If you double the sample size, this component of the sampling distribution of the sample mean decreases by a factor of 1/√2, making the estimate more precise.
What is the standard error?
Different samples from the same population
produce different statistics
This range, derived from sample data and expressed as (lower bound, upper bound), is used to estimate the true population parameter
What is confidence interval?
You randomly select students from your university's roster, ensuring everyone has an equal chance of being picked. This is an example of this type of sampling.
What is simple random sampling?
You flip a coin five times and get all heads. Statistically, is this suspicious?
What is no? (Short runs of data can look unusual, but randomness allows streaks.)
A study of voting chose 663 registered voters at random shortly after an election. Of these, 72% said they had voted in the election. Election records show that only 56% of registered voters voted in the election. Which of the following statements is true about the boldface numbers?
72% is a statistic and 56% is a parameter
P is Low
reject the Ho
When using a large sample, the test statistic for a hypothesis test is often compared to this type of distribution to determine the p-value.
What is normal Distribution?
A survey claims "90% of people love this product,” but the sample consisted only of people who already bought it. This is an example of this sampling mistake.
What is selection bias?
In a fair six-sided die roll, the probability of rolling any one number is this percentage.
What is 16.67% (or 1in 6)?
In a certain region of the country, the proportion of the population with blue eyes is currently 17 percent. A random sample of 100 people will be selected from the population. What is the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion of people with blue eyes for samples of size 100
.17
If the sample size is reasonably large (equal to or greater than a sample size of 30)
what is Central Limit Theorem?
Failing to reject a false null hypothesis constitutes this type of error in hypothesis testing.
What is type II error?
A political poll only gathers responses from people who voluntarily call in or click an online poll, leading to an unrepresentative sample. This bias is known as:
What is voluntary response bias?
Despite each outcome being random, slot machines are programmed to have a set return percentage over many spins, which aligns with this statistical law.
What is the law of large numbers?
A survey of 100 randomly selected dentists in the state of Ohio results in 78% who would recommend the use of a certain toothpaste. The population proportion is known to be p=0.72. For samples of size 100, which of the following best interprets the mean of the sampling distribution of sample proportion of dentists in the state of Ohio who would recommend the use of a certain toothpaste?
The mean of all sample proportions from all random samples of 100 dentists in the state of Ohio is equal to 0.72.
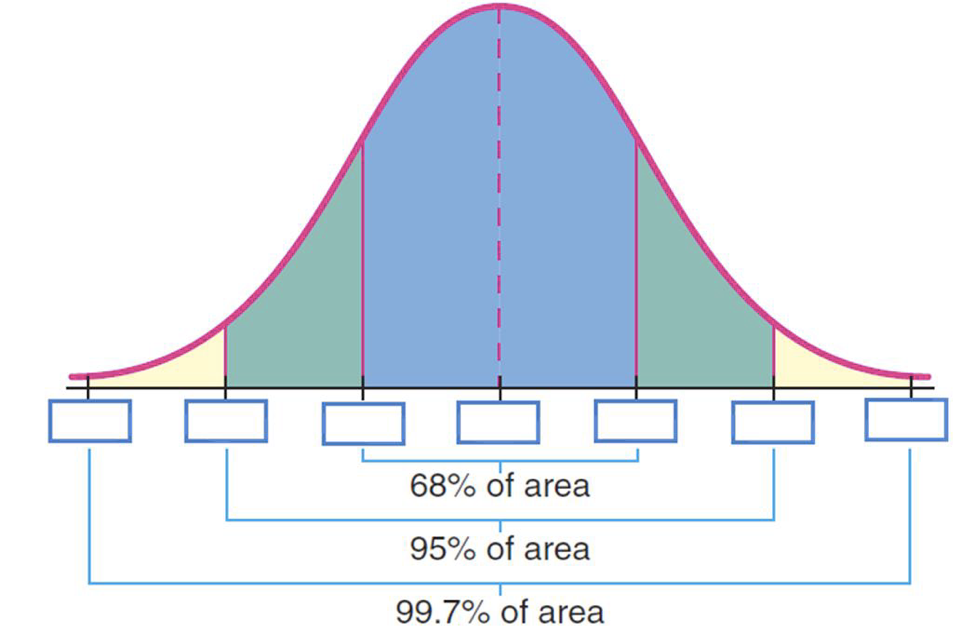
what is 0,68,95,99.7
Rejecting a true null hypothesis is known as this type of error.
What is Type I error?
A study claims to represent all U.S. adults but only surveyed college students. The results suffer from this flaw.
What is under coverage bias?
Casinos ensure their profits using a large number of bets and small individual advantages. This principle mirrors why sample means become more predictable as sample size grows.
What is central limit theorem?
The student newspaper at a large university asks an SRS of 250 undergraduates, "Do you favor eliminating the carnival from the term-end celebration?" All in all, 150 of the 250 are in favor. Suppose that (unknown to you) 55% of all undergraduates favor eliminating the carnival. If you took a very large number of SRSs of size n=250 from this population, the sampling distribution of the sample proportion p-hat would be
approximately Normal with a mean of 0.55 and standard deviation of 0.03
This statistic tells you how much the sample mean is expected to vary from sample to sample and is calculated by dividing the population standard deviation by the square root of the sample size.
What is the standard error?
Changing from a 95% confidence interval estimate for a population proportion to a 99% confidence interval estimate, with all other things being equal
The critical z-scores will go from ±1.96 to ±2.576, resulting in an increase in the interval size: or an increase of 31%.
A restaurant owner surveys diners about service quality—right after they eat an amazing meal. Responses may be skewed due to this type of bias.
What is response Bias
One of the biggest statistical myths is believing that an event that hasn't happened in a while is “due” to happen soon.
Gamblers Fallacy