Mitosis creates genetically __________ cells.
[different or identical?]
Mitosis creates genetically identical cells.
What is the pink structure in ALL nucleotides?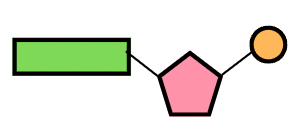
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (must answer the first question correctly first) What is the pink structure in DNA called and what is the pink structure in RNA called?
All nucleotides: Sugar
DNA: Deoxyribose
RNA: Ribose
Create a complementary strand for:
ATT - CGA - AGC - TGG
ATT - CGA - AGC - TGG
TAA - GCT - TCG - ACC
You use ___RNA to determine the amino acids needed to make a protein.
mRNA
True or false: Mutations can be beneficial, harmful, or have no effect.
True!
A parent cell has 10 chromosomes, how many does the daughter cell have?
10 chromosomes.
What is the green structure shown below?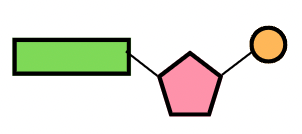
A nitrogen base
The 4 nitrogen bases in DNA are...
What blue structure is shown below?
tRNA
codon; anticodon
Was the mutation shown below....
a. random
b. from a virus
c. from UV radiation
d. from CHROMAKOPIA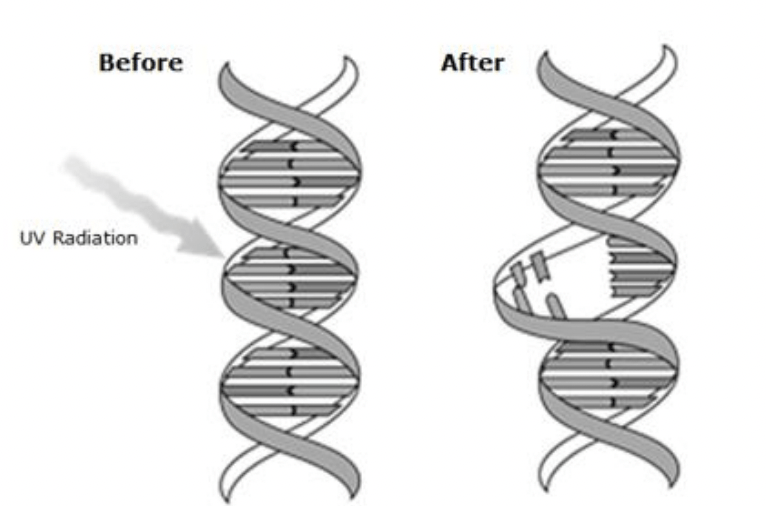
C. from UV radiation
Mitosis happens in __________.
[somatic cells or gametes?]
Mitosis happens in somatic cells.
What is the orange structure?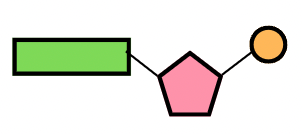
A phosphate group
Which letter is identifying the sugar-phosphate backbone?
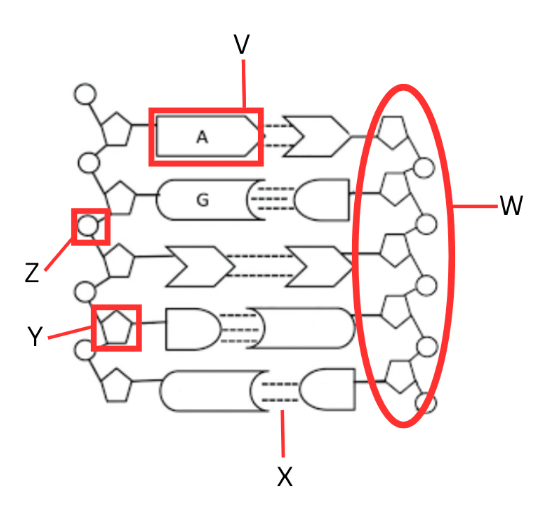
W
List 3 differences between DNA and RNA.
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (must answer the first question correctly first)
List at least 5 differences for double points.
- RNA is single stranded, DNA is double stranded
- RNA has ribose, DNA has deoxyribose
- RNA has Uracil, DNA has Thymine
- DNA is trapped in the nucleus, RNA can leave the nucleus
- RNA is a single strand structure, DNA is a double helix structure
DNA: GTT-CCA-GAA-TGC-ACC
mRNA:
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (must answer the first question correctly first)
Find the correct amino acids for this strand.
DNA: GTT-CCA-GAA-TGC-ACC
mRNA: CAA-GGU-CUU-ACG-UGG
AA: Gln - Gly - Leu - Thr - Trp
Mutations can be caused by _________ (something that causes mutations such as cigarettes).
Mutagens
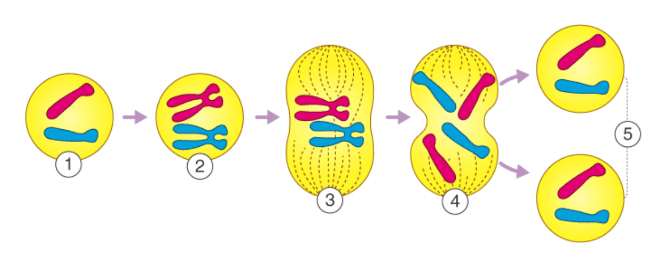
During what step does DNA replication occur?
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (must answer the first question correctly first)
At what step does mitosis start?
Step 1
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (must answer the first question correctly first)
Step 3
Fill in the blanks:
According to Chargaff's Rule, in a DNA molecule, there is always equal percentages of _________ and _________. There are also equal percentages of _________ and _________.
According to Chargaff's Rule, in a DNA molecule, there is always equal percentages of adenine and thymine. There are also equal percentages of guanine and cytosine.
Before DNA replication can start, what 2 changes to DNA's structure need to happen?
DNA needs to unwind and unzip to prepare for replication
What is strand C?
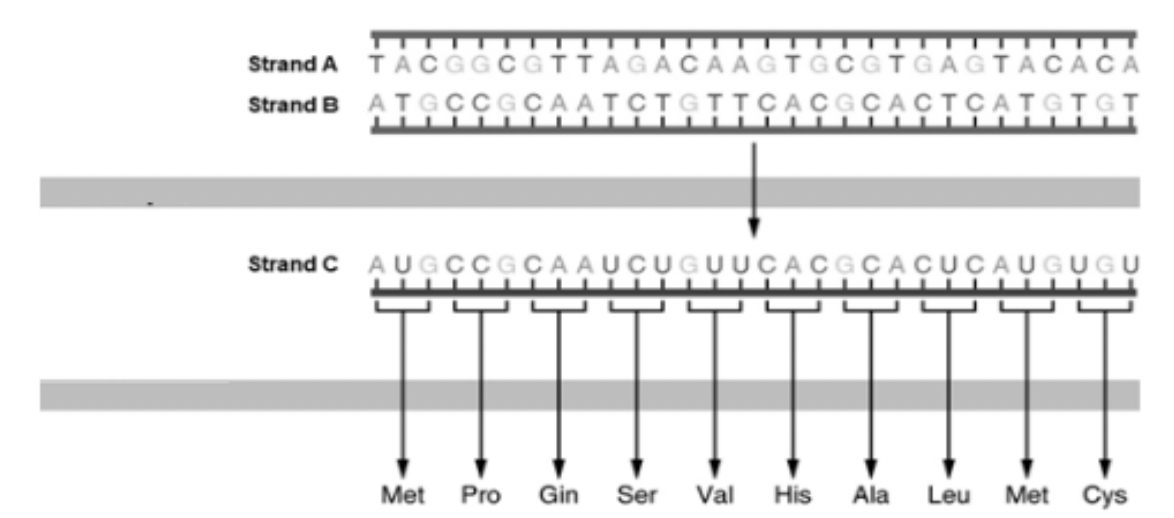
mRNA
__________ uses DNA as a template to make mRNA. _________ is when tRNA delivers the amino acids in the code of mRNA to the ribosome.
[hint: both are a process that start with T]
transcription uses DNA as a template to make mRNA. translation is when tRNA delivers the amino acids in the code of mRNA to the ribosome.
Is this a frameshift or point mutation?
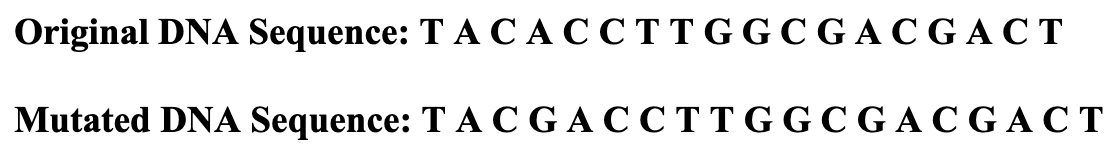
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (must answer the first question correctly first) What type of mutation is shown?
Frameshift.
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY:
Insertion mutation, a Guanine base has been inserted in the 4th base spot
What does Mitosis have to do with a paper cut?
Mitosis is responsible for the creation of identical somatic (body) cells. This process is important in the healing process such as growing new skin to heal a paper cut.
What process is being shown in the image below?
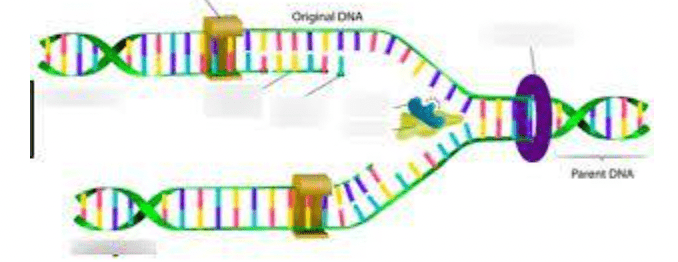
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (must answer the first question correctly first)
Explain why this process is "semi-conservative".
DNA Replication
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: 1 strand from the parent DNA molecule is pairs with 1 new strand in each of the strands created during DNA replication. As such, half of the parent strand is "conserved" in each new strand during DNA replication.
You want to test T-Rex blood to see what DNA nitrogen bases make up the blood sample. The blood is 22% Guanine, solve for the other 3 nitrogen bases.
Guanine = 22%
Cytosine = 22%
Adenine = 28%
Thymine = 28%
Explain the differences between the job of mRNA and the job of tRNA.
mRNA carries the "code" for which amino acids are needed to make a specific protein. mRNA binds to the ribosome and is read by tRNA. tRNA reads the mRNA by binding a matching anticodon to mRNA's codon. tRNA then goes to the cytoplasm and picks up amino acids that it brings to the ribosome. tRNA delivers the amino acids so they can bond together to build the desired protein.
Transcription happens in the.....
**DOUBLE JEOPARDY: (must answer the first question correctly first) Translation happens in the....
Transcription: the nucleus
Translation cytoplasm & ribosome are both acceptable, additional points for saying BOTH
Unknown Mutations 1, 2, 3, and 4 are shown below with how many amino acids the mutation affected. Which two mutations are POINT mutations?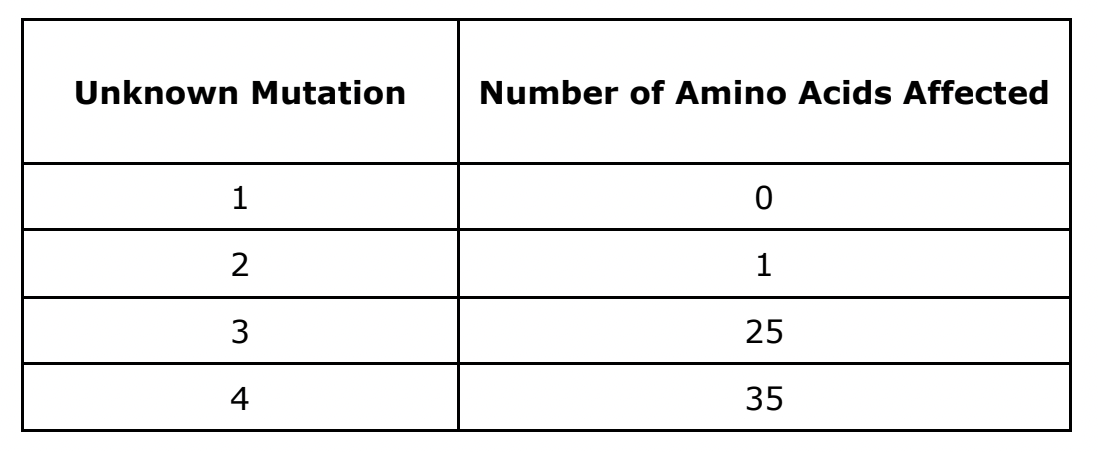
Unknown mutations 1 & 2