This is a never ending process that details how rocks are formed and reformed
The Rock Cycle
Melted metamorphic rock formed inside earth
What is magma?
FITB: Fossils provide evidence of what happened to the Earth in the ______.
Past
FITB: The Earth is _______ changing.
Constantly / always
Typically, an Earthquake is most likely caused by this type of boundary.
Transform boundaries
This typically forms when an organism is buried quickly after death, often in sediment
Fossil
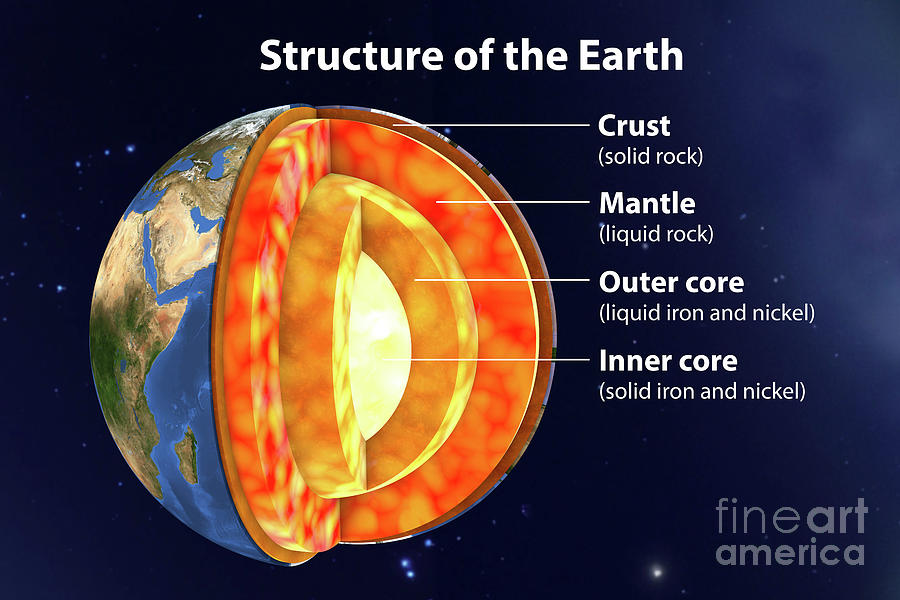
This layer of earth is the coolest and has the least amount of pressure
the crust
Rock formed when heat and pressure inside Earth change sedimentary rock into another kind
Metamorphic Rock
When two plates collide, this landform is usually created
mountains
Fossils are found in this type of rock
Sedimentary Rock
This layer of earth is the hottest and contains the most pressure
Describe the difference between convergent and divergent boundaries
Divergent boundaries move away, and convergent boundaries come together
A fossilized organism found deep within Earth's crust can tell us what about the past?
What kind of organisms existed back then.
Draw a diagram of the inside of earth and label the parts.
Pretend you are a rock in the rock cycle. Explain how you might go through the entire rock cycle.
Sediment compacted together creates sedimentary rock. A sedimentary rock can become a metamorphic rock when heat and pressure is applied. A metamorphic rock that has been melted under extreme heat turns to magma. Once magma is cooled, it becomes igneous rock. Igneous rock that has been through the process of weathering and erosion can once again go through the rock cycle as sediment.
An apartment complex has noticed that their grassy areas are eroding away. What is a method to reduce their erosion problem?
plant more grass, more vegetation
How are surface features such as volcanoes, mountains, trenches, earthquakes, and ocean ridges created by the Earth?
They are formed from the movement of tectonic plates
Deep within Earth's crust in one area of land, scientists found the skeleton of a fish. What does this tell us about the past?
It tells us that the land used to be covered by water