What does the renal hilum do?
Allows blood vessels, ureter, and nerves to pass in an out of the kidney
What is the function of nephrons?
To make urine
What are the 3 stages of urine formation called?
Filtration, Tubular Reabsorption, Tubular Secretion
What is optimal blood pH? (range)
7.35-7.45
What kind of tissue does the urinary bladder contain that allows it to stretch?
What are the 2 major functions of the kidneys?
Filter blood, make urine
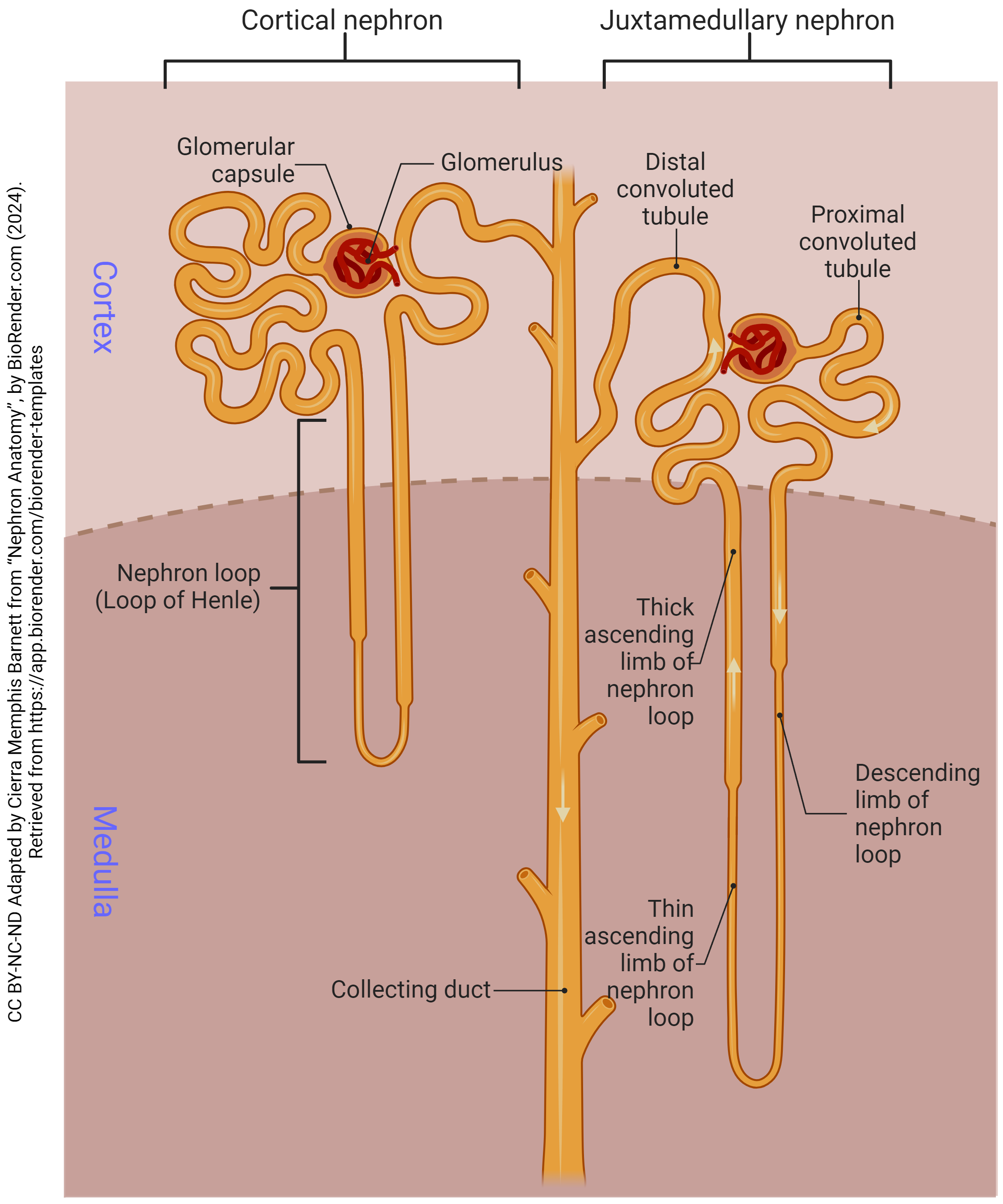
What part of the kidney do the top of nephrons reside in?
renal cortex
What is a synonym for micturition?
Voiding
What is an electrolyte?
An essential mineral/ion needed for normal body functions
What 2 parts of the urinary system use peristalsis to move urine?
Ureters, Urethra
What are the 3 regions of the kidney from outermost to innermost?
Renal cortex, renal medulla, renal pelvis
What is the glomerulus?
a knot of capillaries
200 ml
How do the kidneys maintain acid-base balance? (2 ways)
Making new bicarbonate ions
What step of urine formation is the most help with balancing blood pH?
tubular secretion
What are the calyces purpose?
Collect urine made in the nephrons and drain it into the renal pelvis
What are podocytes?
create filtration slits/holes in Bowman's Capsule
Name at least 2 substances the would be removed from the filtrate and what step of urine formation this would happen during.
Glucose, Water, Amino Acids, Certain Ions (depending on concentration)
Tubular Reabsorption
What is the difference between acidosis and alkalosis?
Acidosis is a blood pH under 7.35 and alkalosis is a blood pH over 7.45
What are two alternate pH controlling systems in the body besides the kidneys?
Blood buffers, respiratory system
What is the purpose of the adipose capsule?
Holds the kidneys in their place to prevent ureter tangling
Draw a picture that shows the difference between a cortical nephron and a juxtamedullary nephron.
Describe what happens during filtration.
The glomerulus filters out anything that is small enough to pass through like water and ions and the substances that are too big like blood cells and proteins are left behind and do not enter the filtrate.
What is one thing angiotensin II does?
vasoconstriction of blood vessels
promotes the release of aldosterone
You are treating a patient who has too few hydrogen ions in their blood. Are they in acidosis or alkalosis and how do you know/
Alkalosis because less hydrogen ions means the blood is more basic and the pH is likely over 7.45