21) Draw the cell cycle.
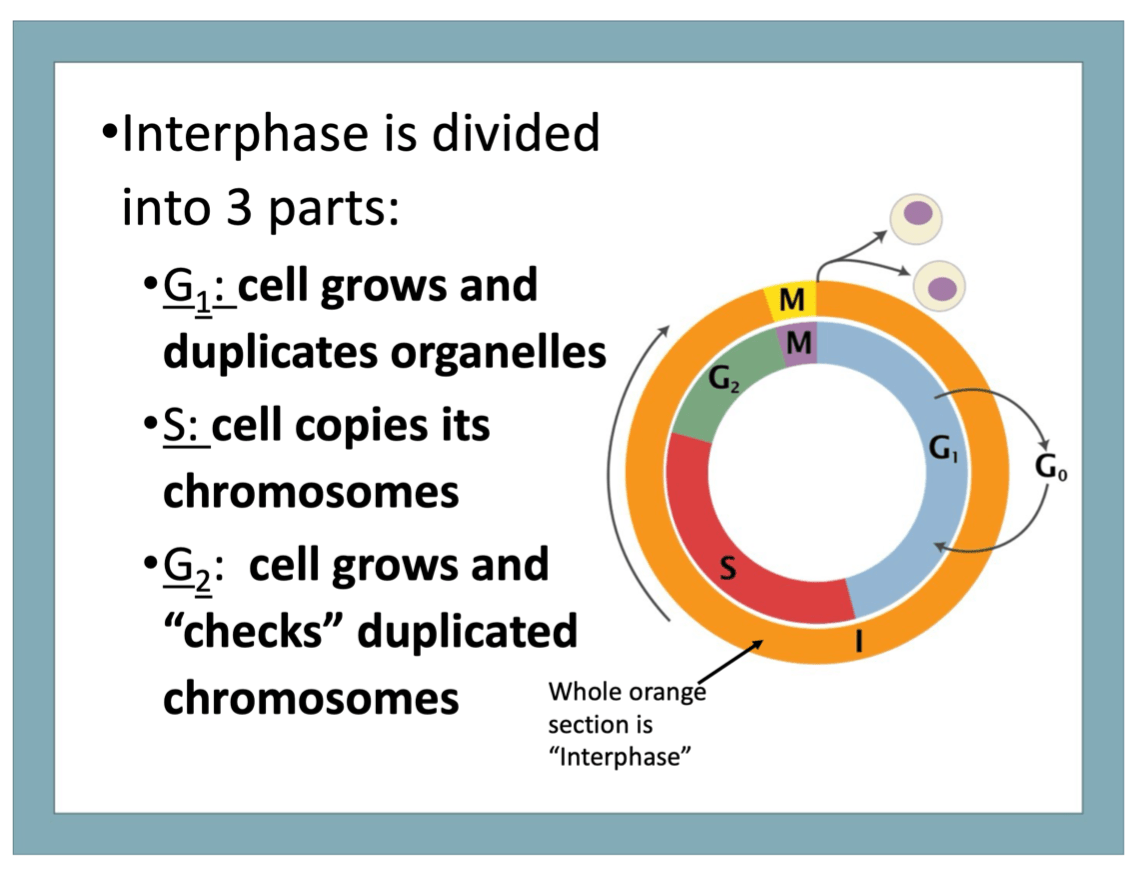
11) Name the 3 stages of interphase and something that occurs in each stage.
G1- cell grows and duplicates organelles
S- cell copies chromosomes
G2- cell grows and checks duplicated chromosomes
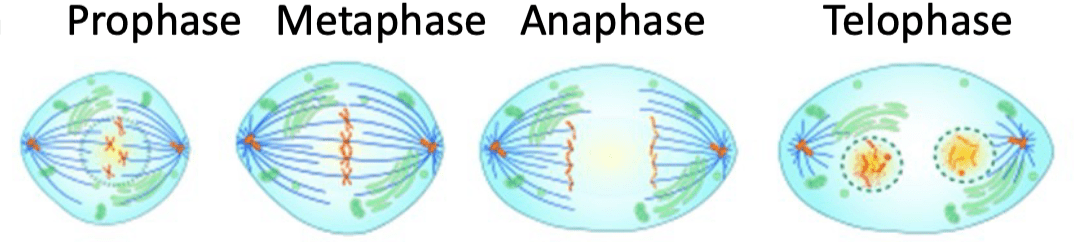
13) Name the phases of mitosis in order.
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
18) List three treatments for cancer.
Radiation, chemotherapy, surgery
14) What are two ways cells control the cell cycle?
External controls through growth factors and signals from other cells; internal controls from cyclins and Cdk.
10) How does cytokinesis differ in plant and animal cells?
In animal cells, the cell membrane pinches together.
In plant cells, a cell plate forms to divide the new cells.
7) Why do cells need to duplicate their chromosomes before mitosis?
Duplicating chromosomes allows each new cell to have a full set of genetic material.
16) How does a carcinogen affect the cell cycle?
Give an example of one.
Carcinogens can mutate the DNA of the cell, causing cyclins to be incorrectly produced. This prevents abnormal cells from stopping at checkpoints and can lead to uncontrolled growth.
Example: tobacco
15) What are cyclins and why are they important?
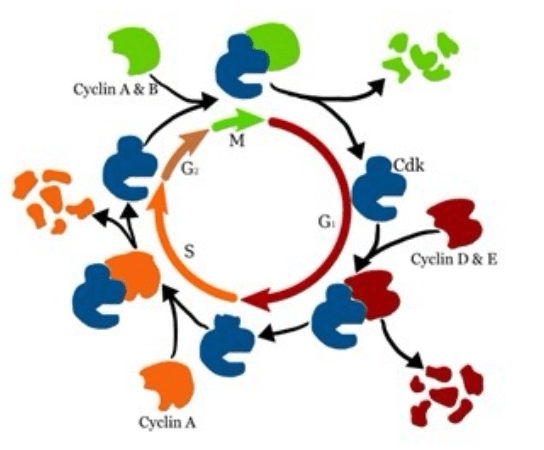
Cyclins are molecules that form and degrade creating checkpoints along the cell cycle.
How does the length of interphase compare to mitosis?

Interphase is much longer than mitosis. It accounts for about 90% of the cell cycle.
Brain Break!
9) Compare and contrast mitosis and cytokinesis.
Both involve division of the cell, but mitosis is the division of the genetic material (chromosomes) and cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm and remainder of the cell volume.
2) Give 2 reasons cells can’t survive at a large size.
The DNA would be overloaded providing instructions for proteins. The cell would also not be able to efficiently exchange materials.
12) Which phase of mitosis is this cell in? Identify the labeled structures.
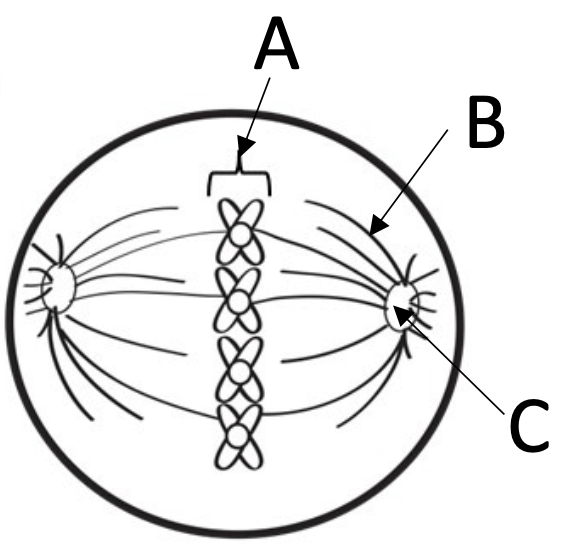
Metaphase
A- chromosome
B- spindle fiber
C- centriole
1) Give 4 differences between asexual and sexual
reproduction.
Most unicellular organisms reproduce
through asexual reproduction, in which
one cell divides into two.
Multicellular organisms can also
reproduce asexually through:
Budding: An outgrowth forms from one
parent organism
Vegetative propagation: Some portions
of certain plants can be cut off and
regrown into a whole new plant
Sexual reproduction involves the joining
of 2 reproductive cells- one from each of
2 parents.
Although asexual reproduction is often
easier (no need to find a mate), sexual
reproduction helps to mix genetic
information which can improve a
species’ survival.
4) Describe the process of binary fission. In which type of cells does this occur?
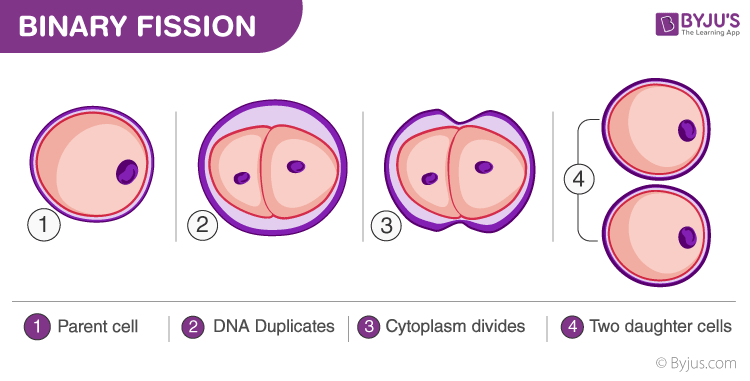
Binary fission involves copying circular DNA and pinching the cell in half. This occurs in prokaryotic cells.
17) When does a tumor get classified as “malignant”?
A tumor is classified as malignant when it has spread to another area of the body from its origin.
8) Identify the labeled items.
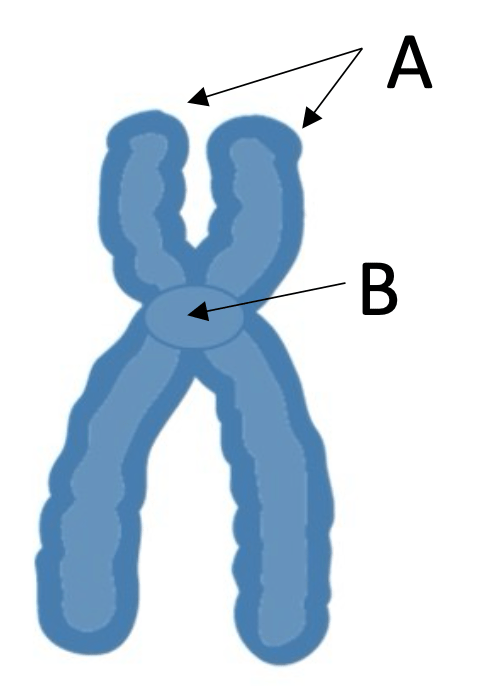
A- sister chromatids
B- centromere
5) Why does chromatin condense into chromosomes before mitosis in eukaryotic cells?
Chromosomes are more organized and compact, causing the DNA to be divided more easily without getting tangled.
22) Draw the 4 phases of mitosis.