Structural unit of skeletal muscle
Sarcromere
area of thick filaments
H band
(H is thicker letter than I)
Role of ATP in muscle contractions
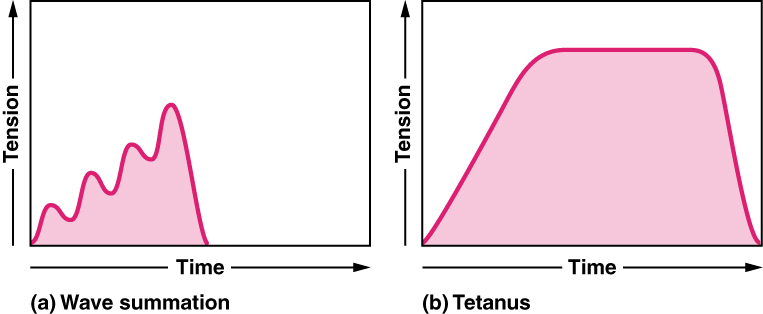 Which graph represents fused tetanic contraction
Which graph represents fused tetanic contraction

The quadricepts provide force for us to move, this is an example of:
Prime mover
Skeletal muscle cell
myofiber
area of thin filaments
I band
Hydrolyze means
to break down
 Which graph represents wave summation?
Which graph represents wave summation?
Graph A
.png) Name this muscle
Name this muscle
Deltoid
bundle of muscles
fascicle
Layers of connective tissue from superficial to deep
epimysium- perimysium- endomysium
what does Calcium bind to after it is released in skeletal muscle?
Troponin
Mr. Goff's noninvasive therapy choice for lower back pain:
TENS unit (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Simulation)
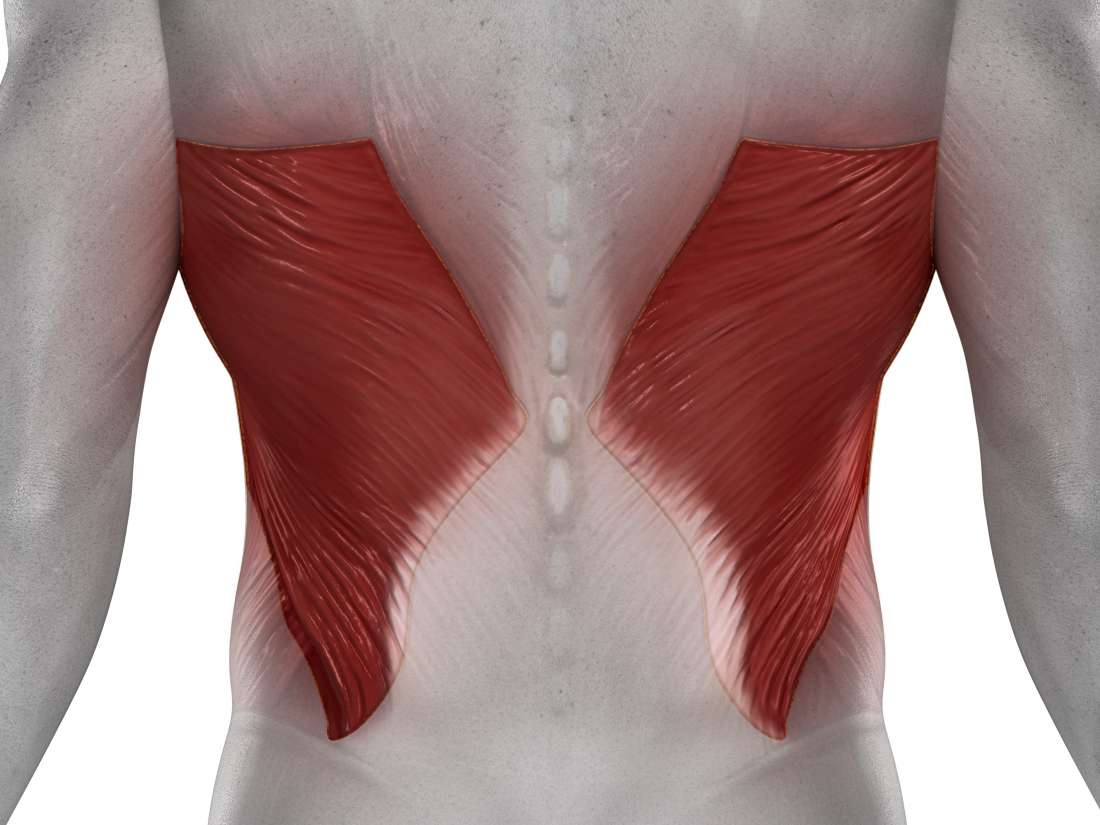 Name this muscle:
Name this muscle:
Latissimus Dorsi
least moveable attachment point of muscle
origin
protein that converts ATP for muscle movement
myosin
mysosin is attached to this (also knows as the thin protein responsible for contraction)
actin
What is the point of using electrical muscle stimulation:
Used to strengthen weak muscles
 In this picture, the which one is an example of the muscle that assists (synergist)
In this picture, the which one is an example of the muscle that assists (synergist)
Brachioradialis
each muscle fiber has this: where synapse attach to muscle to transmit
motor end plate
Area composed of thick myosin (located in the A band)
H Zone
mysoin bridges this gap to cause muscle contraction
cross-bridge
This type of therapy is used to increase muscle contraction by sending electrical impulses to weak muscles
FES (Functional electrical stimulation)
This is responsible for stabilizing joints during muscle movement
Fixator