What is the moving force behind continental drift
The force is Plate tectonics
What are the 3 main layers of the Earth
Crust, Mantle, Core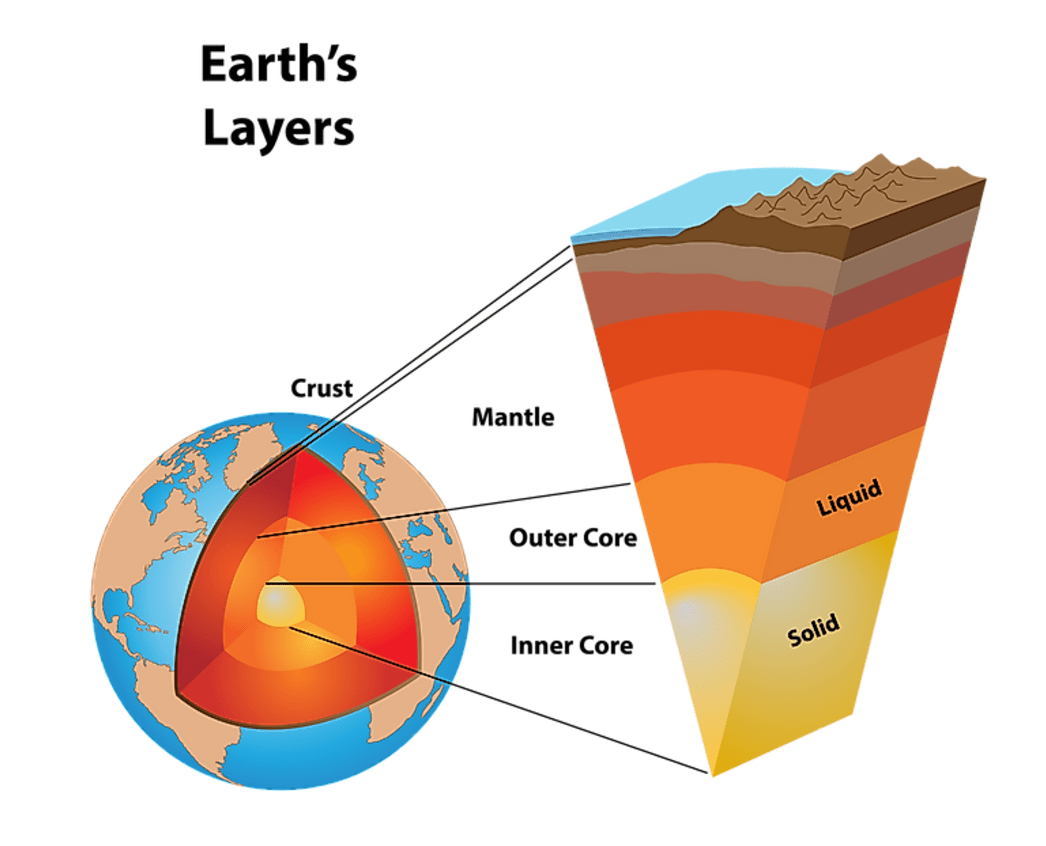
Draw the direction divergent plate boundaries move.
What happens here? What Forms at this boundary?
Divergent plate boundaries: the two plates move away from each other
Mostly underwater- forms mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys
Mountains can be formed through which three types of collisions?
Collision of Continental and Oceanic Crust
Collision of Oceanic vs Oceanic Crust
Collision between Continental Crusts
over 80% of earthquakes occur..
At the ring of fire
Activity that involves the movement of magma toward or onto the Earth’s surface
What is continental drift?
The theory that the continents moved away from what was once a supercontinent.
What are the differences between Oceanic and Continental Crust
Oceanic Crust: Denser, Younger, forms through seafloor spreading at mid ocean ridges, Mafic rocks
Continental Crust- Thicker, Older, composed of more felsic rocks
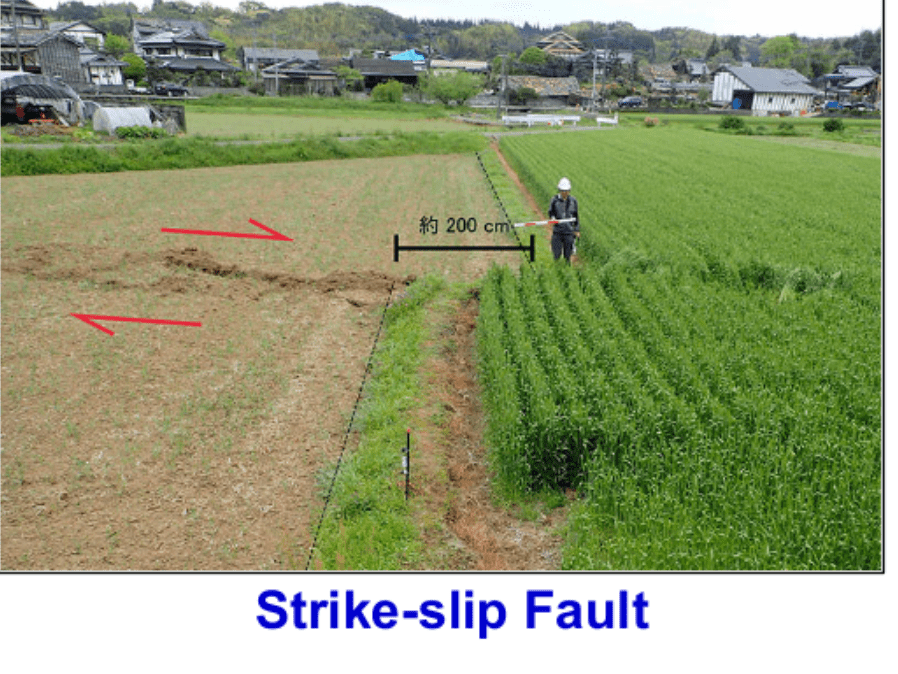
Draw the direction Transform plate boundaries move.
What happens here? What Forms at this boundary?
Two plates sliding past each other forms a transform plate boundary.
ex. San Andreas fault zone
Earthquakes and faults are caused here.
Natural or human-made structures that cross a transform boundary are offset — split into pieces and carried in opposite directions
Can form valleys
What Mountains
When molten rock erupts onto the Earth’s surface
Some are formed on the ocean floorover hot spots or pockets of magma that erupt onto the surface
Volcanic Mountains
The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the
focus
Epicenter
a) Dark colored lava rich in magnesium and iron with lower viscosity causing calmer and smoother flowing eruptions
b) Contains silica with lesser amounts of iron and magnesium with a much lighter color, higher viscosity causing more violent eruptions
a) Mafic lava
b) Felsic lava
What was the name of the supercontinent that existed 200-300 million years ago?
Pangea ("all Earth")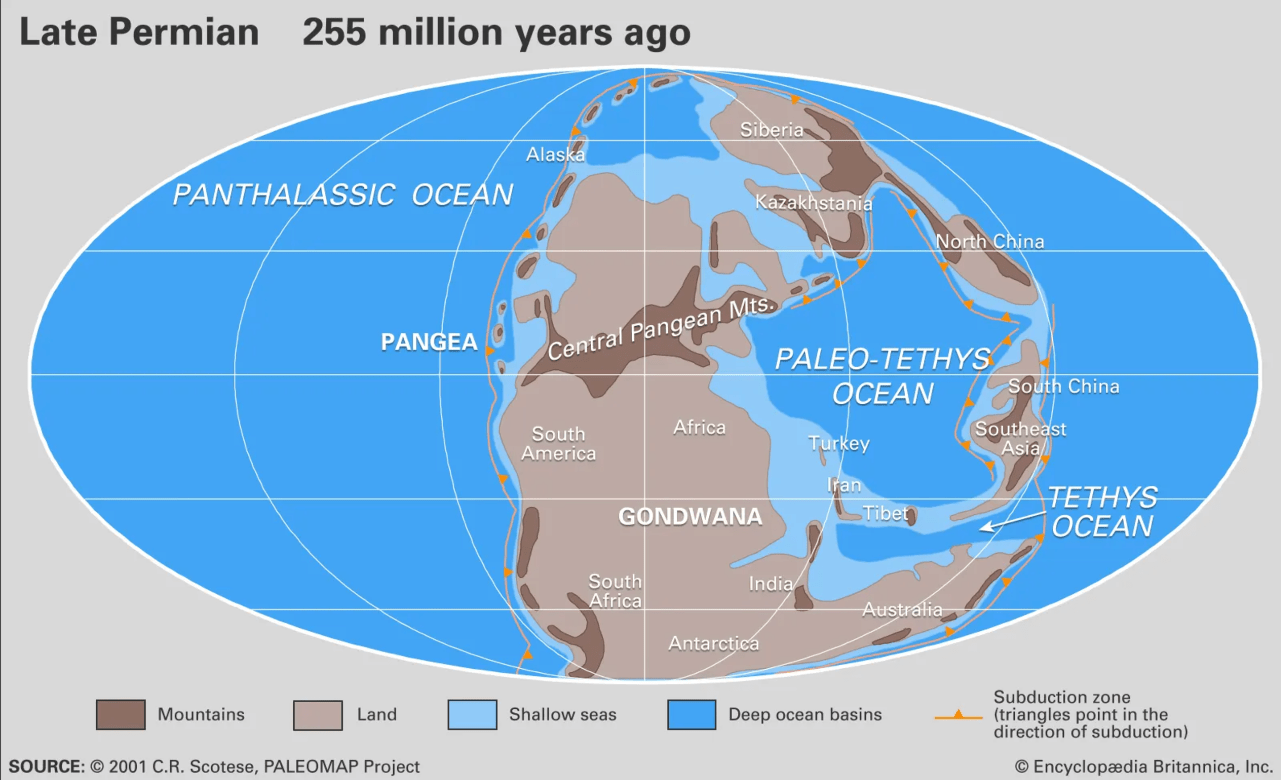
Draw the direction Convergent plate boundaries move.
What happens here? What Forms at this boundary?
When two plates come together, it is known as a convergent boundary
The impact of the colliding plates can cause the edges of one or both plates to form mountain ranges or one of the plates may subduct into a deep seafloor trench
Can form; Mountains, Earthquakes (80%), Volcanoes, and ocean trenches
What type of mountain
An unusual type of mountain is formed when molten rock rises through the crust and pushes the rock layers above it
The molten rock that pushed up the lock layers eventually cools and forms hardened rock
Dome Mountain
The area along the fault where first motion of an
earthquake occurs
Focus
Volcano type
a) gently sloping mountain. Forms when a volcano erupts quietly. Thin layers of lava build up slowly over a large area around the vent
b) steep, cone-shaped hill or small mountain. Forms when a volcano erupts explosively. Ashes, cinders, and bombs pile up around the vent
c) a tall, cone-shaped mountain. Forms when a volcano erupts quietly and then explosively, over and over again. Layers of lava are followed by layers of ash, cinders, and bombs
a) Shield Volcano
b) Cinder Cone Volcano
c) Composite (Stratovolcanoes)
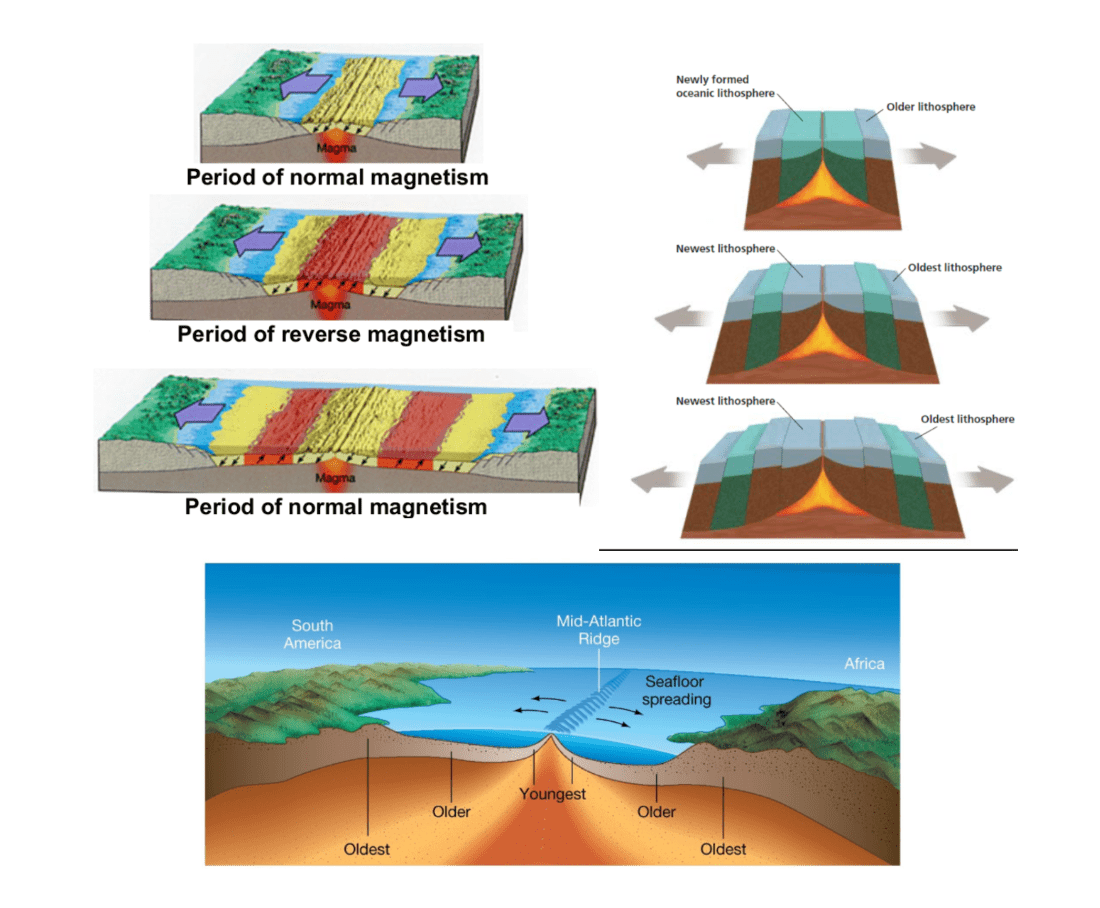
Describe Seafloor spreading. What is evidence of seafloor spreading?
Hypothesized by geologist and WWII navy veteran, Harry Hess in the late 1950's (he also worked with Robert Dietz)
The process by which new oceanic lithosphere (sea floor) forms as magma rises to the Earth’s surface and solidifies at the mid-ocean ridge
- Younger lithosphere is found in the center of mid-ocean ridges
-As magma solidifies to form rock, the magnetic fields of iron-rich materials align with the earth’s magnetic field. Scientists discovered alternating bands of magnetic fields within the ocean floor
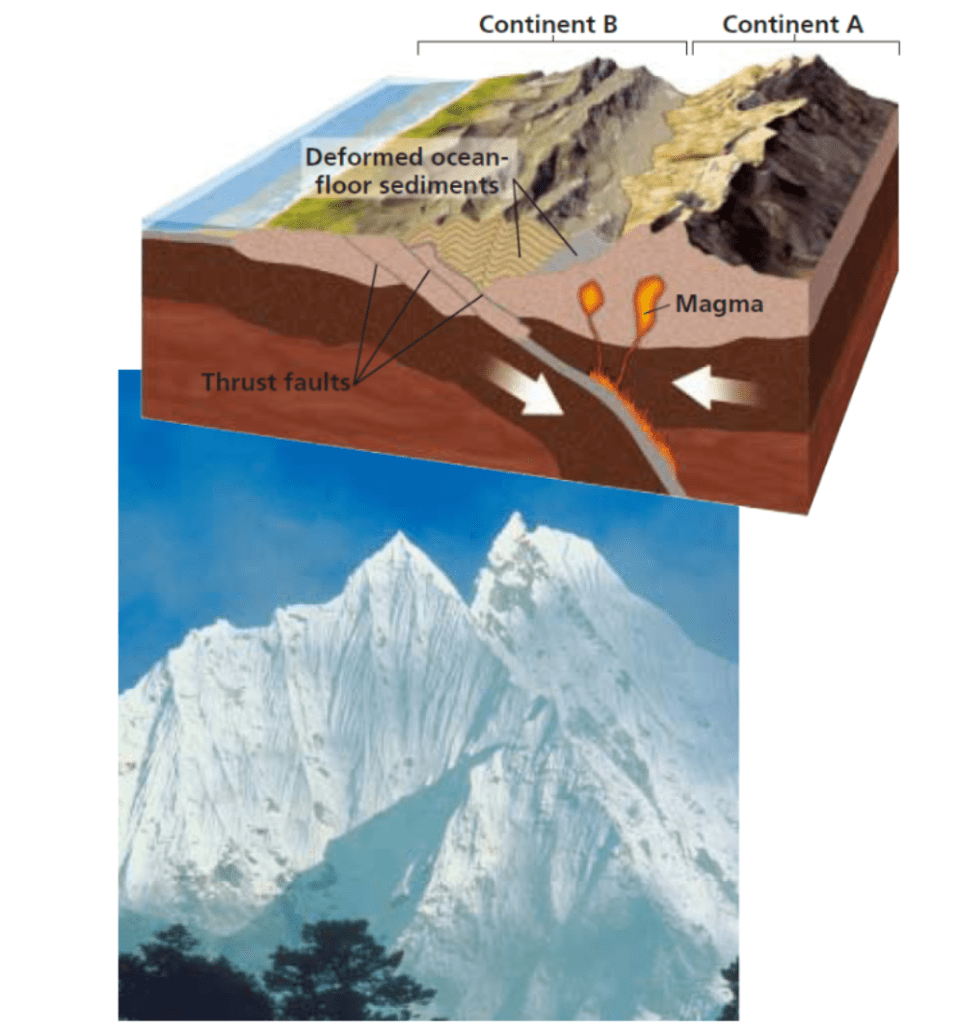
What type of collision is this?
 causes uplifted mountains
causes uplifted mountains
The collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates formed the Himalayas
The collision of two equally dense continental plates
What type of mountains...
are commonly found where continents collide
Tectonic movements have squeezed rock layers like an accordion
Forces may also uplift large areas of flat-topped rocks high above sea level
Folded Mountains and Plateaus
P and S waves are what type of waves?
Body Waves
A) Magma forms under what 3 conditions
What type of lava
b) Very hot magma produces lava called____ (“ropy” in Hawaiian) due to its low viscosity, it flows quickly and hardens into a rippled surface
c) Cooler magma produces lava called ____ with a high viscosity it flows slowly and hardens into rough chunks
Increased temperatures
Decreased pressures
Addition of fluids
b) pahoehoe
c) aa
In 1912, a German scientist named Alfred Wegener proposed a hypothesis that the continents we know today once formed a single landmass. Name and describe the four major pieces of evidence that supported his idea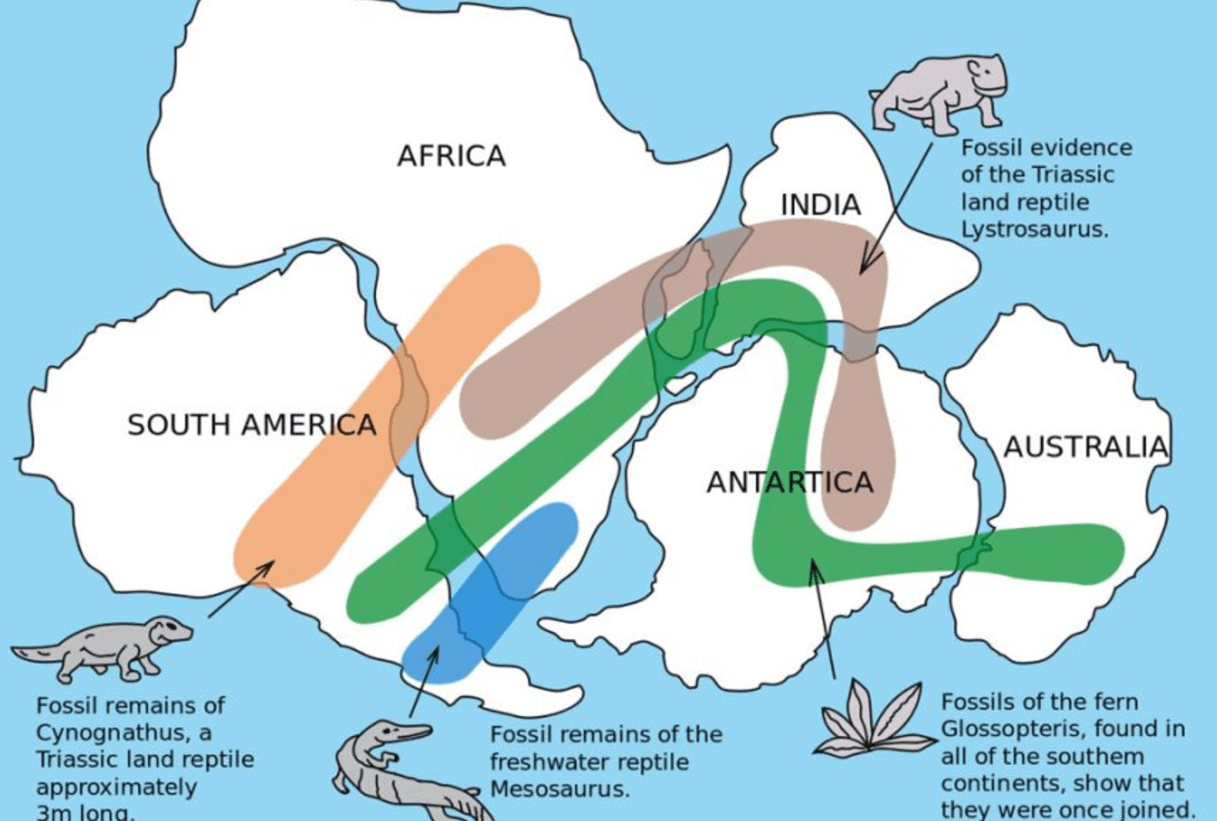
1. The apparent fit of the continents (fit together like a puzzle piece)
2. Fossil Correlation (fresh water and land animal fossils alive at the same time were found on continents separated by oceans)
3. Rock and Mountain Correlation (Identical rocks and mountain structures have been found on different continents)
4. Paleoclimate Data (coal from tropical plant remains found in COLD areas now, and Glacial striations found in WARM areas now- meaning continents moved.)
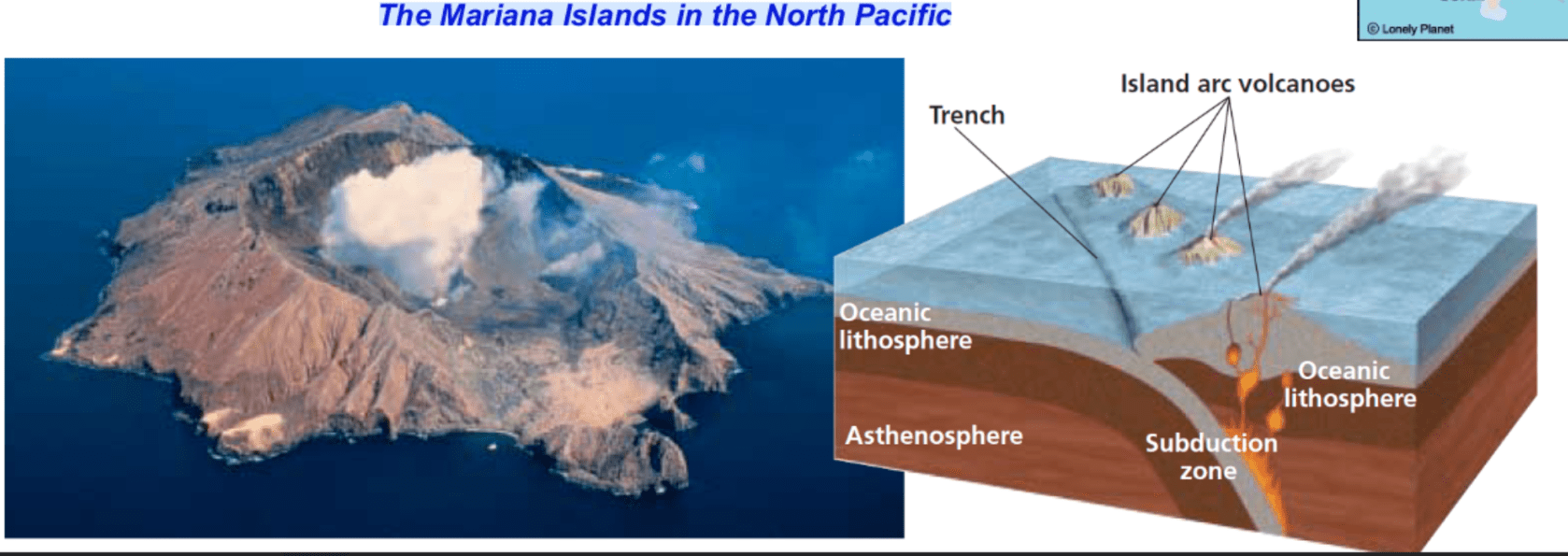
What type of collision is this?
The denser of the two plates subducts under the other plate causing a melting zone.
Rising magma forms an arc of volcanic mountains on the ocean floor
Ex. The Mariana Islands in the North Pacific
the convergent boundary of two oceanic plates
What mountain
Occurs when Earth’s crust is extended and broken into large blocks
Faulting tilts the blocks and causes some blocks to drop down relative to other blocks
Horsts: Uplifted blocks
Grabens: Long, narrow valleys
Fault-block mountains
What seismic waves
a) move the fastest and are compression waves, moving quickly through solids, liquids and gasses
b) can only travel through solid material and consist of shear waves causing rocks to move at right angles to the angle of travel
c)
are the slowest waves and travel slowly over the earth’s surface causing the greatest damage
a- p waves
b- s waves
c- surface waves (Rayleigh Waves and Love waves)
List 3 signs of a potential eruption
An increase in the frequency and intensity of earthquakes
Noticeable steaming or fumarolic activity and new or enlarged areas of hot ground
Subtle swelling of the ground surface
Small changes in heat flow
Changes in the composition or relative abundances of fumarolic gases
What is Plate Tectonics
The theory that Earth's Lithosphere contains "plates" that are slowly moving. This results in various geologic activities such as Mountain Building, Volcanoes, and Earthquakes
What type of collision is this?
Subduction of oceanic plates may uplift portions of the plate causing high mountains
Melting of the subducted oceanic plate may form volcanic mountains on the surface
Ex. The Andes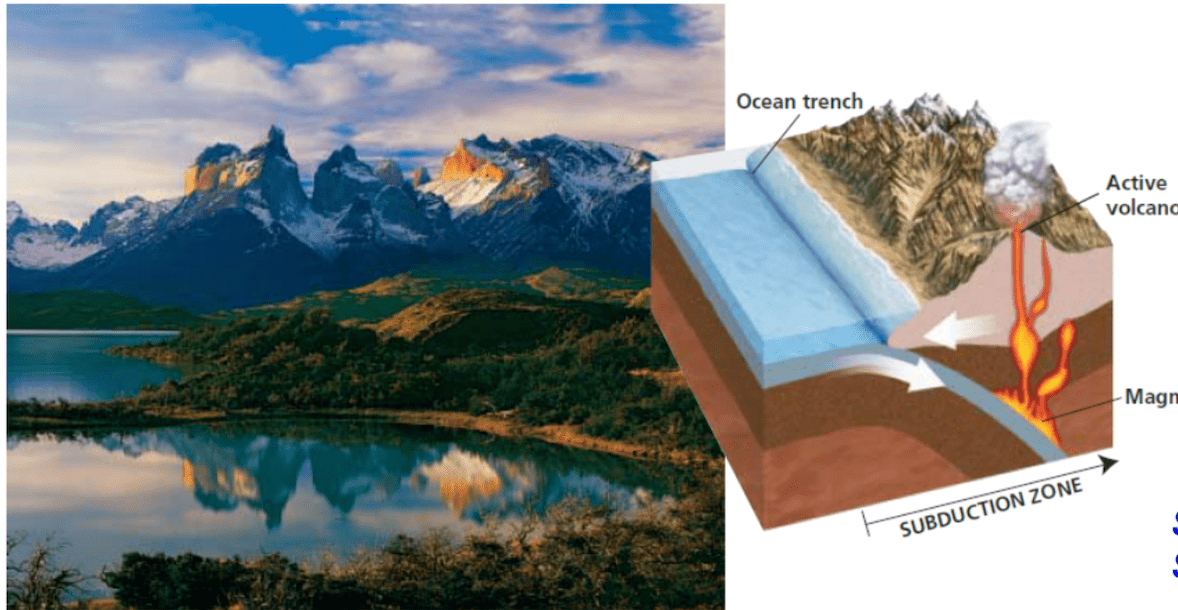
a convergent continental plate and oceanic plate collision
What are these steps part of?
Rocks on each side of a fault move slowly
unless the fault is locked
Stress on the rocks increases leading to deformation
Once stressed to a certain point, they
fracture and separate at the weakest point
The rocks then spring back to their original
shape, or rebound Original position
Elastic Rebound Theory
a) Instrument designed to detect and record
seismic waves
b) how do scientists measure earthquakes (what scale)
a) Seismograph
b) Moment Magnitude Scale
is formed when a magma chamber empties and collapses. This leaves a huge hole. May fill with water to form a crater lake
Caldera