Name 2 organisms that compete in this food web.
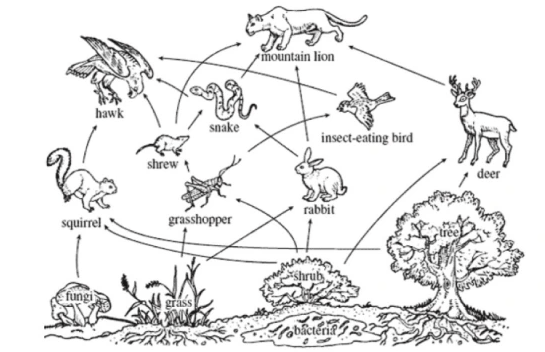
Possible answer- rabbit and deer
Head lice living on a human scalp.
Organism 1: helped harmed not harmed/not helped
Organism 2: helped harmed not harmed/not helped
Symbiotic Relationship: _________________
Lice: helped
Human: harmed
Parasitism
The availability of food, water, shelter and space as well as competition for resources, predation and disease are all examples of
Limiting factors
Identify one way humans are negatively impacting the environment and explain why it has a negative effect.
Answers will vary
Describe what a dependent variable is.
Outcome variable; variable that is measured; depends on the independent variable
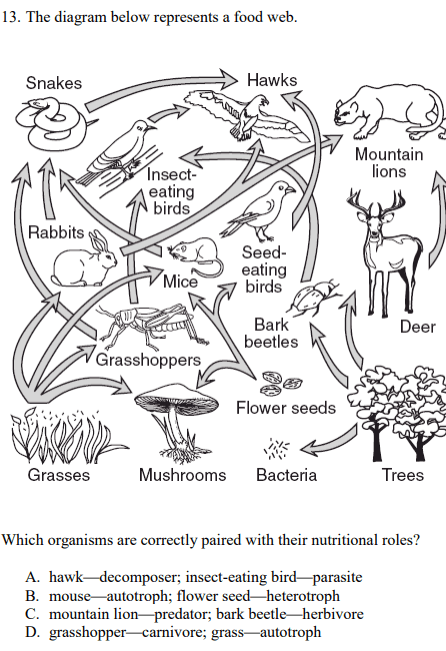
C. mountain lion-predator; bark beetle- herbivore
Bacteria live in the colon of humans and are able to feed off the indigestible food that the human body cannot break down (cellulose of plants). In the process of breaking down the food, the bacteria also make much-needed vitamins that the human body in turn can use to keep healthy.
Organism 1: helped harmed not harmed/not helped
Organism 2: helped harmed not harmed/not helped
Symbiotic Relationship: _________________
Bacteria: helped
Human: helped OR not affected
Mutualism OR commensalism
What is the difference between abiotic and biotic limiting factors?
Abiotic = nonliving
Biotic = living
In a pond, the primary producer is a green alga, Spirogyra; the primary consumer is the crustacean, Daphnia; the secondary consumer is a small fish, the bluegill; and the tertiary consumer is a larger fish, the smallmouth bass. What changes can be expected in the pond if the Daphnia are killed with pesticides? Explain your choice with 1 sentence.
A. The Spirogyra population will probably die
B. The bluegill population will probably increase
C. The Daphnia population will eat something else
D. The smallmouth bass population will die
D. The smallmouth bass population will die
They will not have any food.
Describe what an independent variable is.
Test variable; changes the dependent variable
Which population of consumers in this food web would mot likely be negatively affected by an increase in the mouse population?
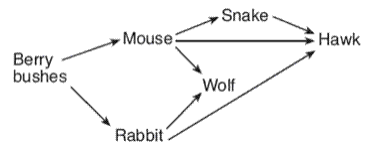
Rabbit- mice would eat more berry bushes, leaving less food for rabbit.
Describe the 3 types of symbiosis using both words and symbols.
Mutualism is when both species benefit (+/+)
Commensalism is when one species benefits and the other is not affected (+/0)
Parasitism is when one species benefits and the other is harmed (+/-)
What can happen to a population if it becomes too large?
They found run out of resources (food, water, shelter) and many can die, leading to a decrease in their population.
Cogongrass, an invasive species introduced by humans, grows in many areas in Florida. Its roots can spread quickly underground. Cogongrass thrives where fires allow it to spread. What is a negative effect that Cogongrass could have on native organisms in its habitat?
It can replace native plants that animals dependent on for food and shelter
Your science class decides to conduct an experiment to learn more about ice. You set one ice cube on the counter at room temperature, and another, same-sized ice cube in the class refrigerator. You predict that since it is warmer on the counter at room temperature, the ice cube on the counter will melt faster. What result would confirm this prediction?
A. When the counter ice cube is melted, the refrigerator ice cube is also finished melting.
B. When the counter ice cube is not quite melted, the refrigerator ice cube is not finished melting.
C. When the counter ice cube is melted, the refrigerator ice cube is not finished melting.
D. When the counter ice cube is not quite melted, the refrigerator ice cube is finished melting.
C. When the counter ice cube is melted, the refrigerator ice cube is not finished melting.
Explain why decomposers are important to a food web.
They decompose/break down dead organisms into nutrients that can be used by plants
Describe a relationship similar to the following:
The bison stirs up insects in the grass, which the cowbird eats.
Any example of commensalism, describing one species benefiting and the other not affected
List 3 biotic and 3 abiotic limiting factors in an ecosystem. Be sure to identify which are biotic and abiotic!
Biotic: food, hunter, predators, disease, shelter
Abiotic: water, shelter, natural disasters, sunlight
Describe the negative effects of deforestation.
Loss of habitat, increased soil erosion
Joshua investigates the effect of varying amounts of sunlight on the rate of plant growth. He experiments by exposing seedlings to different amounts of sunlight each day. He stops the experiment when each seedling reaches 20 cm in height. What is the independent (testing) variable in Joshua's experiment?
A. rate of plant growth
B. time needed to reach a height of 20 cm
C. amount of sunlight per plant per day
D. amount of water per plant per day
C. amount of sunlight per plant per day
1. Identify which population would be the largest in this food web and explain why.
2. Identify what the arrows represent in this food web.
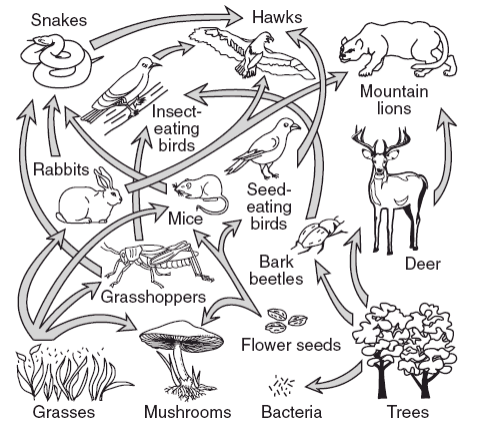
1. Grasses or trees- producers have the most every available to them (sun) so their populations are the largest.
**amount of energy available decreases as you move up the food web**
2. energy flow
Jane went for a walk on the farm. First, she saw a mosquito land on her arm and bite her. Second, she saw a hawk capture a mouse. Last, she noticed a bird riding on the back of a cow and eating the bugs off it. What is the order of the relationships Jane saw at the farm?
parasitism, predation, mutualism
What is the term for the maximum number of individuals of a species an environment can sustain?
Carrying capacity
Describe how humans are increasing air pollution and how that is causing global climate change.
Humans are adding more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which is trapping more heat, causing the temperature to increase and the climate to change.
In Dr. Jeff's climate change video, he conducted an experiment where he set up 2 identical tanks and put normal air in one and added carbon dioxide to the other. He monitored the temperature over time.
List the independent variable, dependent variable, control group, and 3 constants in this experiment.
Independent variable: amount of carbon dioxide
Dependent variable: temperature
Control group: tank with normal air
Constants: heat source, tank size, soil, thermometers, umbrellas, location of thermometer