From where do plants get their carbon atoms?
A: Carbon from the Soil
B: CO2 from Atmosphere
C: Oxygen released during Cellular Respiration
D: From H2O in the Soil
B: CO2 from Atmosphere
Define the following terms:
1. Herbivore:
2. Carnivore:
3. Omnivore:
1. Herbivore: an animal that eats plants
2. Carnivore: an animal that eats meat
3. Omnivore: an animal that eats BOTH plants & animals
Any relationship where two or more species live closely together.
Symbiosis
If the death rate exceeds the birth rate, what will happen to the population size?
The population will decrease
The first organisms to grow in an area. Ex: lichen

Pioneer Organisms/Species
The badger occupies a unique niche in its ecosystem by digging burrows which provide shelter for other animals. What is the definition of niche in biology?
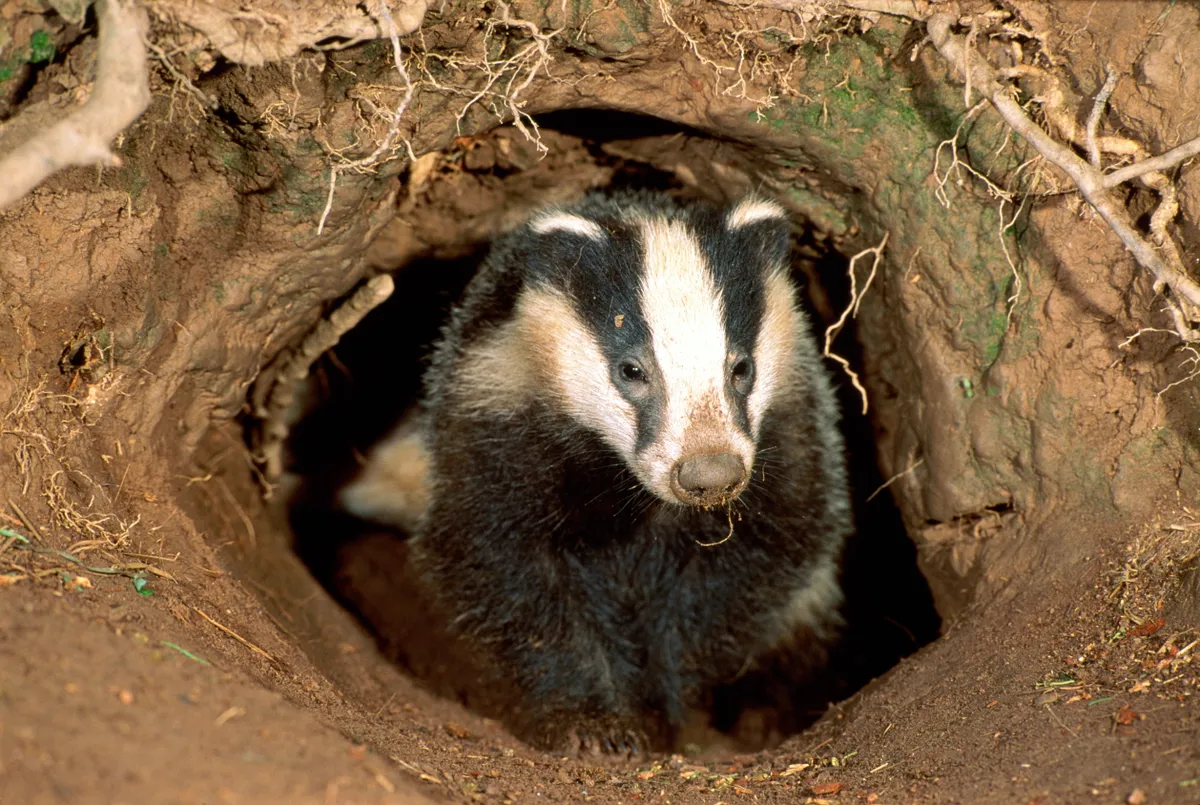

The role an organism plays in an ecosystem
If scientist wanted to study animal interactions would they use a food web or food chain and why?
Food web: Food webs show all the ways energy is transferred; Food chains only show a single way energy is transferred in an ecosystem.
In this relationship, one organism is harmed (but not killed) at the benefit of the other.
Parasitism
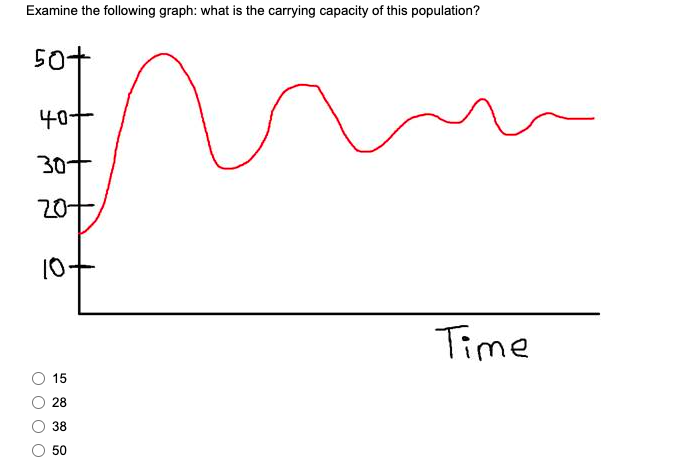
38
This type of succession happens in areas of brand new land where nothing grew before
Primary Succession

List the levels of ecology in order from smallest to largest
Individual (smallest), Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biosphere (largest)
How many primary consumers are shown? Name them.
3 (grasshopper, mouse, rabbit)
Mycorrhizal Fungi grows in the soil around trees like the Ginkgo. The Fungi helps the Ginkgo take in more water and nutrients while the Ginkgo supplies sugar to the Fungi. What type of relationship is this?
Mutualism or Mutualistic
Which color on the graph below represents the prey?

Red
A stable ending state of succession. Ecosystems will remain at this state until a disturbance.
Climax Community

Which level of ecology does this picture show?
Ecosystem (living + nonliving things)
Assume the producers in a trophic pyramid have 7500 calories of energy. How much energy will be available to SECONDARY consumers?
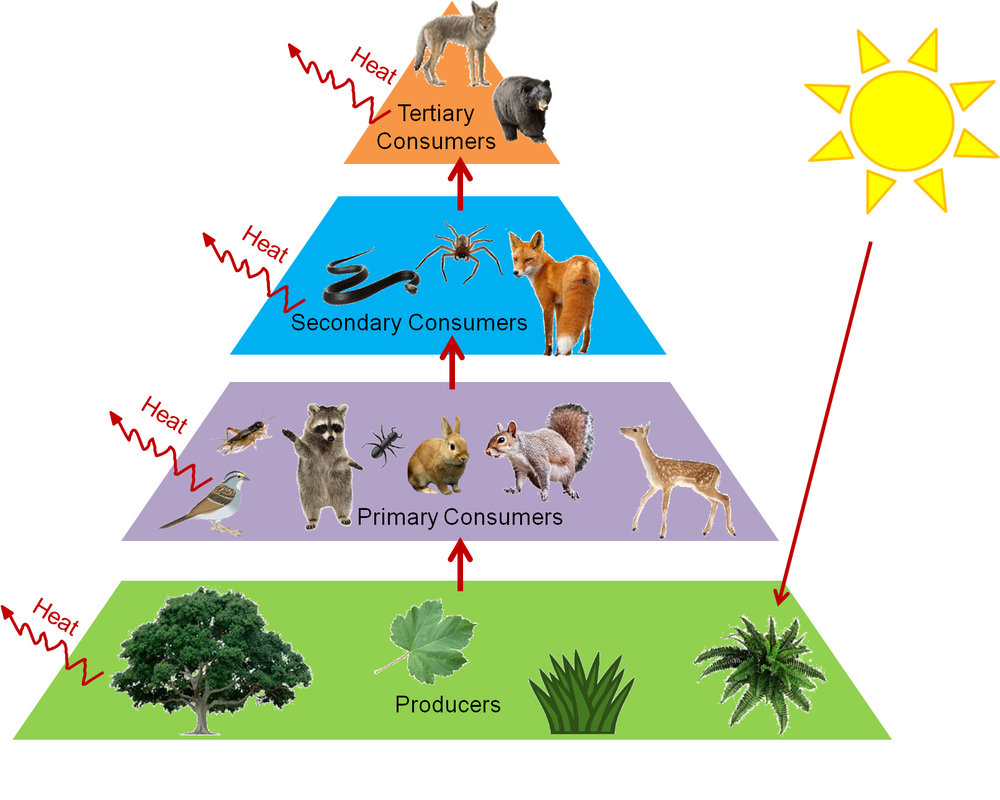
75 calories
In this relationship, one organism benefits while the other is unaffected. ( + | 0 )
Commensalism or Commensal
Which color on the graph below represents the predator?

Blue
Order these pictures of succession from first to last. (EX: A, B, C, D)

D, A, C, B
Carbon gets released into the air & absorbed out of the air in the carbon cycle.
List 2 ways carbon gets released into the air:
List 1 way carbon gets absorbed/taken out of the air:
Released:Cell respiration, burning fossil fuels, decomposition
Absorbed: Photosynthesis
What percent of energy is transferred to the next level on a trophic pyramid?

10%
(how much is lost as heat?)
What are two disadvantages of group behavior? Example: A pack of wolves
Increased spread of disease, competition for food, competition for mates, harder to hide from prey.
When did the birth rate exceed the death rate on the graph below?
A: Between years 13 and 14
B: Between years 8 and 9
C: Between years 6 and 8
C: Between years 6 and 8
What makes ecological succession to more complex organisms possible?
Changes in abiotic factors like soil, nutrients, and water.