The following initial rate data for the reaction A + B --> C were obtained. Write the rate law expression for this reaction.
Trial [A] [B] Initial Rate (mol/L*s)
1 0.15 M 0.15 M 3 x 10-2
2 0.15 M 0.30 M 3 x 10-2
3 0.30 M 0.30 M 1.2 x 10-2
rate = k[A]2
Is the following Reaction Energy profile depicting a reaction that is exo- or endothermic?
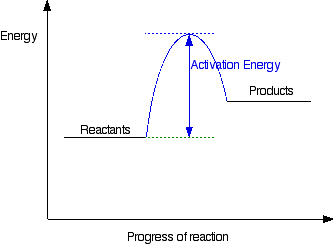
What is endothermic?
Name one change that can be made to a chemical reaction to decrease the rate at which it occurs.
What is, decrease concentration, increase volume, decrease pressure, decrease temperature, remove a catalyst, etc.
Identify the catalyst in the following reaction mechanism.
A + B --> C + D
D + E --> B + F
What is compound/element B?
The reaction of CH3COCH3 + I2 --> CH3COCH2I + HI is run under carefully controlled conditions in the presence of an excess acid. Write the rate law for the reaction using the following data.
Trial [CH3COCH3] [I2] Initial Rate (mol/L*s)
1 0.100 M 0.100 M 1.16 x 10-7
2 0.0500 M 0.100 M 5.79 x 10-8
3 0.0500 M 0.500 M 5.79 x 10-8
Rate = k[CH3COCH3]
What is the name used to describe what occurs at the peak of a reaction energy profile like the two shown below?

What is a Transition State?
The temperature is altered in two trials of an experiment where the following reaction occurs: 2 NO2(g) --> NO3(g) + NO(g)
If the temperature is increased, describe what is happening to the rate of consumption of NO2
What is the rate of consumption is increasing.
Identify the intermediate in the following reaction mechanism.
Overall: 2 NO2Cl(g) --> 2NO2(g) + Cl2(g)
Step 1: NO2Cl --> NO2 + Cl (slow)
Step 2: NO2Cl + Cl --> NO2 + Cl2 (fast)
What is Cl?
The following reaction was observed and the following data was collected. Write the rate law for the overall reaction.
H3AsO4 + 2H3O+ + 3I- --> HAsO2 + 4H2O + I3
Trial [A] [H3O+] [I-] Initial Rate
1 0.001 0.010 0.10 3.70 x 105
2 0.001 0.010 0.20 7.40 x 105
3 0.002 0.010 0.10 7.40 x 105
4 0.001 0.020 0.10 1.48 x 106
Rate = k[H3AsO4][H3O+]2[I-]
Determine the order of this unknown reaction by analyzing these reaction order graphs.
What is Zeroth Order?
Assume that NO(g) reacts according to the rate expression below:
rate = k[NO]2[H2]
How does the rate change if the concentration of H2 is doubled?
The rate would double.
NO(g) and O2(g) react to form NO2(g). The rate law of the reaction is rate = k[NO]2[O2]. If the reaction occurs in a single elementary step, what is the overall reaction equation for this reaction?
What is 2NO + O2 --> 2 NO2
NO will react with bromine according to the reaction:
2 NO + Br2 --> 2 NOBr
Experimentally, the following data were obtained:
Trial [NO] [Br2] Initial Rate (mol/L*s)
1 1.0 M 1.0 M 0.80
2 1.0 M 2.0 M 1.60
3 2.0 M 2.0 M 6.40
Determine the rate law, and the value for the rate constant k with the correct units.
Rate = k[NO]2[Br]
k = 0.80 1/m2 * s
Determine the reaction order, and the rate constant k for the reaction depicted below.
Time [NO2] ln[NO2] 1/[NO2]
0 1.00 x 10-2 -4.605 100
60 6.83 x 10-3 -4.986 146
120 5.18 x 10-3 -5.263 193
180 4.18 x 10-3 -5.477 239
240 3.50 x 10-3 -5.655 286
300 3.01 x 10-3 -5.806 332
360 2.64 x 10-3 -5.937 379
What is Second Order
k = 0.775 L * M-1 * s-1
The gas-phase reaction A2(g) + B2(g) --> 2AB(g) is assumed to occur in a single step. Two experiments were done at the same temperature inside rigid containers. The initial pressures of A2 and B2 used in experiment 1 were twice the initial pressures used in experiment 2. In which experiment would the initial formation of AB be higher?
What is experiment 1.
Determine the reaction slow step and the rate law for this mechanism.
Step 1: ?
Step 2: NO3(g) + CO(g) --> NO2(g) + CO2(g)
Overall: NO2(g) + CO(g) --> NO(g) + CO2(g)
What is...
Step 1: NO2(g) + NO2(g) --> NO3(g) + NO(g)
rate = [NO2]2