A foley catheter and/or the drug misoprostil are used for this.
What is cervical ripening for induction?
This complication of pregnancy may cause abdominal pain, back pain, vaginal bleeding
Causes: Short umbilical cord, injury to abdomen when pregnant, or a sudden loss of uterine volume
Risk factors: Advanced maternal age, smoking, cocaine use, diabetes, pregnancy induced hypertension, increased uterine distention
What is placental abruption?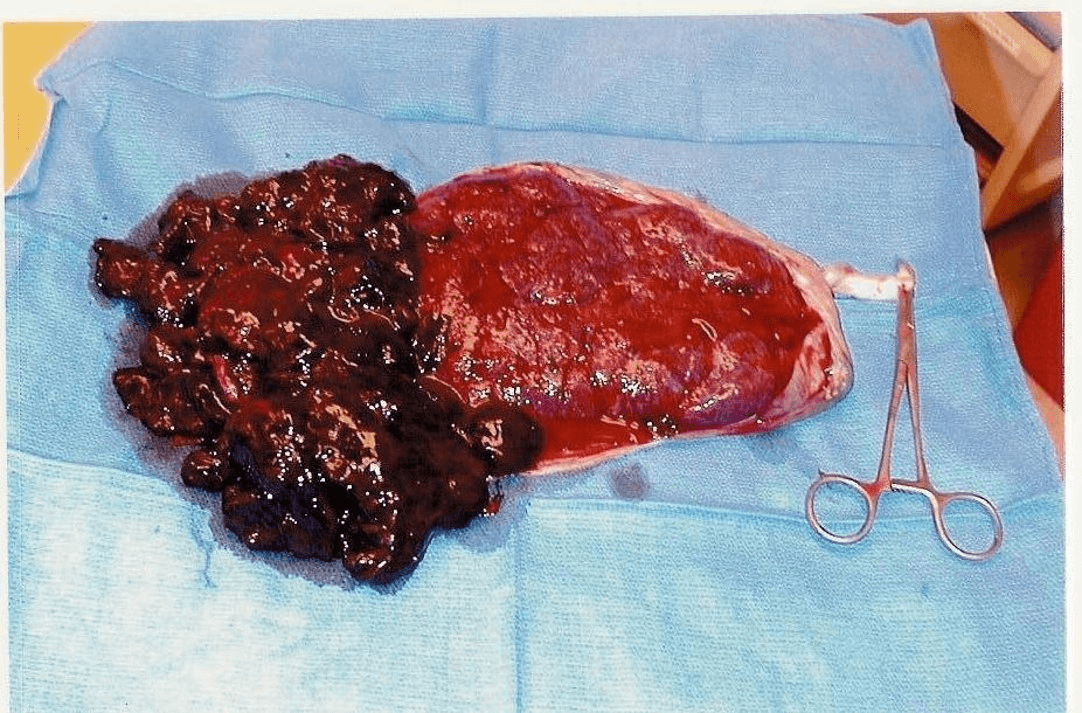
This complication of pregnancy can lead to overly large, fragile babies.
Screening for this disease occurs around 20 weeks
Diet, exercise, and supplementary insulin can help regulate this disease
Diagnostic & screening test is called a Glucose Tolerance Test
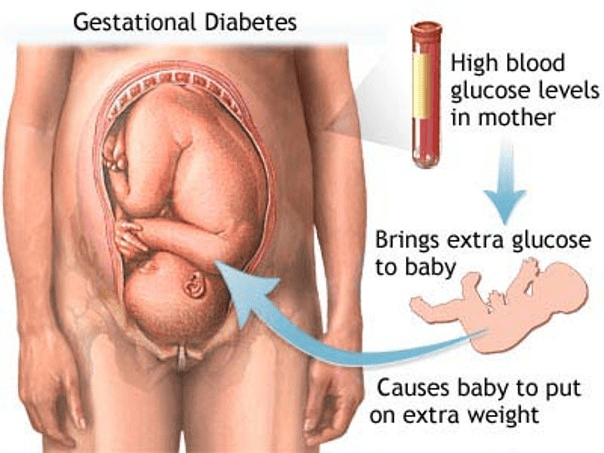 What is gestational diabetes?
What is gestational diabetes?
This common intervention is used to help hydrate a birthing parent and also to deliver other medications.
What is an IV port/heparin lock?
This usually resolves with time or non-medical interventions to get back on a normal curve
What is a variation?
Pitocin is used to produce these once the client's cervix is ripened.
What are contractions?
This complication of pregnancy causes painless vaginal bleeding and can mean very strict bed/pelvic rest, inversion and cesarean birth.
Risk factors: many previous pregnancies, scars from previous cesarean births, twin/higher order pregnancy
What is placenta previa?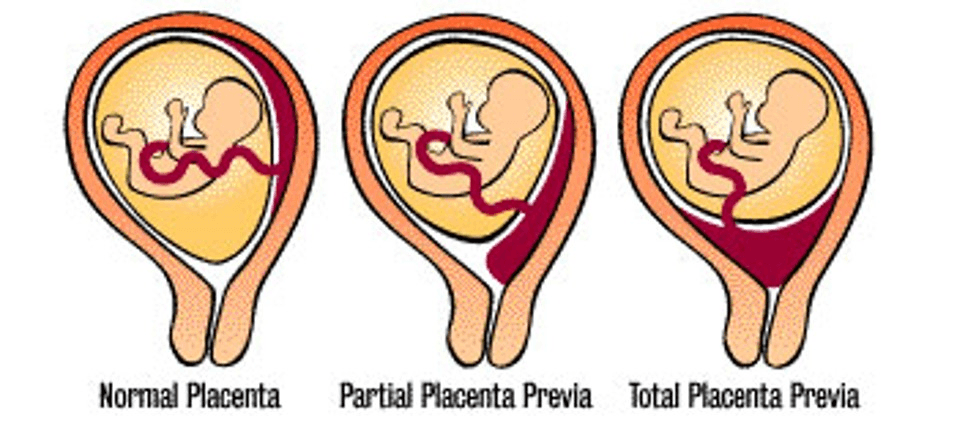
This complication of pregnancy can result in small-for-gestational age babies. Often, the client feels well in spite of symptoms
Symptoms include: protein in the urine, high liver enzymes, blood pressure over 140/90, spots or stars in the pregnant person’s vision, headaches
What is gestational hypertension/preeclampsia?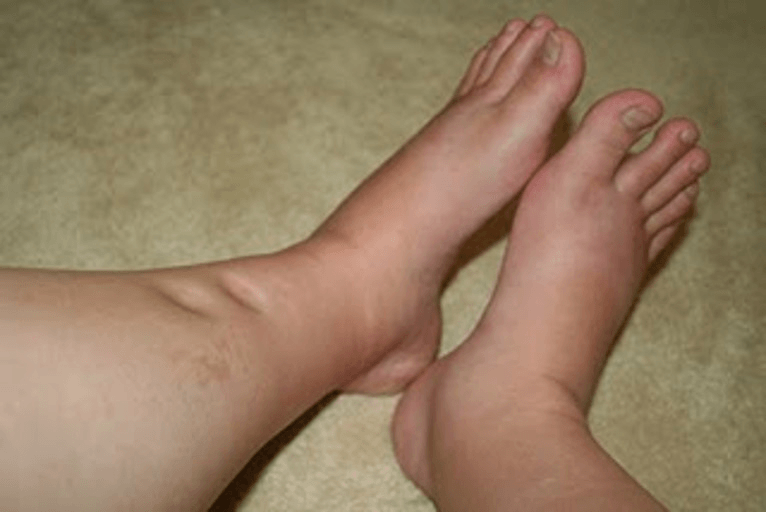
This chemical may be used to speed the delivery of the placenta and prevent or treat post-partum hemorrhage
What is pitocin?
These usually require medical interventions to increase the chance of a good outcome
What are complications?
This intervention can be used to increase contractions as well as allow for other other tools to be used inside the uterus.
What is artifical rupture of membranes (breaking the water)?
This complication of pregnancy puts babies at greater risk for still birth, causes fundal/ultrasound measurements less than expected for gestational age, and may be caused by heart disease in gestational parent, high altitude, twins or more, placenta problems, high blood pressure
Risk factors: Drugs, alcohol, smoking, poor nutrition
What is intrauterine growth restriction?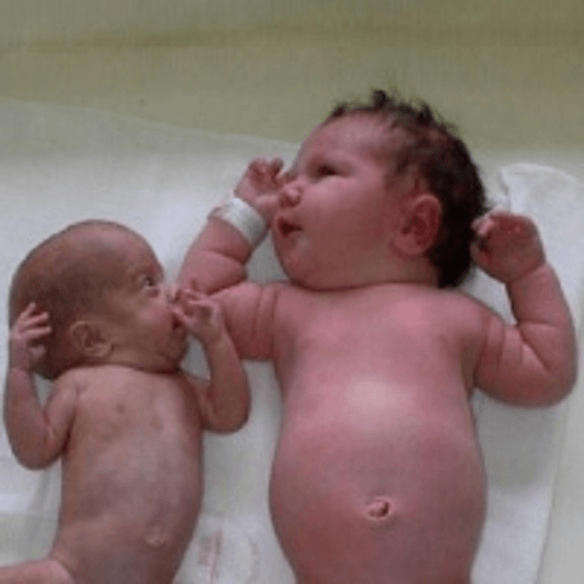
This complication of pregnancy has a higher risk of birth injury, a 3-7% occurrence rate, a 60% correction rate with external cephalic version, and often means a cesarean delivery in the USA, but not in Canada
What is breech or transverse presentation?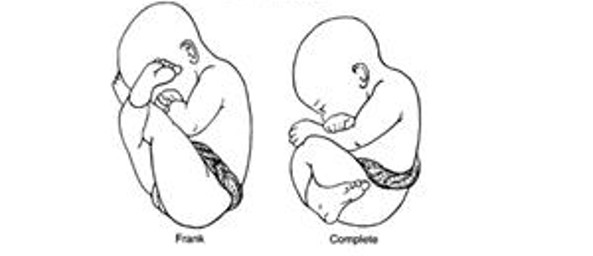
These tools can be used to speed a birth in the second/pushing stage of labor
What are forceps and vacuum?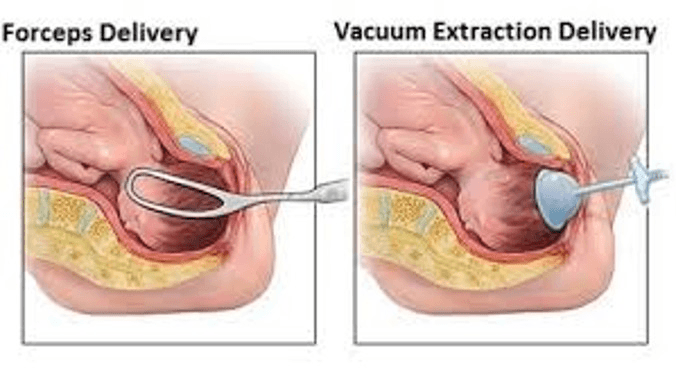
This is any action, treatment or tool used to improve a situation
What is an intervention?
These are the three ways a fetus' heart rate may be monitored.
What is intermittent (low risk), continuous (medium risk), and internal (high risk)?
This complication of pregnancy can leave babies are more prone to: immature lungs and immune system, an inability to regulate suck-swallow reflexes, an inability to thermoregulate, and time in NICU.
Risk factors include: multiple gestation, urinary tract infection, smoking, stress/racism, poor nutrition, assisted reproductive technology to achieve pregnancy
What is premature birth?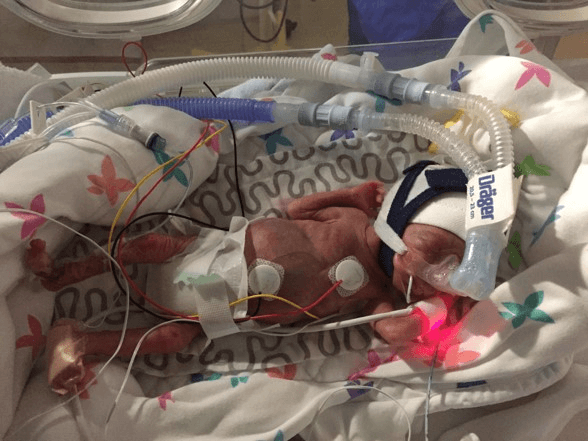
This complication of pregnancy increases the risk of: meconium passage during labor, large baby, placental insufficiency, less moldable skull bones, and can be emotionally and physically frustrating for client, partners, extended family & friends
What is post-term pregnancy?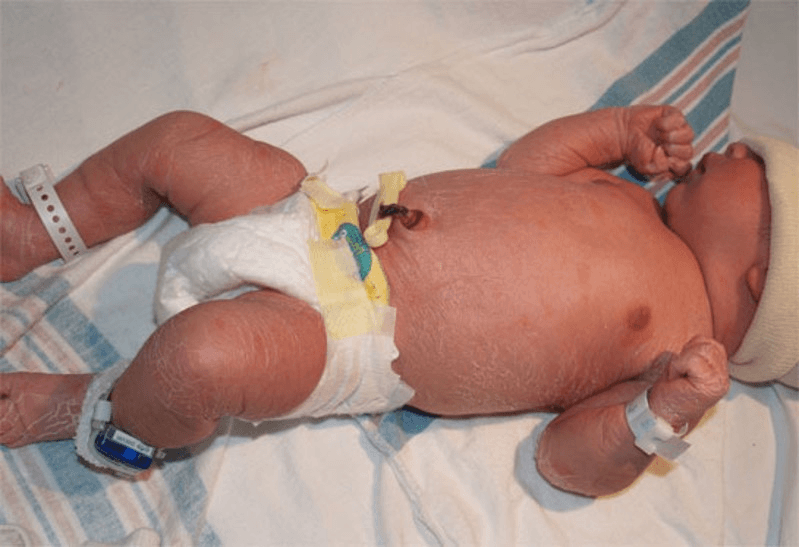
This medication may be used when a client is having a prolonged, painful early stage of labor.
What is morphine and phenergan?
These are most helpful for variations, have few serious side effects, don't go inside the body, work with the body's natural functions and rely on time to work
What are non-invasion interventions?
When this complication happens, these tools may be used: internal fetal scalp electrode, fetal scalp stimulation, oxygen mask, position changes, stopping pitocin, IV fluids, intrauterine pressure monitor, amnioinfusion.
What is indeterminate or low/absent fetal heart rate?
This complication of pregnancy effects 45 million Americans and can be treated with Acyclovir to prevent outbreaks
Babies infected at birth are at risk for: Permanent eye damage, brain damage, damage of internal organs, death
What is genital herpes?
This tool can be used to assess whether contractions are strong enough to cause cervical change.
What is an intrauterine pressure catheter?
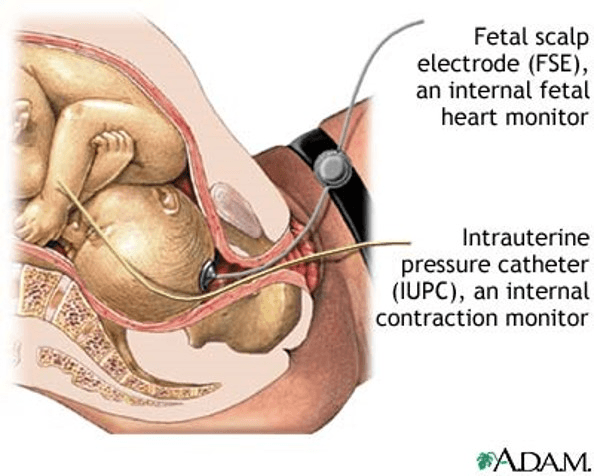
These are most helpful with complications and may have more serious side effects, circumvent the body's natural functions, and are used when no time is left.
What are invasive interventions?