Define the law of conservation of energy in your own words.
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed.
What is the formula and unit for work?
Work = force x distance
Unit = joules (J)
Gravitational Potential Energy
These are the subatomic particles that move around during charging.
Electrons
A change in momentum is known as
impulse
This is the height of the wave
amplitude
Given the graph below, Molly was pushing her dresser for 12 meters, but eventually she found that she not have to increase her force needed to push on the dresser to keep it moving anymore. At what meter-marker did she stop adding more force into pushing on the dresser?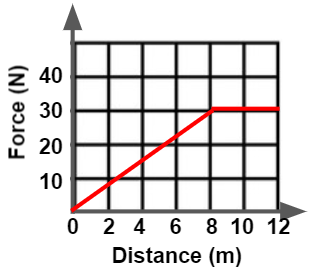
8 seconds
A force of 50 N is used to push a chair 25 cm across the floor. What is the increase in energy (work done) as a result of this movement? (Hint: 100 cm = 1 m)
12.5 J of work
A tennis ball is thrown upward. Prior to reach the peak of its ascent, what type(s) of energy does the ball have?
No steal question! Two negatively charged particles of -5C and -8C are placed 5 meters apart. Will they attract or repel?
repel
What is the momentum of a 10 kg object traveling at 10 m/s? (Include units)
100 kg-m/s
decreases
Give an example of a scenario in which no work is done.
....
This is the variable used to calculate power, that work does not need.
It is 1983. You have just gotten your first job at Mountain Creek for the summer. You new manager tells you that there is a coaster they need to test out called the "Cannonball Loop." He says he will give you $100 dollars (aka: 400 Jeopardy points) if you can identify the types of energy you will have at the top of the loop section of the Rollercoaster. A picture is shown.
KE and PE
Give an example of a conductor...
...
What is the only type of collision where kinetic energy is conserved?
elastic
As a sound moves towards you, the wavelength of the sound...
decreases
**DAILY DOUBLE**These are the two things that must happen in order to say work has been done...
1. Force must be applied
2. Object must move parallel to applied force
From the graph below, how much work is complete between 8 and 12 seconds?
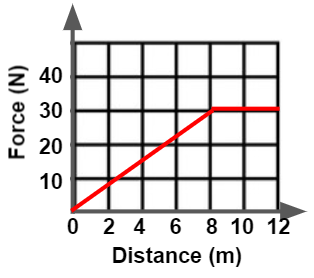
120 J
Give an example of a situation when you would have GPE, KE, and EPE all at once.
....
The difference between conduction and induction is...
Two objects collide and stick together, this is known as a............ collision
inelastic
Two waves are out of phase, this means....
**DAILY DOUBLE**Two people of the exact same weight are climbing up from the football field. Person A chooses to use the stairs and Person B chooses to use the hill. Person A takes 30 seconds and Person B takes 20 seconds to get up the hill. Compare their work done and their power.
Work is equal.
Person B is more powerful because it took them less time.
Two students race up the stairs. Student A performs 10 J of work, but get up the stairs in 5 seconds. Student B perform 20 J of work and get up the stairs in 10 seconds. Who is more powerful?
Neither, both 4 Watts
How much gravitational potential energy does a 120 N hiking backpack have when it is sitting on a ledge 25 meters above the ground?
3,000J
Find the force on two charged particles, one with a charge of -5 C and one with a charge of 10 C, placed 5 meters apart.
1.78 x 1010 N
What is true about momentum at all times?
The wavelength must be measured between....
two identical points
A block of 10 kg is placed at the top of a ramp that is 10 meters high. What is the energy of the block? (Type and Amount)
GPE and 980 J
Fair Game: Any group may answer to win points. Show your work on a piece of notebook paper.
An object with a mass of 320 kg is lifted by way of an elevator for 3 minutes. The object moves an overall distance of 4 kilometers. What is the work done?
12,544,000 J
A spring with a spring constant of 200 N/m is compressed 0.3 meters. How much elastic potential energy is stored in the spring?
9 J
Describe the process of conduction.
1. Touch charged objects
2. Electrons run away from each other
3. Charge splits evenly
4. Pull apart
Two cars collide and stick together. The one car is going 10 m/s to the right while the other car is going 5 m/s to the left. If both cars are 100 kg, how fast will they be going when they are together?
2.5 m/s
The Doppler Effect applies to what type of waves?
Electromagnetic (sound, light, etc.)
Fair Game: Any group may answer to win points. Show your work on a piece of notebook paper.
A 10 kg block has 100 J of energy at the top of a ramp. At the bottom of the ramp, it slides into a spring (spring constant k=10) and compresses it. How far will the spring be compressed?
4.47 meters
Fair Game: Any group may answer to win points. Show your work on a piece of notebook paper.
An object with a mass of 200 kg is lifted by way of an elevator for 2 minutes. The object moves an overall distance of 4 kilometers. What is the power?
65,333.33 W
Fair Game: Any group may answer to win points. Show your work on a piece of notebook paper.
A 10 kg block has 100 J of energy at the top of a ramp. At the bottom of the ramp, what is the blocks velocity?
4.5 m/s
Describe the process of induction.
1. Bring charged object close
2. Electrons run into ground wire
3. Unplug ground
4. Take away charged bar
5. Positive charge in end
If the change in momentum for a car of mass 100 kg traveling at 10 m/s coming out a stop is 100 kg-m/s. What is the impulse?
100 kg-m/s
Concave mirrors give what types of images?
It varies.