and Seasons
These four rocky planets are closest to the Sun.
What are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars?
This force keeps planets in orbit around the Sun. Mass and distance determine how strong it is.
What is gravity?
This number tells how stretched out an orbit is. It equals this: distance between foci ÷ length of major axis
What is eccentricity?
This law explains why planets move faster when closer to the Sun.
What is Kepler’s Second Law?
This is a huge cloud of gas and dust in space where stars can form.
What is a nebula?
These four large planets are made mostly of gas and ice.
What are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune?
A planet moves fastest at this point in its orbit.
What is perihelion?
An orbit with an eccentricity close to 1 looks like this.
What is very long and oval-shaped?
This law says planets move in elliptical orbits.
What is Kepler’s First Law?
These are substances, like water or carbon dioxide, that easily turn into gas.
What are volatiles?
This tool helps scientists see faraway objects, like planets, in space more clearly.
These are caused mainly by the Moon’s gravity pulling on Earth’s oceans.
What are tides?
Eccentricity is found by dividing the distance between foci by this.
What is the length of the major axis?
This law says planets farther from the Sun take longer to orbit.
What is Kepler’s Third Law?
This is a stream of charged particles constantly flowing outward from the Sun.
What is the solar wind?
These planets are more dense because they are made of rock and metal.
What are the inner planets?
The Moon orbits Earth while Earth orbits this object.
What is the sun
In June, this hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun and has summer.
What is the Northern Hemisphere?
What law does this picture demonstrate:
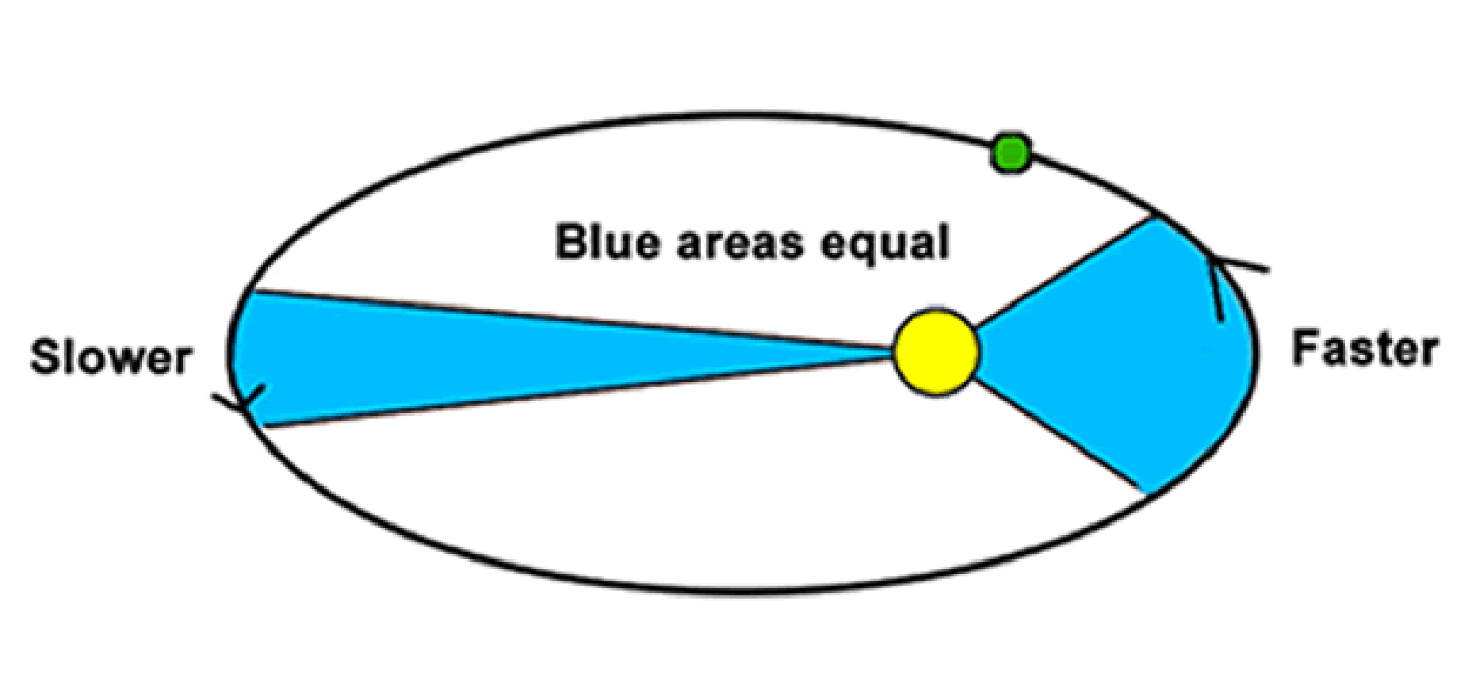
Keplers 2nd Law
This is a spinning disk of gas and dust around a young star where planets form.
What is a protoplanetary disk?
Describe the difference between the Heliocentric model and Geocentric Model.
The Heliocentric model puts the SUN at the center of the universe.
The Geocentric model puts EARTH as the center of the universe.
Fossils, ice cores, and glaciers are examples of this.
What is evidence of past climates?
The angle of sunlight and this affect how much energy Earth receives.
What is length of daylight?
Which law does this image illustrate:
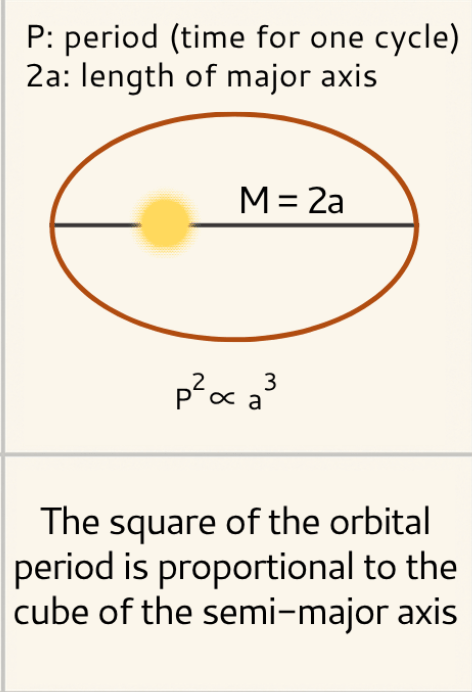
Keplers 3rd Law:
The TIME it takes for a planet to complete a full orbit around the sun is proportional to the cube of the planet’s average distance form the sun
This word means the amount of solar energy that reaches Earth’s surface.
What is insolation?