How do you define a species?
A group of individual organisms that can produce viable offspring.
_______________ are the preserved remains, or traces of remains, of ancient organisms.
Fossils
Humans regulate their internal body temperature within a very narrow range. This is an example of ____________________.
Homeostasis
Name two types of bacteria.
Examples - E. Coli, Strep, Staph, TB (tuberculosis), botulism, tetanus, cholera, salmonella, pertussis (whooping cough).
Name three types of viruses.
Examples - HIV, ebola, COVID, influenza, rabies, HPV, varicella, herpes simplex, etc.
How do you define an adaptation?
Any type of variation that helps an organism survive in its environment.
What can be determined from looking at the embryos of different organisms?
It indicates that the organisms share a recent common ancestor.
Darwin described his theory of natural selection as __________________.
Decent with modification.
How do vaccines work?
They stimulate an immune response against future infections.
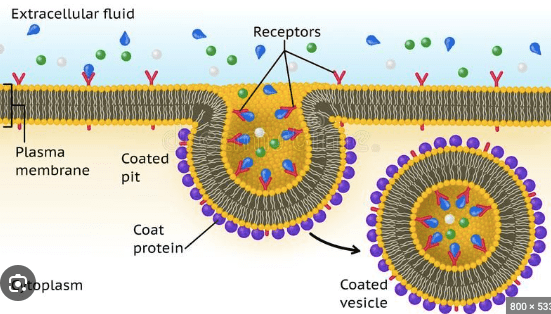
How do retroviruses (like HIV) enter a host cell?
Endocytosis (they bind to receptors on the surface of cell membranes).
What is the definition of fitness?
The ability of an organism to contribute its genes to future generations.
What are homologous structures?
Anatomical structures with shared evolutionary origin that have the same function.
How do humans produce specific breeds of dogs?
Through artificial selection.
How do bacteria reproduce?
Asexually, they duplicate themselves (binary fission).
How do viruses replicate?
They need to enter a host cell and "hijack" their organelles so they can insert their genetic material and replicate.
How do mutations change populations over time?
Mutations generally have no effect on a population since they are simple changes in DNA.
Define and give an example of a vestigial structure
A structure that no longer serves a purpose in an organism. Examples in humans - wisdom teeth, appendix, coccyx (tailbone).
Explain how antibiotic resistance developed as a result of widespread use of penicillin. How is this an example of natural selection?
When Penicillin was first developed, it was considered a "miracle drug" because it extended the lifespan of humans. Over time, it was over prescribed and given to many people that didn't have bacterial infections. This caused some strains of bacteria to become resistant to penicillin.
This is an example of natural selection because the bacteria that can successfully adapt to the environment will survive and reproduce, creating a new strain of resistant bacteria.
MRSA is a strain of bacteria that is resistant to which antibiotic?
Methicillin
Which of the following best explains why new types of influenza viruses can develop?
Rapid reproduction allows mutations to be introduced into viral populations.
Define speciation and give an example.
When a smaller group of the main population is geographically isolated and forms a new species.
Ex) a population of birds from the mainland won't mate with the birds on isolated islands.
The structures of the front flipper of a whale and the forearm of a wolf have similar bone structure and derive from a common ancestor. This is an example of __________.
Homologous Structures
Charles Darwin proposed that evolution by natural selection was the basis for the differences that he saw in similar organisms as he traveled and collected specimens in South America and on the Galapagos Islands. Explain the theory of evolution by natural selection as presented by Darwin.
Darwin theorized that a species of finch from the mainland made its way over to the Galapagos islands. Over time, the finches that best adapted to the different environmental conditions were able to survive and reproduce.
The finches wouldn't mate with each other if they were visibly different, so they diverged into completely different species of finches.
A scientist places an antibiotic drug in a petri dish containing a strain of E. coli bacteria. How is this likely to affect the bacterial population?
Those with strong resistance to the antibiotic will survive and multiply, and eventually the resulting population will become resistant.
A biologist conducts an experiment to determine whether a fish is infected with a virus or a bacterium. The biologist takes a sample of cells from the fish and isolates the infectious agent. Next, the biologist sets up two test tubes. Test tube X contains nutrients and fish cells. Test tube Y contains nutrients but no fish cells. The infectious agent is then placed in the two test tubes. The biologist determines that the infectious agent reproduced in one of the test tubes.
Which of the following will allow the biologist to determine whether the infectious agent is bacterial or viral?
Viruses can only reproduce in test tube X.