area of the brain that processes stimuli related to touch and pain
parietal lobe
the largest region of the brain
cerebrum
a condition caused by the degeneration of motor neurons in the spinal cord and in the brain's medulla and cortex
ALS
the generalized term that describes the neurological disorder in which cells in the brain do not function correctly, causing seizures
epilepsy
chronic, slow-progressing disease characterized by dyskinesia, dystaxia, paresthesia, and muscle weakness
MS
causes a loss of sensation
anesthetic
1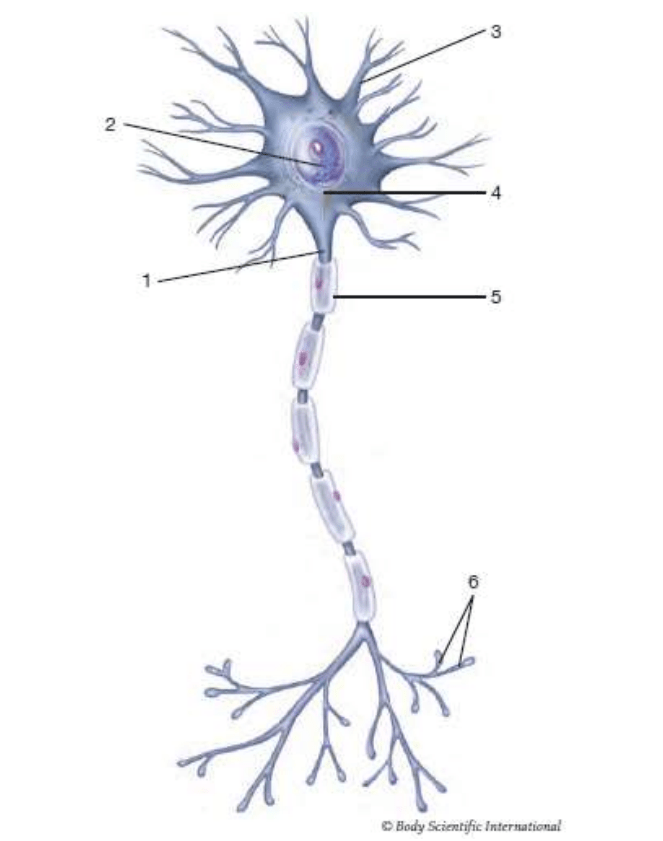
axon
part of the brain that controls balance and equilibrium
cerebellum
area of the brain that controls language processing
temporal lobe
inflammation of the gray matter of the spinal cord
polio
abnormal, localized dilation of a blood vessel in the cerebrum
cerebral aneurysm
the sudden blockage of blood flow to the brain that results in death of the brain tissue
CVA
reduces feelings of anxiety
anxiolytic
2
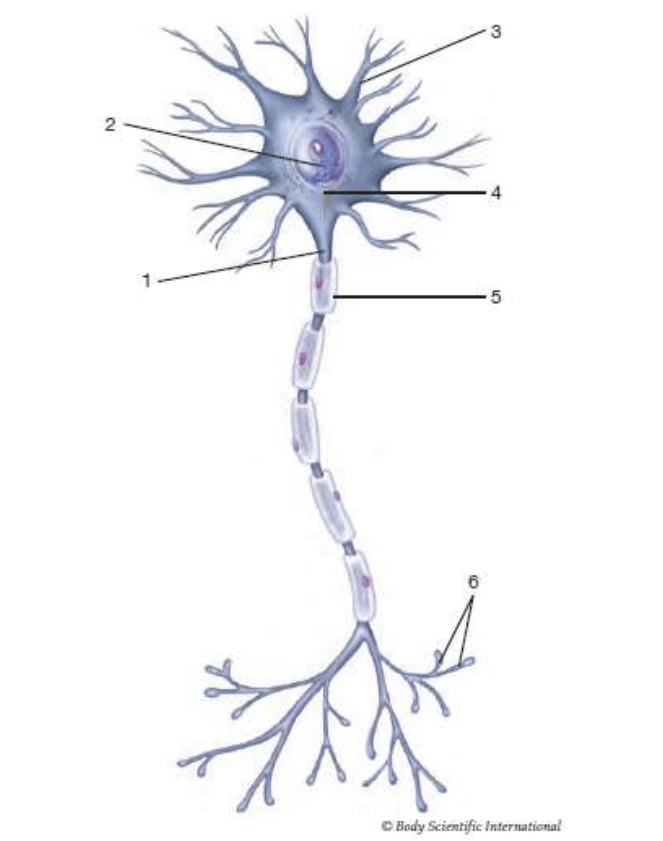
nucleus
area of the brain that is the "seat of your personality"
frontal lobe
the site of three key glands
diencephalon
condition characterized by unilateral facial paralysis
bell's palsy
condition in which neuromuscular communication is disrupted and the muscles become severely weakened
MG
a brief stoppage of blood flow to a part of the brain
TIA
promotes sleep and loss of consciousness
hypnotic
3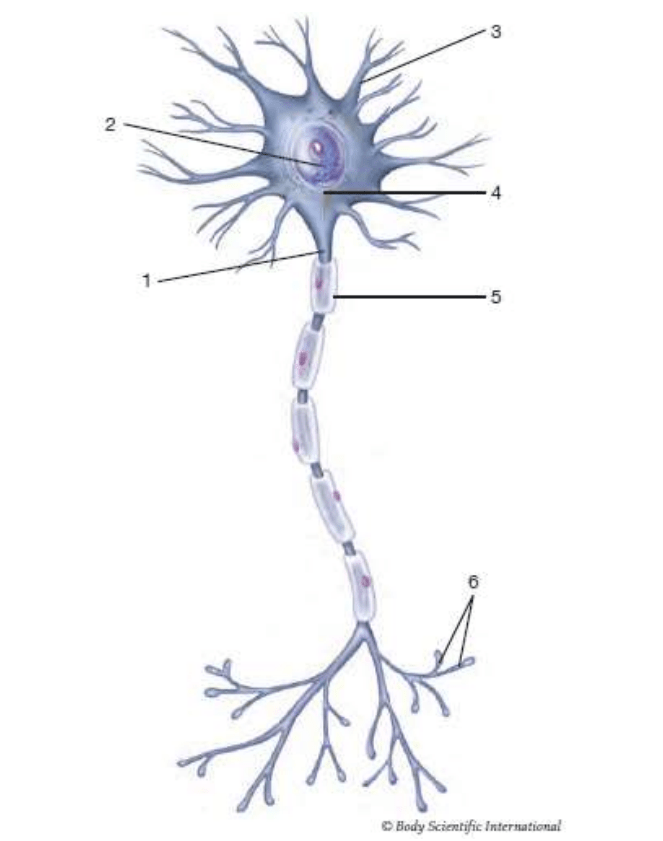
dendrite
serves as the conduit for sensory information between the cerebrum or cerebellum and the rest of the body
brain stem
area of the brain that controls hunger, thirst, and digestion
hypothalamus
a condition in which a newborn baby's meninges protrude through an opening of the skull or spinal cord
meningocele
a disruption of electrical activity in the brain characterized by violent muscle contractions and loss of consciousness
grand mal seizure
a condition that occurs at or before birth which affects movement and muscle tone
CP
relieves pain
analgesic
5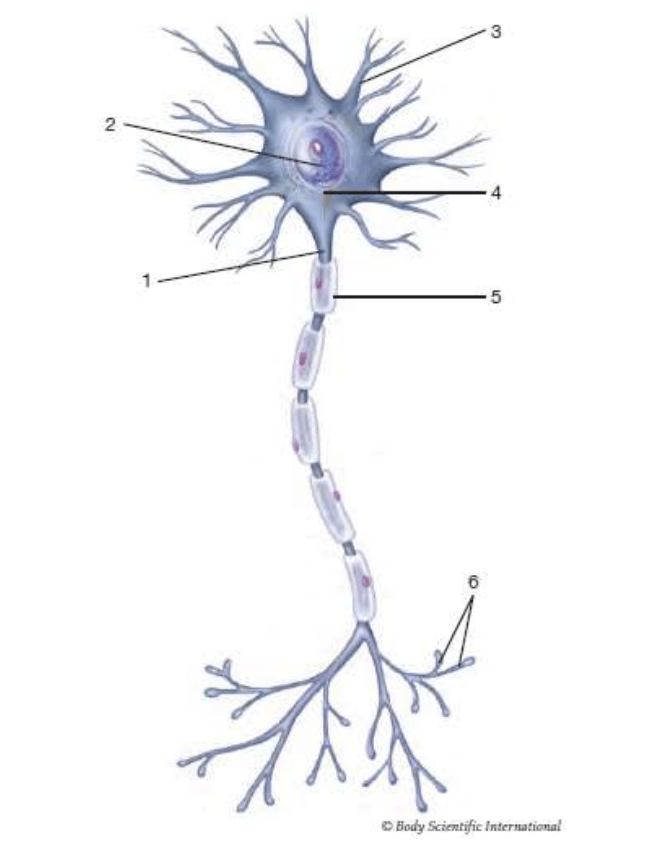
myelin sheath
convolutions on the surface of the brain
gyri
gland that secretes melatonin
pineal gland
condition generally discovered in newborns, in which a portion of the spinal cord and meninges protrudes through an opening in the spine
myelomeningocele
inflammation of multiple peripheral nerves, causing progressive muscle weakness. Usually occurs during or after recovery from an infectious disease
GB syndrome
accumulation of CSF in the ventricles of the brain, which results in cephalomegaly and may cause brain damage
hydrocephalus
produces a soothing or tranquilizing effect
sedative
6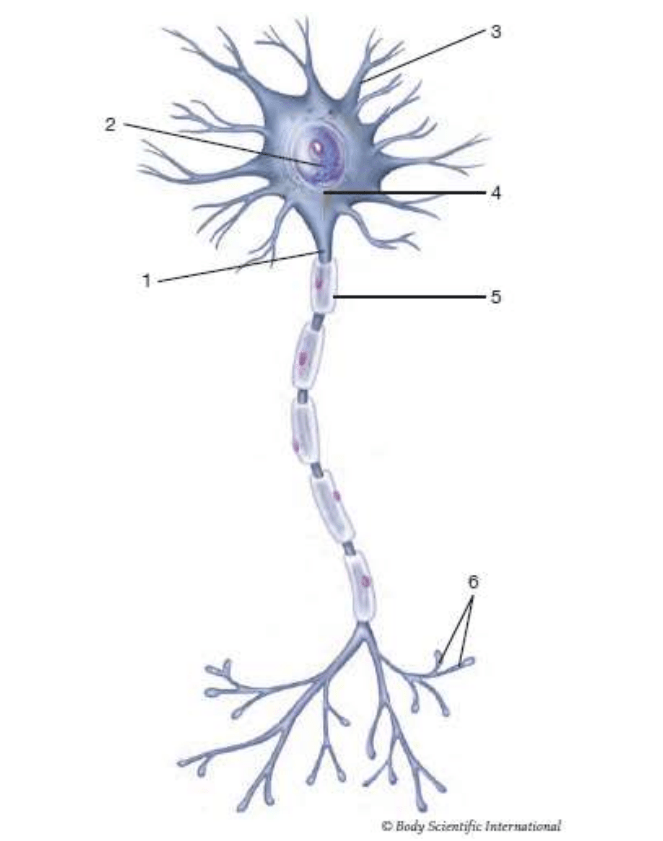
axon terminals