What unit does q (charge) have in Coulomb's law?
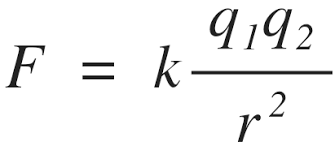
Coulomb (C)
How do objects become negatively charged?
They gain electrons from another object.
What two factors affect Coulomb's Law?
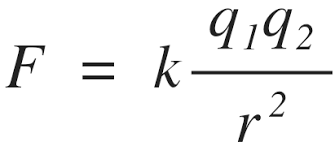
1. magnitude of the charges (q1 and q2)
2. distance between the two charges (r)
What do electric field lines represent?
The force felt by a positive point charge.
What is the difference between an insulator and a conductor? Give an example of each one.
Insulators hold onto their electrons tightly. Ex: plastic
Conductors allow their electrons to flow freely throughout Ex: copper
What unit is Fe measured in?
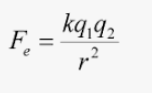
Newtons (N)
How do objects become positively charged?
They lose electrons.
What are the relationships between the following variables in Coulomb's law?
a. magnitude of the charges (q1 & q2) and Fe
b. distance between the two charges (r) and Fe
a. magnitude of the charges (q1 & q2) and Fe = directly proportional
b. distance between the two charges (r) and Fe = inverse squared
Based on the electric field line, determine the charge on each object A-D.
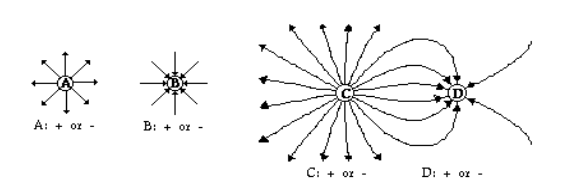
A = +
B = -
C = +
D = -
Explain how to ground objects and what grounding does to the object.
You ground objects by connecting them to a large source of electrons via a conducting path.
Grounding will remove excess electrons or add electrons to charged objects thereby removing their charge and rendering them neutral.
What is the value and units for Coulomb's constant, k?
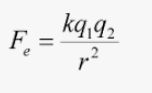
Describe a way to make the electroscope pictured.
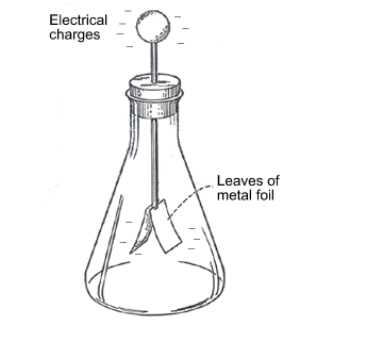
Touch a negatively charged object to it (conduction) OR bring a positively charged rod next to it, then ground it (induction)
You half the distance between two charges and double the magnitude of one charge. By what factor does the electric force change?
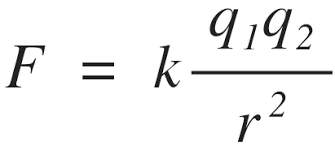
8x Fe
Give an appropriate charge for QA and QB.
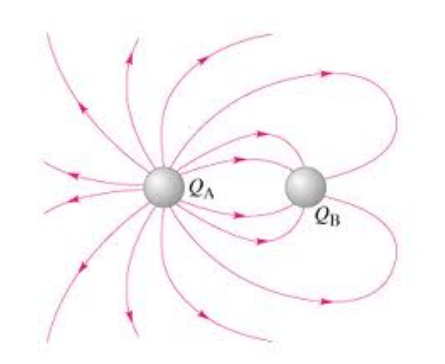
QA =+2
QB = -1
Explain why neutral objects are attracted to any charged object.
Neutral objects will become polarized when near a charged object. This will create a positive side and negative side to the object giving the appearance of a net charge and making it attract the charged object.
What units are the following variables measured in:
a. acceleration
b. energy
c. speed
a. acceleration = m/s2
b. energy = J
c. speed = m/s
A positively charged rod is brought near a neutral electroscope, which of the following electroscopes will it look like?
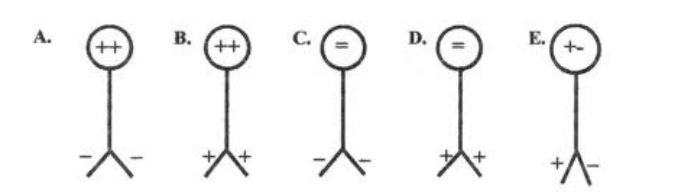
D
The force between two objects is 100 N. What will the new force be if you triple the magnitude of each charge and double the distance between the two charges?
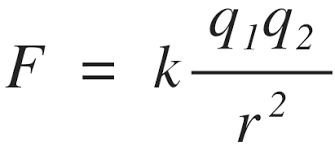
9/4(100) = 225 N
Rank the two sets of charges in order of increasing strength.
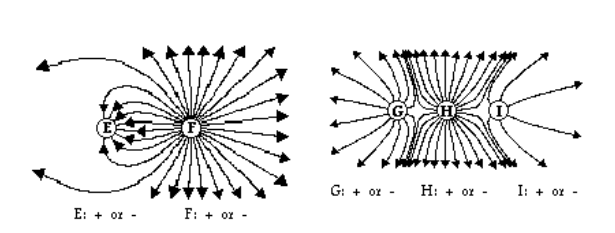
E < F
I < G < H
Explain what the triboelectric series is.
The triboelectric series is a list of materials in order of their affinity for electrons. Materials near the top will lose electrons to materials near the bottom when charging by friction.

What units are the following variables measured in:
a. momentum
b. impulse
c. spring constant (k)
a. momentum = kg*m/s
b. impulse = N*s
c. spring constant (k) = N/m
Describe how to make 3 of the electroscopes pictured have the charge distributions shown.
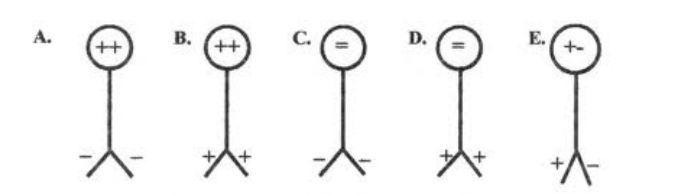
A. Bring a negatively charged rod near the top (polarization)
b. Touch it with a positively charged object (conduction)
c. Touch it with a negatively charged object (conduction)
d. Bring a positively charged rod near the top (polarization)
e. Ground a charged electroscope
The force between two objects is 50 N. What will the new force be if you 1/2 the magnitude of each charge and triple the distance between the two charges?
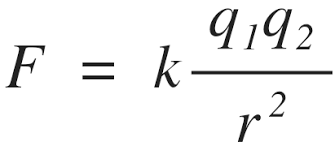
1/36(50) = 1.39 N
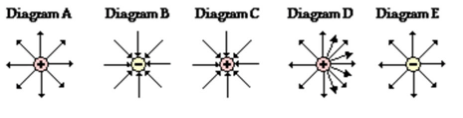
Which of the following electric field line drawings are incorrect? Explain what is wrong with them.

Name three people that Physic's units have been named after. First and last names needed.
Isaac Newton = Unit for force (N)
Charles Augustin de Coulomb = Unit of charge (C)
James Prescott Joule = Unit of energy (J)
James Watt = Unit of power (W)