What is the purpose of meiosis? Where in the body does meiosis occur?

The purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes (sperm and egg); Germ cells (Ovaries and Testes).
What are the three ways in meiosis that encourage genetic variation?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chromosomes-567300453df78ccc15fd3c19.jpg)
Crossing Over, Independent Assortment, and Fertilization.
What is the idea of “blending inheritance?” Why is this model incorrect?
![]()
Blending inheritance is the idea that traits from each parent blend together in offspring. This is incorrect as Mendel describes the particulate nature of genes as seen by heterozygotes displaying the dominant allele’s phenotype.
What is the difference between phenotype and genotype?
A genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism whereas a phenotype is the observable traits produced from an organism’s genotype.
List all of the phases of meiosis (including those of interphase) in order.

G1 Phase, S Phase, G2 Phase, Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I/Cytokinesis, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II/Cytokinesis, Gametes
When does crossing over and independent assortment occur in meiosis?

Crossing over occurs during Prophase I and independent assortment occurs during Metaphase I.
Assume that in humans, curly hair (W) is dominant over straight hair (w). Could a baby that is homozygous for straight hair have a father that is homozygous for curly hair and a mother that is heterozygous for curly hair? Why?
No because a cross between WW and Ww would produce genotypes of WW and Ww (both encoding for curly hair).
Identify the following as homozygous or heterozygous. If homozygous, distinguish if it is recessive or dominant. (a) Gg, (b) dd, (c) MM
(a) Heterozygous; (b) Homozygous Recessive; (c) Homozygous Dominant.
What is the major difference between metaphase I and metaphase II in the process of meiosis?

In metaphase I, homologous chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate. In metaphase II, sister chromatids line up on the metaphase plate.
Describe how fertilization results in greater genetic variation? How many chromosomes from each parent are inherited by the embryo?

During fertilization, one gamete (with unique genetic makeup) from each parent combined to form a zygote. This allows for a combination of traits derived from the genetically unique gamete provided by each parent. Each parent contributes 23 chromosomes to the zygote.
A round seeded plant (R) is dominant to a wrinkled seeded plant (r). What parental genotypes will produce offspring that are 50% heterozygous and 50% homozygous recessive?
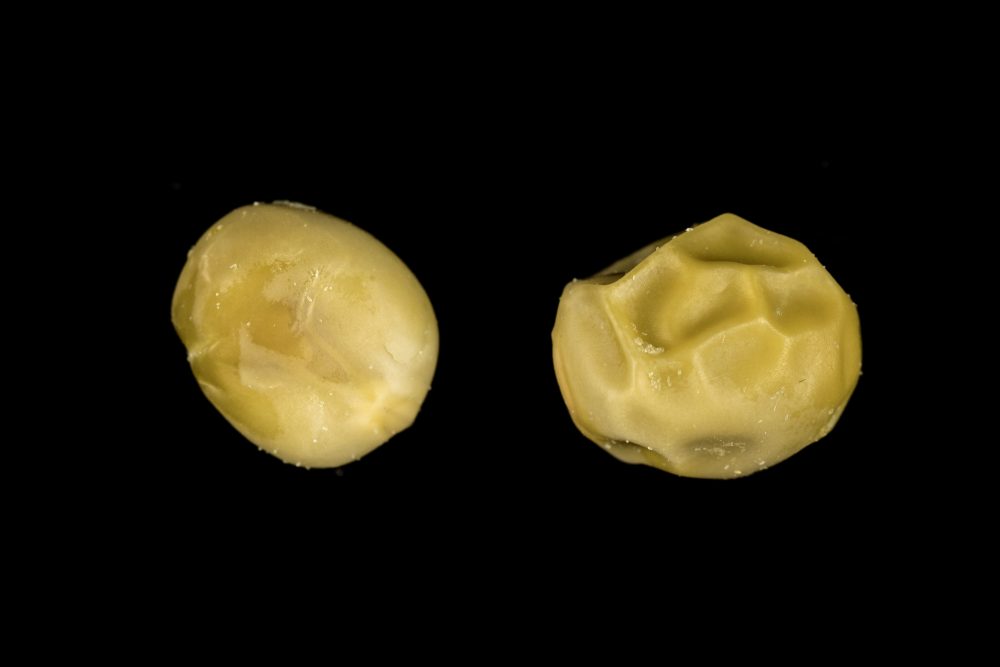
Rr and rr.
What is the difference (or relation) between a gene and an allele?

A gene encodes for a specific trait. An allele is the various versions of that trait (or gene).
Describe the parent and daughter cells of meiosis. Include number of cells, haploid or diploid, and number of chromosomes. Are the daughter cells identical or unique to the parent cell?
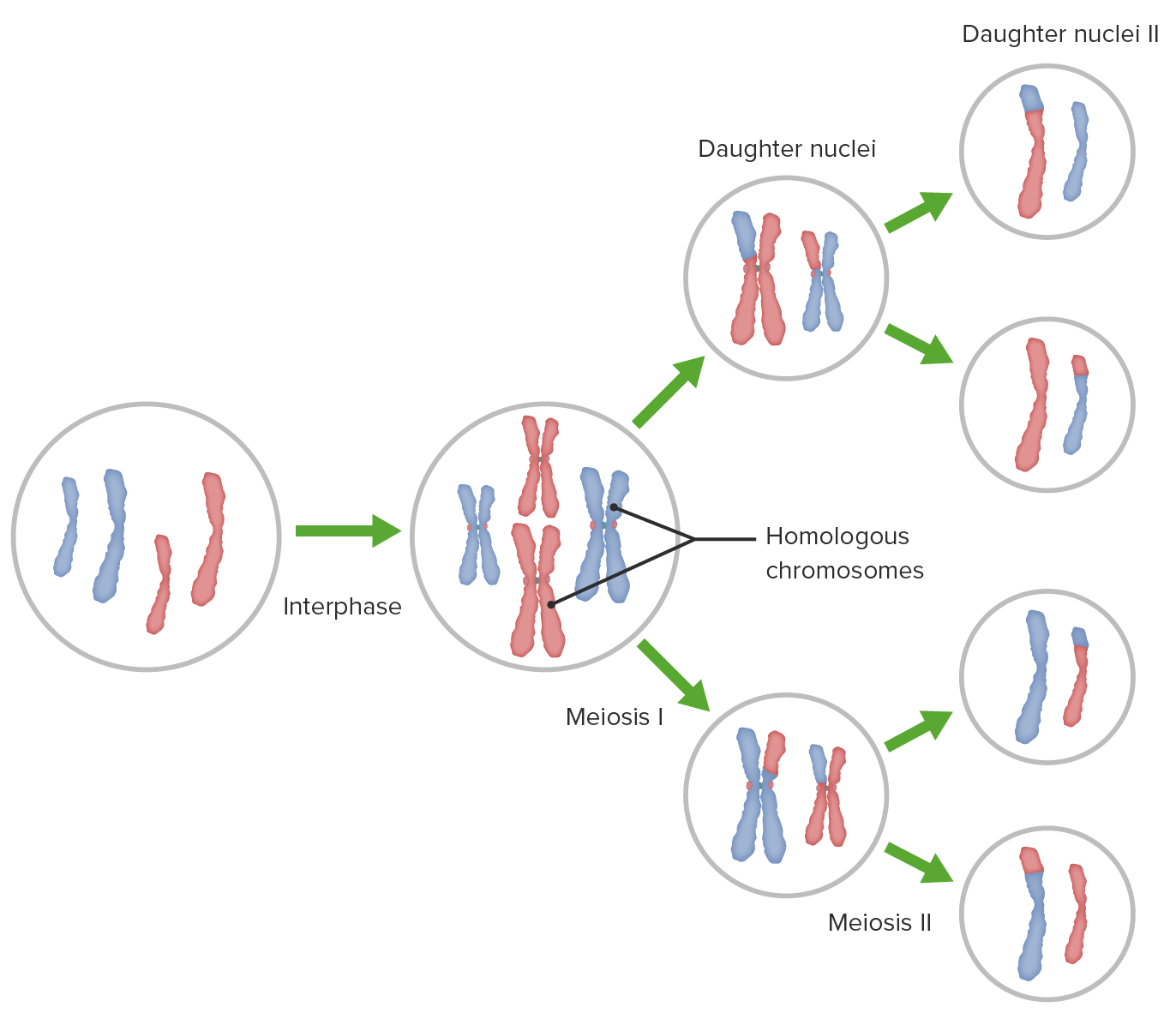
Parent (One, diploid parent cell with 46 chromosomes); Daughter (4, unique, haploid daughter cells with 23 chromosomes).
Describe (or draw) the process of crossing over. How does this lead to greater genetic variation?
Crossing over occurs when homologous chromosomes pair up and the sister chromatid from one homologous chromosome swaps segments of DNA with another. This leads to new combinations of traits in offspring.
List and explain Mendel’s three laws of genetics.
Law of Dominance: One allele will always cover or mask another allele for a trait; Law of Segregation: Alleles from the parent are separated when they are given to their offspring; Law of Independent Assortment: One trait does not affect the other.
Describe the difference between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids?
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes (one maternal and one paternal) that contain genes (but not necessarily alleles) for the same traits. Sister chromatids are two identical chromatids created by DNA replication in S phase.
List the number of chromosomes and sister chromatids in each cell at the end of each of these stages in meiosis: G1 Phase, S Phase, Telophase I/Cytokinesis, Telophase II/Cytokinesis.

G1 Phase (46C, 46SC), S Phase (46C, 92SC), Telophase I/Cytokinesis (23C, 46SC), and Telophase II/Cytokinesis (23C, 23SC).
Describe the process of independent assortment. How does this lead to greater genetic variation?

When homologous chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate during Metaphase I, they are randomly and independently assorted. This allows for different combinations of chromosomes for both sets of daughter cells (mixture of parental traits).
If you are doing a test cross to determine the genotype of an unknown guinea pig with a dominant trait (such as rough fur), what type of guinea pig should you use to mate with it? Why?
![]()
A heterozygous guinea pig as it has the possibility of producing offspring with recessive traits (in the case the unknown guinea pig was heterozygous). If a homozygous guinea pig was used, it would produce offspring with dominant traits regardless of the other parent’s genetic makeup.
What is a tetrad? When are they formed?
The stacking of a pair of homologous chromosomes; observed during Prophase I.