A type of matter formed by chemically joining two or more elements
Compound
Boiling point, solubility, color, taste and density are all examples of…
Physical properties
How do particles in a solid move?
They vibrate
In a solution, the substance that is being dissolved is the…
Solute
An object has a mass of 15 g and a volume of 4.5 cm3. Find its density.
3.33 g/cm3
Hydrogen, Gold, and Iron are all examples of…
Elements
A sheet of metal is 2 cm wide, 10 cm tall and 1.5 cm long. It has a mass of 42 grams. What is its density?
1.4 g/cm3
The most common state of matter in the universe is…
Plasma
Which of the following will speed up the dissolving of a solid solute in water?
A.Cooling the solution
B.Grinding up the solvent
C.Freezing the solute
D.Stirring the solution
D. Stirring the solution
*Bose-Einstein condensates are used to simulate conditions in…
Black holes
This is another name for a homogeneous mixture
Solution
Which property of matter measures a substance’s ability to dissolve?
Solubility
The amount of energy needed to change a material from the solid state to the liquid state is called…
Heat of fusion
What characteristic of water makes it an excellent solvent?
It is polar
*List two examples of where plasma can be found.
Stars and neon lights
Explain the difference between compounds and mixtures.
Compounds are chemically combined, mixtures are physically combined.
Aluminum has a density of 2.7 g/mL. When a piece of it is placed in a graduated cylinder with 11 mL of water, the water rises to 20 mL. Find the mass of the aluminum.
24.3 grams
Matter that has a fixed volume but no fixed shape is…
Liquid
Explain the difference between unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated solutions.
Unsaturated = can still add more solute
Saturated = holds the maximum amount of solute at a given temperature.
Supersaturated = more solute than can be held
Draw the flowchart used for classifying matter.
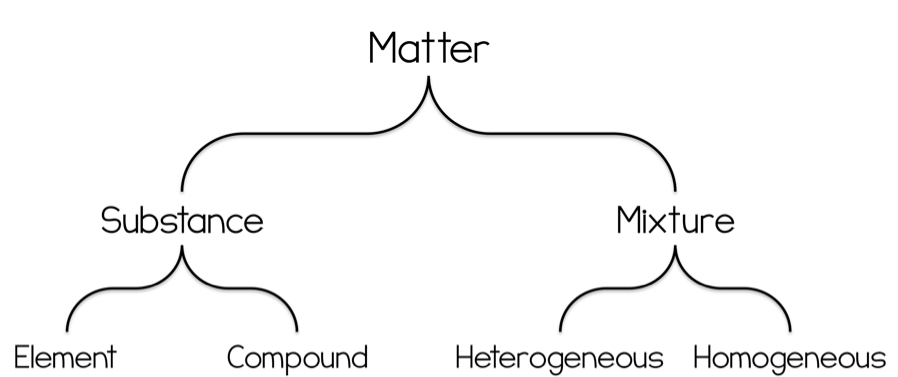
Determine if the following mixtures are homogeneous or heterogeneous:
1.Saltwater
2.Vegetable soup
3.Milk
1.Homogeneous
2.Heterogeneous
3.Heterogeneous
*Sketch a heating curve and label the parts.
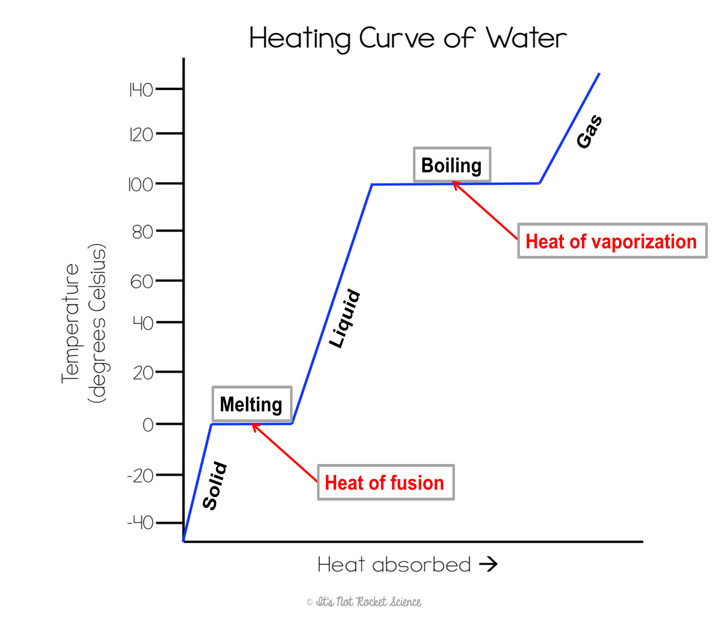
Think about the changing states of matter diagram. Write the names for the following transitions:
1.Gas -> Liquid
2.Liquid -> Solid
3.Gas -> Solid
1.Condensation
2.Freezing
3.Deposition
Explain the process of dissolving.
•Negative ends of water attract to positive ions in solute. Positive ends of water attract to negative ions in solute.
•Water pulls ions away from crystal and surrounds the ions
•Continues until all ions are surrounded by water
List 3 of the signs that a chemical reaction has occurred.
Release of light
Temperature change
Odor change
Sudden color change
Gas given off
Sudden appearance of a solid (called a precipitate)