What size foley comes with the standard adult kit?
16 French
This is the most common source of human exposure to methylmercury
Eating contaminated seafood
Excessive loss of bicarbonate from the urine leads to this condition
Metabolic Acidosis
This is the most common type of kidney cancer
Renal Cell Carcinoma (90%)
Any condition that seriously damages the glomerular capillary membrane that results in glomerular capillary permeability to plasma proteins.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Post void volume considered to be urinary retention in adults
> 250mL (+/- 50mL)
This is the type of foley that has a rigid curve at the end to assist in getting around the prostate
Coude (Tiemann or Olive are variations)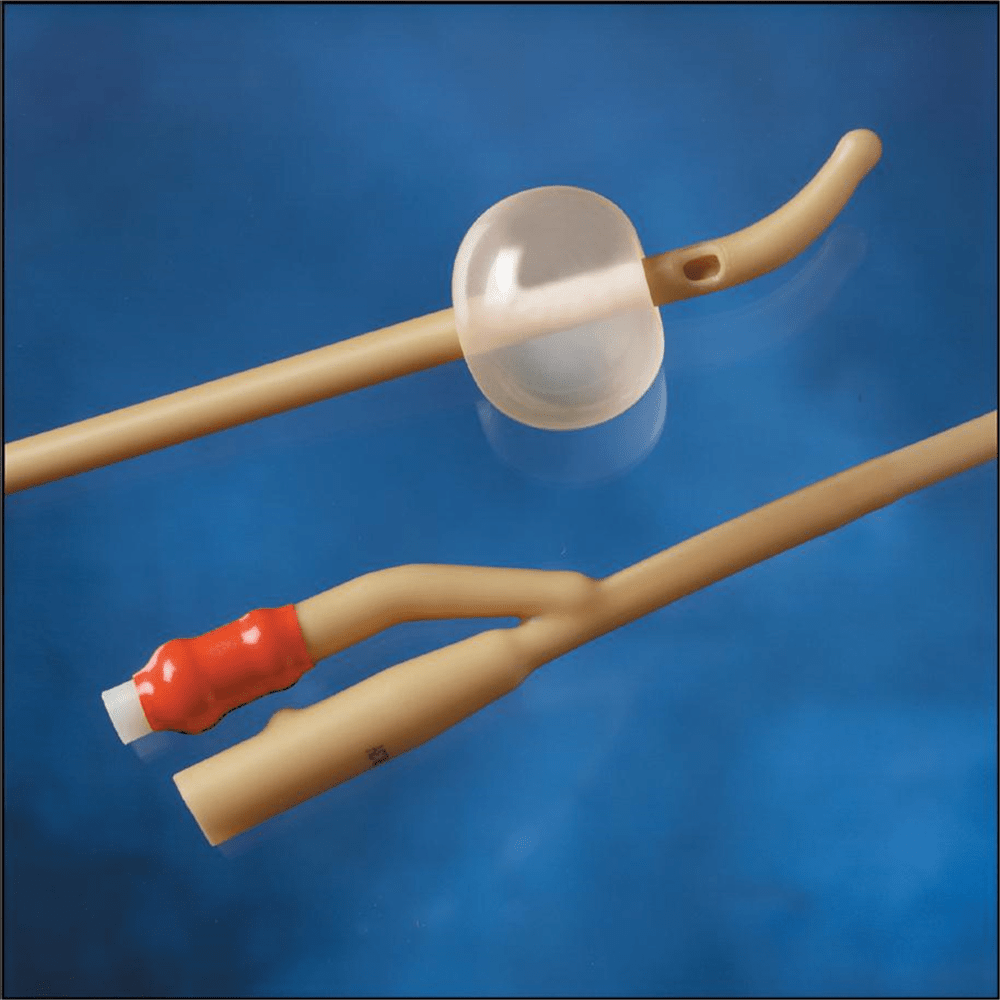
What class of antibiotics is commonly associated with renal toxicity, particularly when administered at high doses or in patients with impaired renal function?
Aminoglycosides
A dialysis patient comes to the ER for not feeling well. Name three things/tests/questions that you want immediately.
1. EKG
2. IV access
3. Critical care profile/potassium level
4. Name of Nephrologist
5. When was their last run of dialysis
6. Meds (Calcium gluconate)
This is the most common kidney cancer in children
Wilms Tumor (Nephroblastoma)- 6% of all childhood cancers
This presents as hematuria, hypertension, oliguria, and edema. It can be due to a primary renal disease or a clinical manifestation of other glomerular renal pathology
Nephritic Syndrome

Name this Foley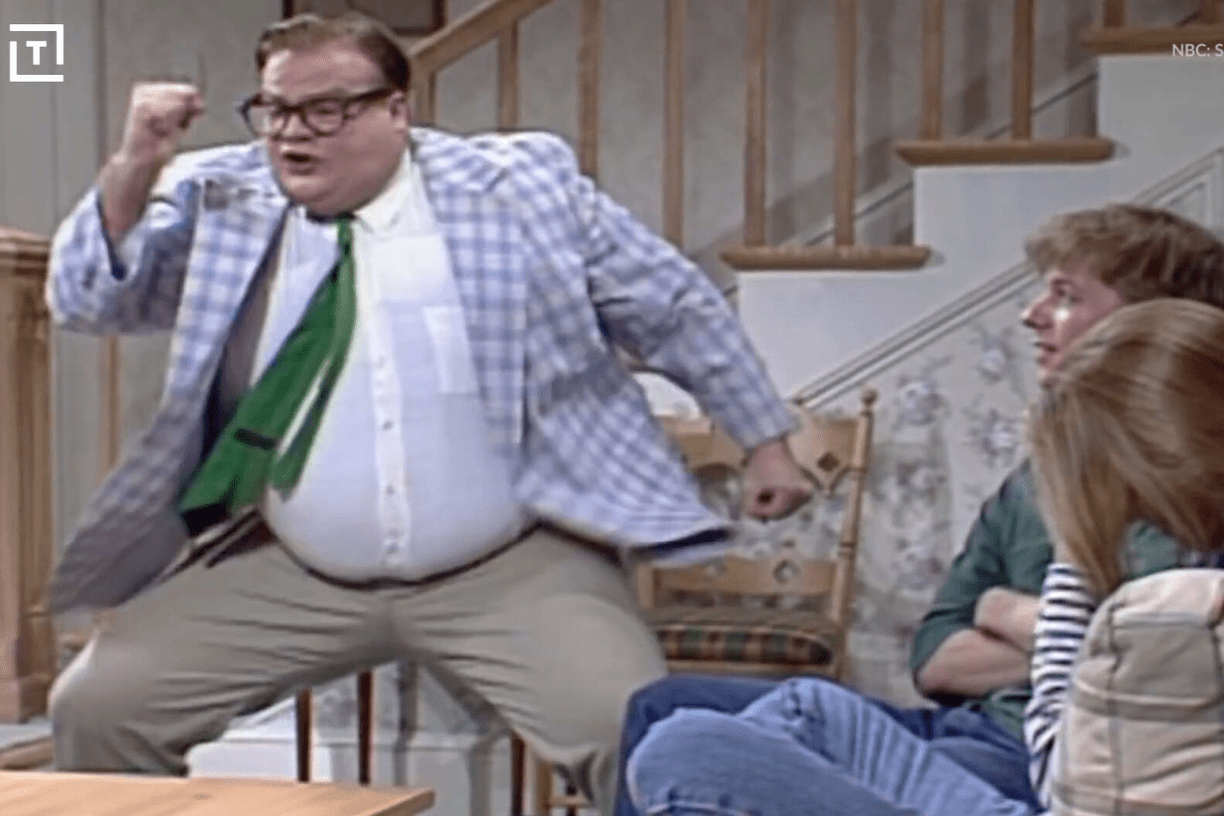
Matt Foley
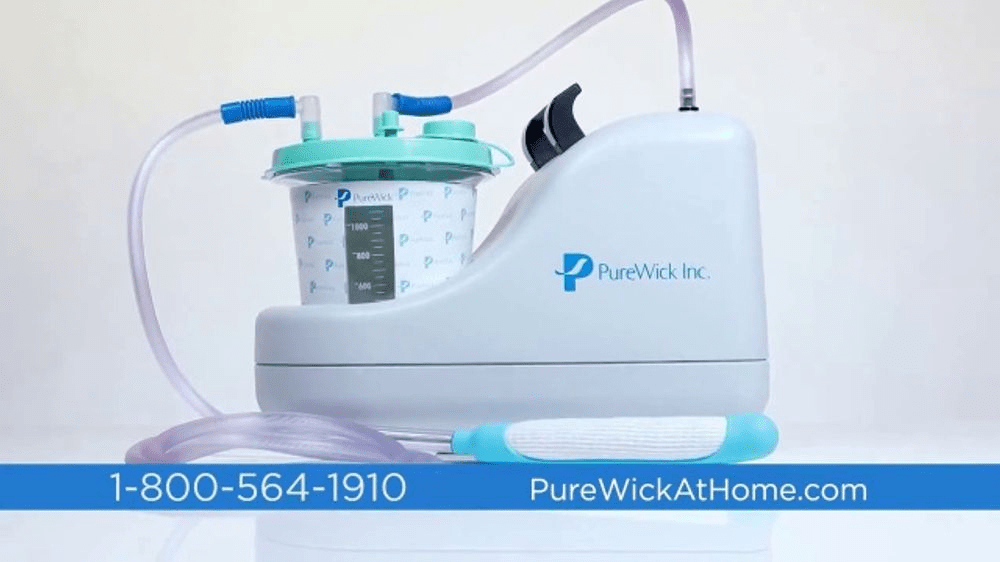
This is an external device for female patients for collecting urine that is hooked to suction
Purewick
This heavy metal, often found in industrial settings, can cause renal toxicity and is well known for its distinctive sweet smell when it interacts with air.
What is Mercury?
Name 3 initial treatment modalities for people with hypercalcemia and renal impairment
1. Fluids
2. Hemodialysis
3. Diuretics
4. Bisphosphonates (Pamidronate, Zoledronic Acid, Alendronate)
Mnemonic (with words/descriptions), reasons for emergent dialysis
A: Acidosis
E: Electrolytes
I: Ingestion or Overdose of drugs or meds
O: Overload (Fluid)
U: Uremia with encephalopathy or pericarditis
Strep pharyngitis, Scarlet fever and impetigo can lead to this complication in the kidneys
Post-Streptoccocal Glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
A surgeon uses part of the patient's intestines to form a pouch that is connected to the ureters and urethra after the diseased bladder is removed.
Neobladder
This is the type of foley catheter that can be threaded over a guidewire or glidewire
Council Tip Catheter
What type of renal toxicity is commonly associated with the use of NSAIDs and is characterized by a reduction in blood flow to the kidneys?
Acute Interstitial Nephritis
What is FENa? What is the calculation? AND how do we use it?
FENa: Fractional Excretion of Sodium
This is the most common initial finding in bladder cancer.
Hematuria
This is a chronic kidney disease occurs when the protein immunoglobulin A (IgA) builds up in the kidneys causing inflammation and reducing the kidney's ability to filter waste
Berger's Disease (IgA Nephropathy)
This is the hormone that the kidneys excrete that stimulates the bone marrow to product red blood cells
Erythropoietin
What is the post void volume above which children are considered to have urinary retention.
> 20mL
This chemical compound is metabolized into oxalate, which in turn precipitates to calcium oxalate crystals within the tubular lumens and can lead to kidney injury
Ethylene Glycol
Renal tubular acidosis is a condition where the kidneys fail to acidify the urine effectively, resulting in metabolic acidosis. What electrolyte imbalance is commonly associated with this condition?
Hyperchloremia
This is an aggressive kidney cancer that predominantly afflicts those with sickle cell trait, sickle cell disease or sickle hemoglobinopathies. By the time it is diagnosed, 90% of patients will already have metastatic disease.
Renal Medullary Carcinoma
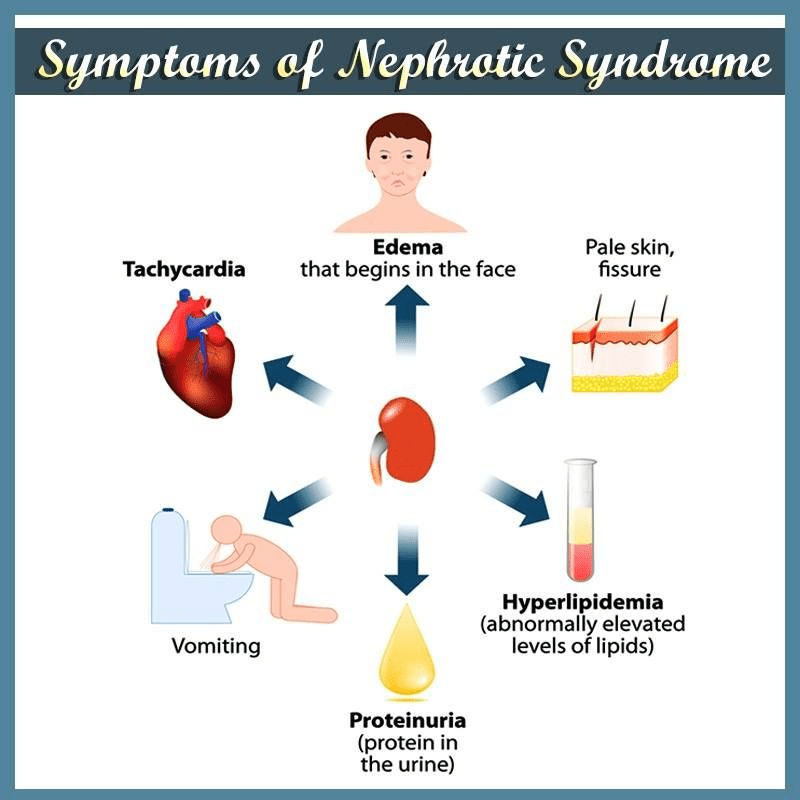
Name 3 symptoms or abnormal lab findings in a patient with Nephrotic Syndrome
1. Edema
2. Proteinuria
3. Hyperlipidemia
4. Tachycardia
5. N/V
If a patient's urinalysis is positive for blood, but negative for RBCs, what is the most likely condition?
Rhadomyolysis