What's the understanding of polymer construction with hydrolysis or condensation?
This works only for condensation, molecules join together but lose some like water as body products.
What is the Polysaccharides that deals with plants?
Starch
What is the terminology that requires one saccharides?
Monosaccharides
What are two reasons why lipids are different than other macromolecules?
Filled with hydrocarbons and a nonpolar covalent bond.
Explain what denaturing is and its effect on proteins?
Denaturing is the damaged and disturbed of both the secondary and tertiary structures. When a protein is denatured, secondary and tertiary structures are changed. The peptide bonds of the primary structure between the amino acids are left intact. That means a protein can't perform all the functions.
What does a diagram of hydrolysis look like?

Which polysaccharides deals with animals? 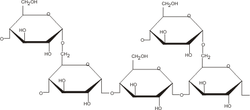
Glycogen
What is the terminology that requires two saccharides?
Disaccharides
How are fats made/ destroyed using water?
Fats are consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms so there are organic solvents in water.
Fats break water's hydrogen bonds so they are insoluble to water.
What are 3+ features of prions?
Misfolded proteins, not a life form, and no genetic material, ingesting nervous tissue, and infectious agent.
What does condensation look like?

What polysaccharides deals with cell walls?
Chitian
What is the terminology that requires three saccharides?
Oligosaccharides
Why is HDL a good cholesterol using structural components?
they transport fat molecules out of artery walls and help prevent atherosclerosis.
Explain how prions vary in structure from a protein?
convert normal body proteins in destructive proteins
Why are few monomers needed?
Very few monomers are needed by arrangement is determined by structure and function infinite number of arrangement.
Which polysaccharides deals with dietary fiber?
Cellulose
What is the terminology that requires four saccharides?
Polysaccharides
What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA is a polymer with ribose and phosphate backbone. They have four different bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. RNA is a polymer with a ribose and phosphate backbone. RNA also has four different bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
State the monomer of proteins and how many there are?
There are 20 amino acid monomers combined end to end up to a thousand of amino acids long.
What are the four main classes of macromolecules?
The four main categories are Lipids, Carbohydrates,Proteins and nucleic acids
Which polysaccharides goes with which and demonstrates its function?
Starch and glycogen are highly compact polymers that are used for energy storage.
Cellulose and chitin are linear polymers that are used for structural support in plants and animals, respectively.
What is glucose and state the function ?
Glucose, a monosaccharide, is made by plants during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight.
List the five bases of nucleic acids?
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil.
What is a prion?
misfolded protein that mixes with normal proteins and convert them to more prions.