What type of galaxy do we live in?
Spiral galaxy
Stars are born here:
What 2 properties of stars are used to plot stars on the HR diagram?
Temperature and brightness
The big bang theory says that the universe has been ____________ for the last 13.8 billion years.
Expanding
Point to the spot on the image below where we could find our solar system in the Milky way galaxy?
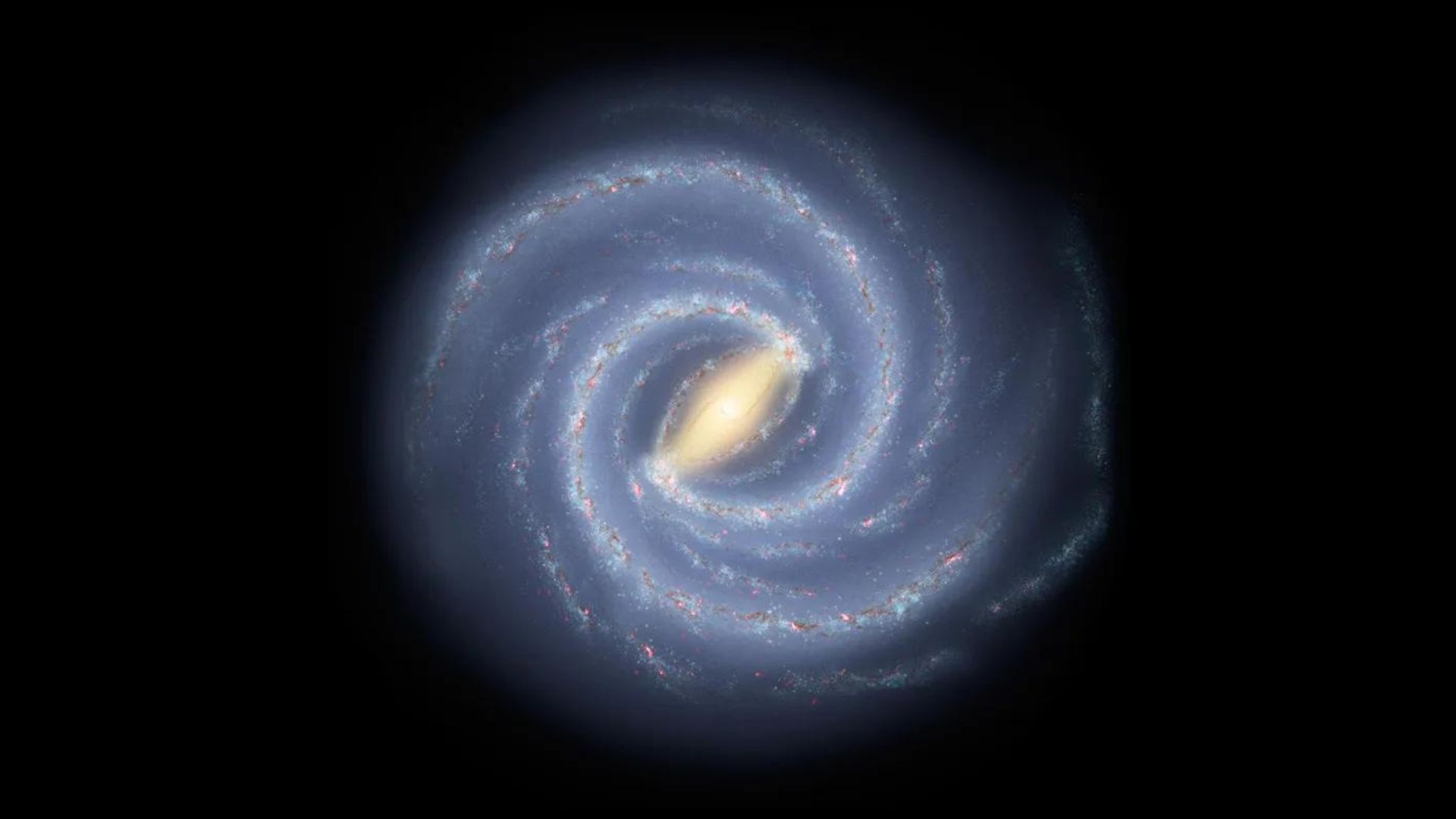

(The correct spot)
Stars spend about 90% of their life in this stage?
Main sequence
What do we call the stars that fall on the long diagonal line on the HR diagram?
This phenomenon is evidence of the big bang theory's idea that the universe is expanding.
Redshift
What is a light-year
The distance that light can travel in a year.
This is the last stage in the life cycle of an average mass star:
White dwarf
What type of stars have the lowest luminosity and are in spectral classes F-B?
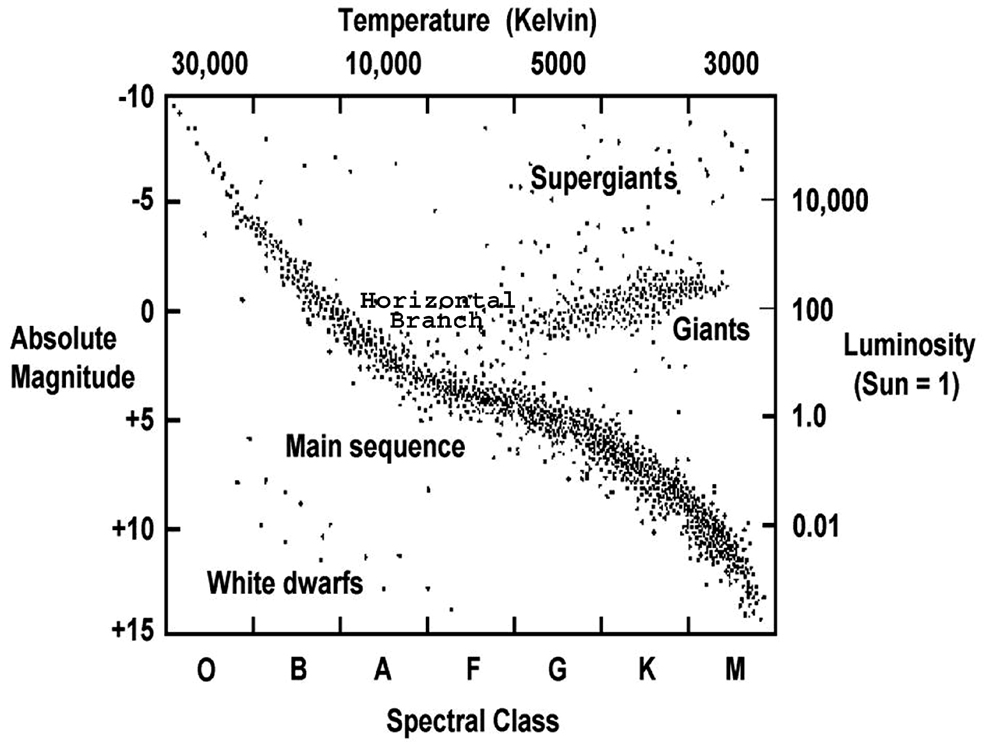
White dwarfs
What is redshift?
When galaxies/stars are moving away from us, their spectral lines are shifted towards the red side of the spectrum.
What feature do scientists use to classify galaxies?
Their shape.
Reorder this list from largest to smallest:
Moon, Universe, Galaxy, Planet, Nebula, Solar system, Asteroid, and Star
Universe --> Galaxy --> Nebula --> Solar system --> Star --> Planet --> Moon --> Asteroid
What is a planetary nebula?
When a giant star runs out of fuel, it gently releases its outer layer in every direction; leaving only the core behind.
Name the main sequence stars in this HR diagram from coolest to hottest?

Barnard's star, Proxima Centauri, Tau Ceti, Sun, Alpha Centauri A, Procyon, Vega, Sirius, then Spica.
The universe has microwave radiation known as CMB everywhere we look. How is this evidence of the Big Bang Theory?
Explain how looking at the stars/galaxies in the night sky is the same as looking as million/billions of years into the past.
It takes light million/billions of years to get from those distant galaxies/stars to Earth, so by the time it gets here, that much time has already passed, so they are not where we are currently seeing them, that is how they appeared million/billions of years ago.
In detail, explain the life cycle of a massive star. Include WHY a star goes from stage to stage.
A star is born in a nebula because of gravity, then it is in the main sequence, eventually the core runs out of hydrogen and the star expands into a supergiant, then when it runs out of fuel again it will explode in a supernova and become either a neutron star or a black hole.
Explain how the HR diagram shows the life cycle of a star?
The youngest stars are at the top left of the main sequence, then as they get older they go along the main sequence, when they run out of fuel they become a giant or super giant, then when a giant runs out of fuel it becomes a white dwarf.
Explain how the cosmic background radiation started as gamma rays, but is now microwaves, and how it's related to the big bang theory.
The theory states that 13.8 billion years ago the big bang released the gamma rays all around the universe, but as the universe has expanded over time, those waves have been extended (red shifted) into x-rays, then UV rays, light, waves, infrared, and finally microwaves.