4 Risk Factors for DVT
Age >40 years old
Malignancy (cancer)
Immobilization (bed rest, paralysis of legs, extended travel)
Fracture of pelvis, hip, or long bones
Myocardial infarction, stroke
Previous DVT or PE
CHF or respiratory failure
Pregnancy and postpartum
Oral contraceptives and HRT
Extensive dissection at major surgery
Trauma (multiple)
Hereditary factors
Obesity
Central venous lines, pacemakers
Intravenous drug abuse
Elongated, dilated tortuous veins
Varicose Veins
a collection of synovial fluid associated with the knee joint.
Popliteal (Baker's Cyst)
Describe the findings...
CFV DVT
A condition in which a venous thrombus dislodges from the vein wall, and propagates to the arteries of the lungs, and causes a pulmonary embolism (PE).
Venous thromboembolism
What are the 3 factors of Virchow’s triad?
Hypercoagulable state
Venous stasis
Vein wall injury (vein trauma)
Patient Position for a venous reflux study
Standing with nonbearing of the leg being imaged
Differentiation between a ruptured popliteal cyst and hematoma on ultrasound
popliteal cyst will communicate with knee joint and hematoma will not
What is the pathology?
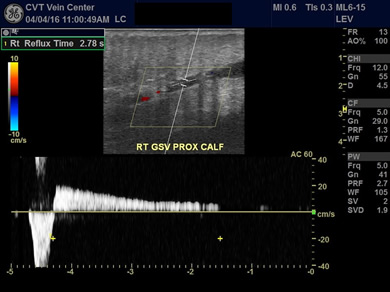
3 Symptoms of PE
Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
Chest pain
Hemoptysis (spitting up blood)
Sweats
Cough
Calf discomfort on passive dorsiflexion
Homan's Sign
normal reflux time
less than 0.5 seconds
Can mimic a DVT especially in the groin
Lymph Node
What does the red arrow point to?
SVT
2 symptoms of SVT
Local erythema
Tenderness or pain
Palpable subcutaneous “cord”
What occurs when venous blood is unable to overcome hydrostatic pressure, resulting in blood stasis in the lower leg?
Venous Hypertension
What is the criteria to determine if a perforator has reflux?
Color is demonstrated going to deep to superficial veins
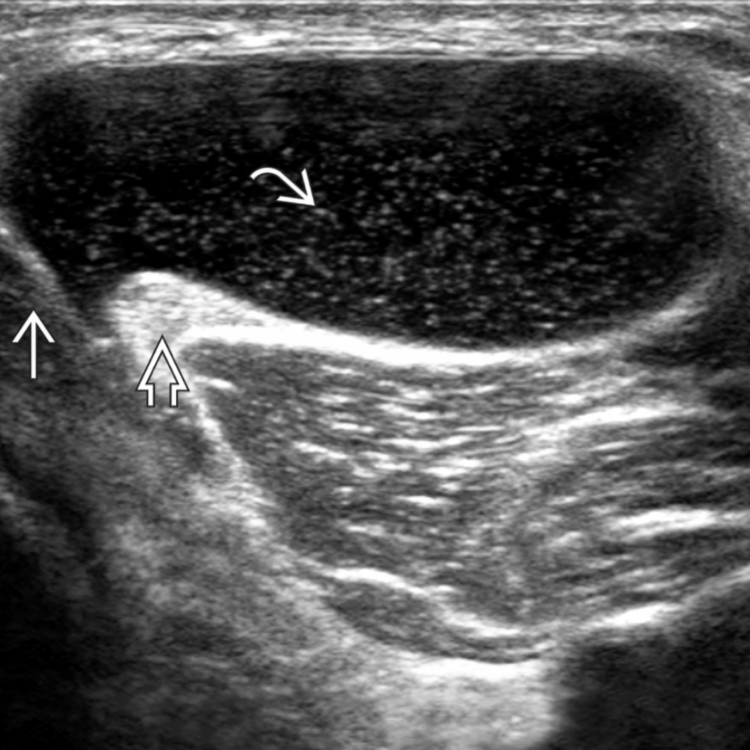
Popliteal (Baker's) Cyst
What is the pathology seen
May-Thurner Syndrome (Left iliac vein compressed by right iliac artery)
Left iliac Vein is compressed against the 5th lumbar Vertebra by the Right Iliac Artery
May-Thurner Syndrome
Two Differences between acute and chronic DVT
Acute - less than an week old, hypoechoic or anechoic, not adhered to wall, soft and spongy appearance
Chronic - more than a week old, echogenic and cause wall thickening, adhere to vein wall, dense and calcified
3 Symptoms of venous ulcer
Near medial Malleolus
Mild pain
Shallow and irregular
Venous Ooze (Wet and weepy)
chronic and severe condition that involves significant long-term edema fluid buildup
Lymphedema
What does the size of the GSV signify?
GSV Reflux (measure above 9mm)
What type of testing is done with the below image?
PPG