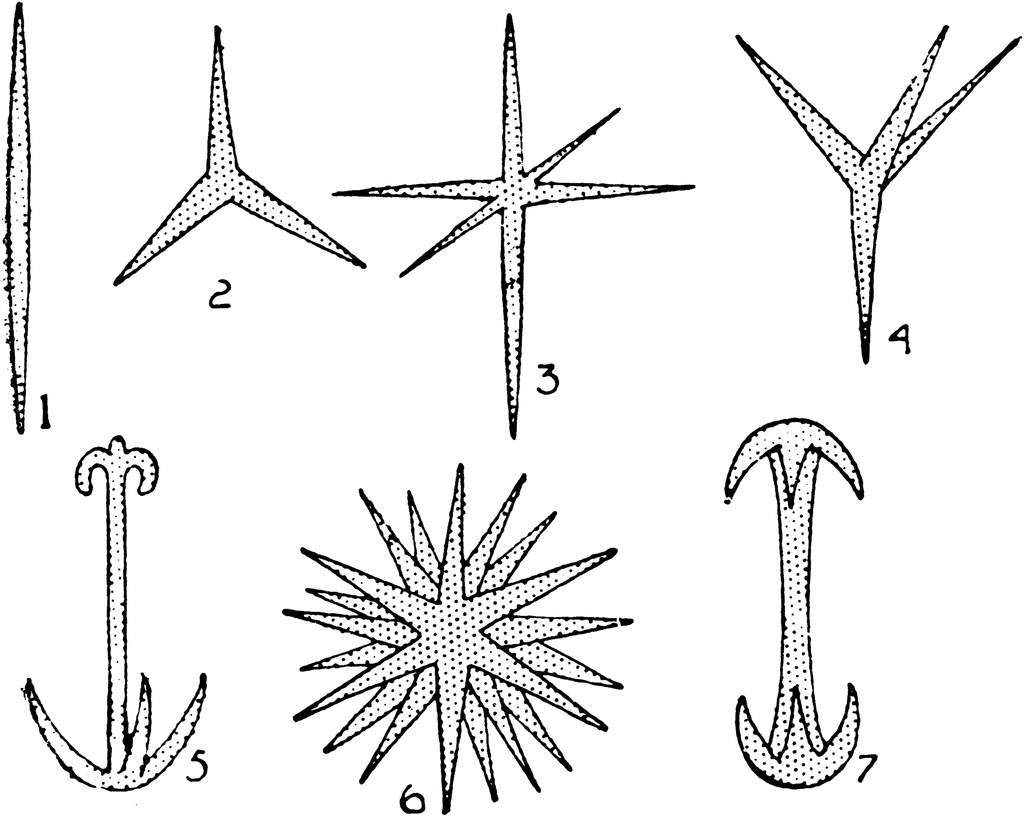
What are spicules?
This is the simplest body plan of a sponge.
What is an asconoid body form?
What cnidarian class includes box jellyfish?
What is Cubozoa?
These three materials are transferred from the symbiotic algae to the coral host.
Current scientific research suggests that this disease is caused by a bacterium called Cysteiniphilum litorale.
What is White Band Disease?
This flexible protein forms a matrix of gelatinous fibers in between cell layers of a sponge.
What is spongin?
This class of deep-sea sponges have a skeleton of six-rayed spicules made of silica.
What is Hexactinellida?
This term refers to an individual organism that makes up a part of a colony.
What is a zooid?
This is the method of symbiont acquisition in which algae is taken up by the host from surrounding seawater during the coral's lifetime.
What is horizontal transmission?
These byproducts of photosynthesis cause severe oxidative stress in corals, potentially leading them to expel their algal symbionts under certain conditions.
What are reactive oxygen species?