This states that gravity is a universal, fundamental force.
What is Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation?
Kepler's 2nd Law states that this increases as the orbital radius decreases.
What is orbital velocity?
This is another form of the equation 1/f
What is period?
Spring periods depend on these two properties to oscillate.
What are spring stiffness and mass?
Simple pendulums' periods depend on these two properties
What are gravitational acceleration and length?
Newton's Universal Law of gravitation states that gravitational force depends on this.
What is the product of the masses divided by the radius squared?
This property defines the shape of an orbit.
What is eccentricity?
This is frequency multiplied by 2 pi
What is angular frequency?
This is the point where the spring force is minimized.
What is the equilibrium point?
This is the point where gravitational potential energy is maximized.
What is the max amplitude (or max height)?
This is the mass of a 1,000 km radius planet where the surface acceleration is measured at 20 m/s.
What is 3x1023 kg?
Kepler's 3rd Law states that this is proportional to the orbital radius cubed.
What is period squared?
This graph shows a particle with this period
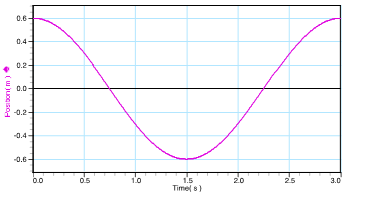
What is 3 seconds?
This is where a velocity vs time graph would be located when the mass is at xm.
What is a zero?
This is the period of a simple pendulum that takes 3 s to get from xm to -xm.
What is 2 seconds?
This is the radius of a planet who has an escape speed of 15 km/s and a mass of 5x1025 kg
What is 2x107 m or 2x104 km?
This equation combines Kepler's 3rd Law and Newton's Law of Gravitation
What is T2/R3 = 4pi2/GM
This is the particle's kinetic energy at equilibrium when it has a total mechanical energy of 17J.
What is 17 J?
This is the maximum acceleration of a particle with a displacement of 5 cm and a frequency of 0.5 Hz.
What is 0.5 m/s2?
This is the max speed of a 2 kg simple pendulum whose total energy is 16 J.
What is 4 m/s?
This orbital maneuver would cause the orbital energy of a spacecraft to double
What is double the orbital radius?
This is the ratio of orbital periods of a spacecraft that doubles its radius.
Tf = 8Ti
What is a larger amplitude and mirrored on the time axis?
This is the new period if I quadruple the stiffness of a spring oscillator.
What is Tf = 0.5Ti
This is the new period of a T = 1 s simple pendulum on a planet with a gravitational acceleration 1/8th of Earth's.
What is Tf = 2.8Ti?