The purpose of using enzymes is to
lower the activation energy
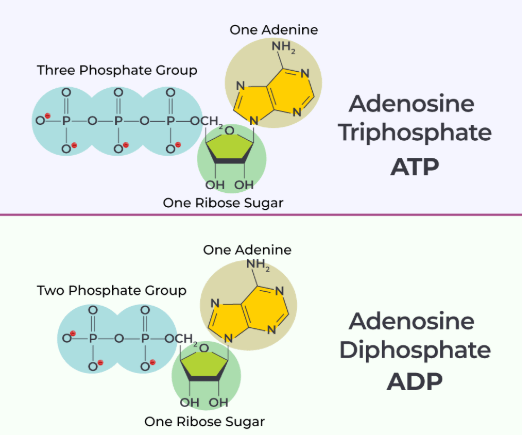
What is the difference between ADP and ATP?
ADP has 2 phosphates
ATP has 3 phosphates
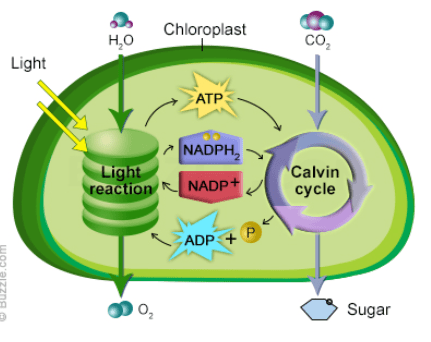
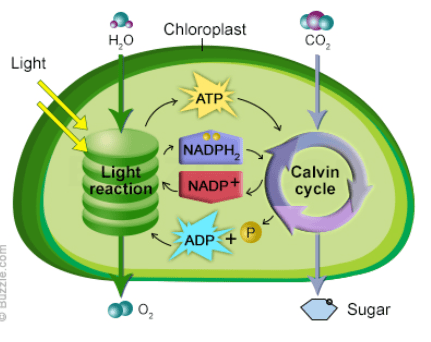
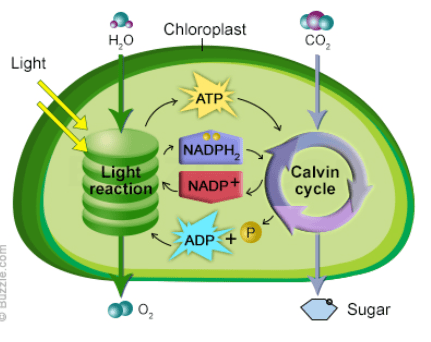
The organelle responsible for photosynthesis.
chloroplast
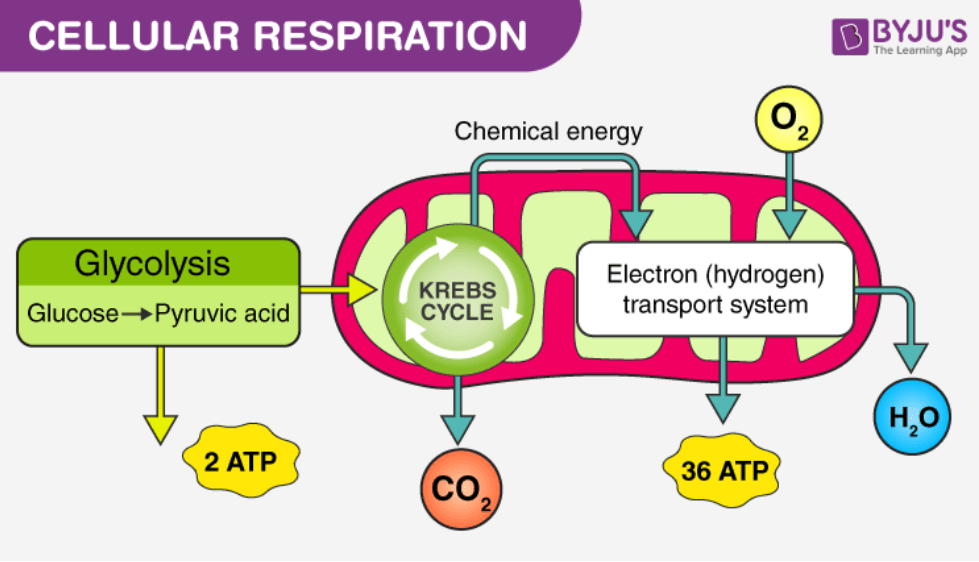
The name of the process that uses oxygen to make ATP
cellular respiration
Where fermentation occurs
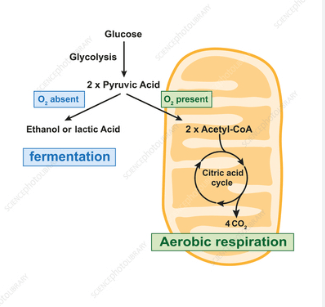 cytoplasm
cytoplasm
What happens to enzymes after they are used
they are recycled and used again
Where is the energy located in ATP?
The chemical bond between the 2nd and 3rd (last) phosphate.
The process that produces NADPH and ATP
Light dependent reaction
The first process of anerobic respiration
glycolysis
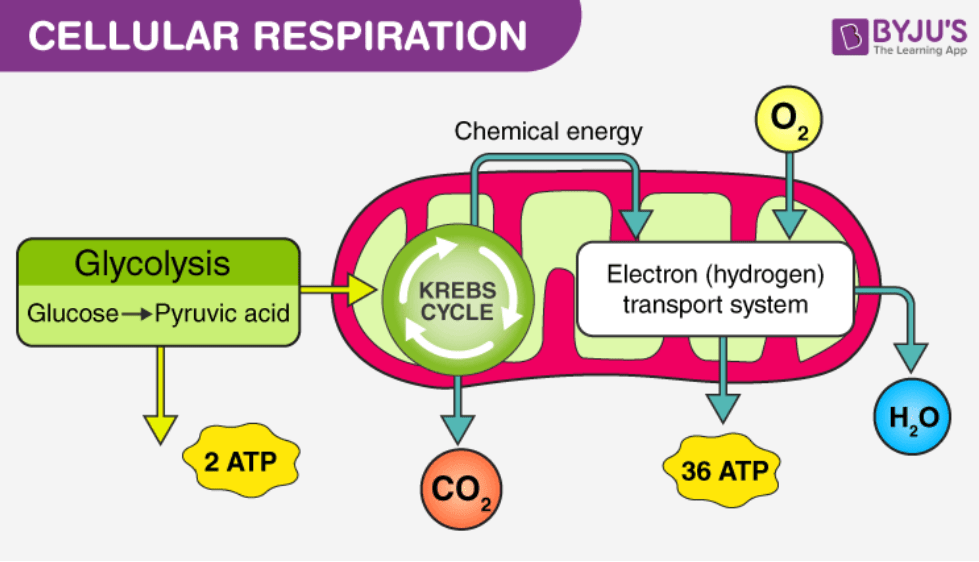
Why fermentation occurs
Lack of oxygen
What happens to enzymes if the temperature is too high or too low?
low - it has low energy and doesn't work well
high it denatures (changes shape) and stops working
What organisms need ATP?
All living organism - plants, animals, fungi, protists, prokaryotes (bacteria/archea)
The location of the process that uses the Electron Transport Chain
Thylakoid Membrane
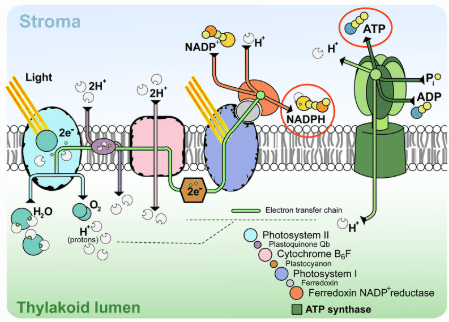
The location of the Kreb's Cycle
The mitochondrial matrix
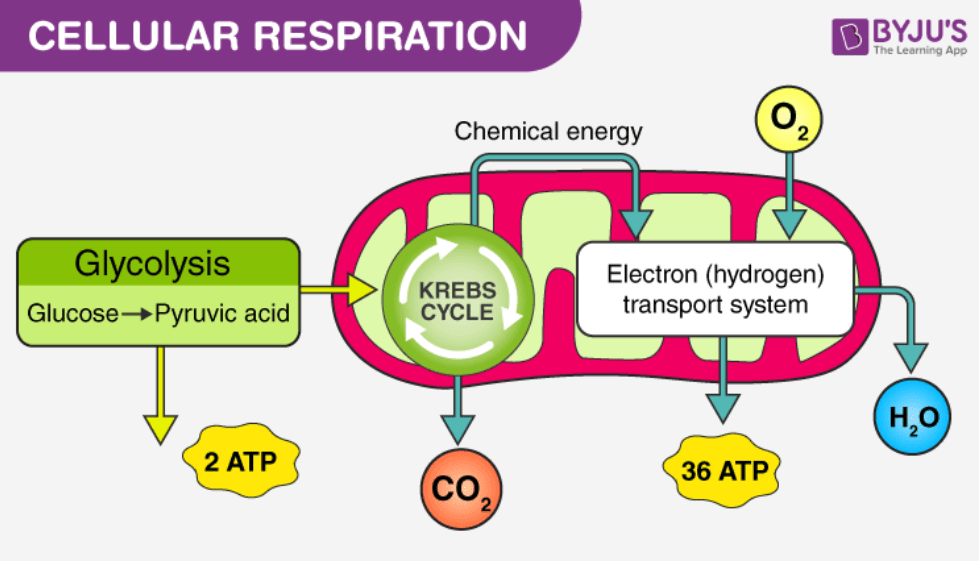
The process that begins fermentation
glycolysis
Molecules that stop a chemical reaction from occurring
Inhibitors
Identify the three parts of ATP.
LABEL them A>B>C
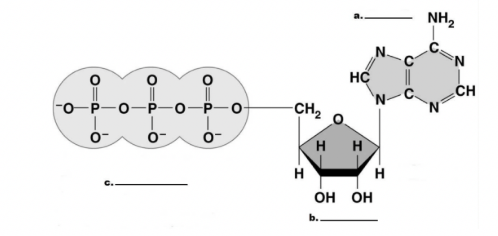
A - Adenine
B - Ribose
C - 3 Phosphates
Where the light independent reaction takes place
stroma
The location of the electron transport chain
Mitochondrial Membrane
The organisms and products of alcohol fermentation
yeast produce ethanol, 2 ATP, CO2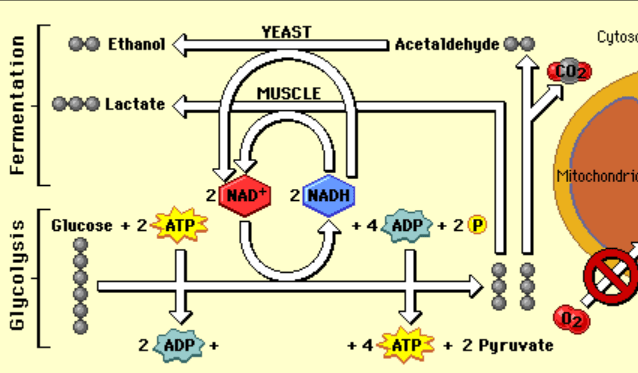
What the part of an enzyme where the substrate attaches
active site
How is ATP made?
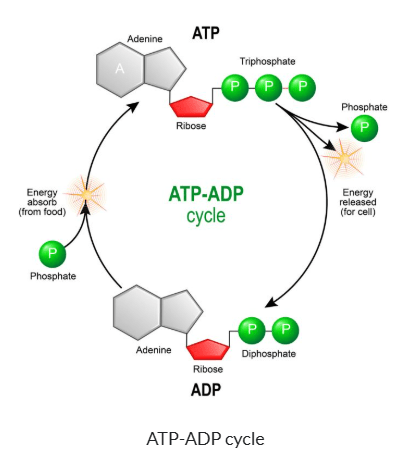 must have: A phosphate is added to ADP
must have: A phosphate is added to ADP
(using ATP synthase)
The main product of the Calvin Cycle
Glucose - C6H12O6

The final main products of the entire process of cellular respiration
32-36 ATP; Carbon dioxide; water
The organisms and products of lactic fermentation
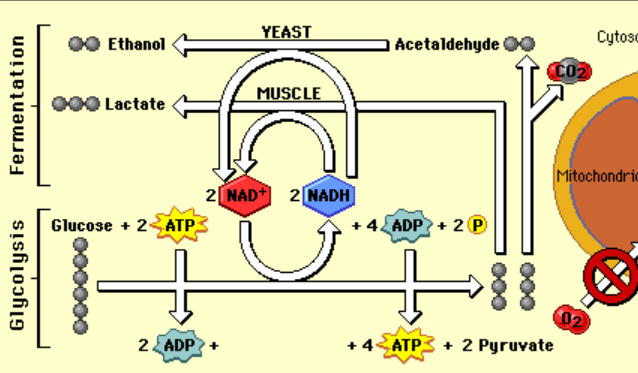 muscles and bacteria
muscles and bacteria
lactic acid and 2 ATP