This subatomic particle does not affect an atom's net charge
What is a neutron?
This side of the periodic table has the most conductive elements.
What is the left side?
This is the element shown in the PES graph below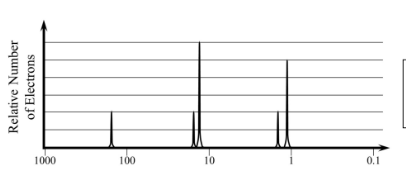
Chlorine (Cl)
This is a place electrons cannot be
what is a node
The mass of an atom depends on these two subatomic particles
What are protons and neutrons?
This corner of the periodic table has elements with the highest first ionization energy
What is the top right corner?
This is the PES of the element before this on the periodic table
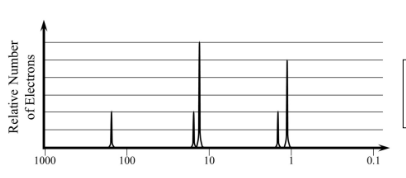
What is a diagram that is the same except the last peak is 1 shorter (only 4 high)
This is the color of light most likely emitted by an atom with the excited state configuration 1s22s12p1
What is red light?
A chlorine ion with 18 electrons has this net charge
What is -1?
Between K, Li, Cl, and F, this element has the largest atomic radius
What is K?
This is the electron configuration for sulfur, based on the fact that the electron configuration for Oxygen is 1s22s22p4.
What is 1s22s22p63s23p4
This is the excited state configuration basedd on the fact that a Be atom that absorbed energy had an electron jump from 1s to 2p.
What is 1s12s22p1
A neutral oxygen atom with average mass has this many protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What is 8 each of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
This is why valence shell attraction to the nucleus decreases down a column even though protons increase.
What is a greater number of electron shells (increasing distance to nucleus and electron repulsions)
This is a planetary model for an atom with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s1
shows 3 shells, 1st shell has 2 electrons, 2nd shell has 8 electrons, 3rd shell has 1 electron
This was our evidence for nodes in an atom
What is Atoms only emitting specific lines of color, not a rainbow of all colors