The shape of DNA
What is a double helix?
DNA replication occurs in which direction?
What is from 5' to 3'.
The location of transcription in eukaryotes
What is the nucleus
The location of translation in eukaryotes
What is the cytoplasm?
what is a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA
The shape of RNA
What is a single strand?
The function of helicase is to
What is unzip the DNA strand?
The flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins to traits is known as
What is the central dogma?
What is the purpose of translation?
What is to make proteins from mRNA?
This type of mutation occurs when one nucleotide is change for another one.
What is a substitution?
The base pairs in DNA are
What is a A-T, G-C?
The enzyme that adds DNA nucleotides to the new strand of DNA
What is DNA polymerase III?
What is the purpose of transcription?
What is to make mRNA from a DNA template.
What types of RNA are involved in translation?
What is tRNA, rRNA, and mRNA?
This type of mutation occurs when a nucleotide is added
What is an insertion?
This RNA nucleotide replaces Thymine (T)
What is a Uracil (U)?
The enzyme that adds a piece of RNA primer so that DNA polymerase can start adding nucleotides is called
What is Primase?
During elongation of transcription, what does RNA polymerase do?
What is adds RNA nucleotides to build a strand of mRNA.
During elongation of translation, these groups of three nucleotides on mRNA code for amino acids. What do you call these groups of three?
What is a codon?
Determine the type of mutation that occurred:
Original DNA: ACTGGTTCTAAGTCG
Mutated DNA: ACTGTTCTAAGTCG
What is a deletion?
This type of RNA is responsible for carrying amino acids to the ribosome during translation.
What is a tRNA?
The difference between the leading and lagging strands
What is the leading strand is synthesized continuously while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously, creating Okazaki fragments that need to be bonded together by ligase.
After termination, how is RNA modified before it leaves the nucleus?
What is a 5' cap and a poly-A tail are added to protect it from enzymes in the cytoplasm.
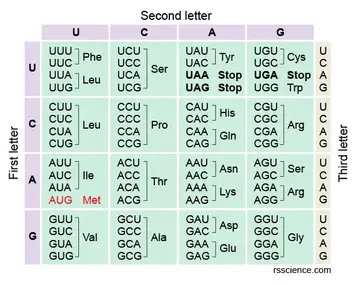 Use the image to translate the following mRNA:
Use the image to translate the following mRNA:
AUG - GCU - GUG - UAC - UAG
What is MET - ALA, VAL, TYR, STOP
Why do cells regulate which genes are turned on and which are turned off?
What is because they have different functions?