Abnormal impulse formation or reentry in the ventricular myocardium or purkinje system producting depolarization wavefront that propagates through the ventricles independent of activation from atrium or AV node
what is a PVC?
the mechanism of accelerated idioventricular rhythm is
What is automaticity
Best initial treatment for idiopathic VT in the absence of structural heart disease
beta blockers or catheter ablation
In patients with HCM who have _______ or ______ an ICD is a class I recommendation if meaningful survival is greater than 1 year.
Sudden Cardiac arrest due to VT or VF OR spontaneous sustained VT causing hemodynamic compromise or syncope 
First line therapy for long QT syndrome
What are beta blockers? 
_______ is Characterized by transient or persistent coved type ST elevations in at least one right precordial EKG lead and associated with syncope and sudden death due to ventricular arrythmias. ICD is recommended for patients with cardiac arrest or syncope due to arrythmia with classic pattern.
brugada syndrome
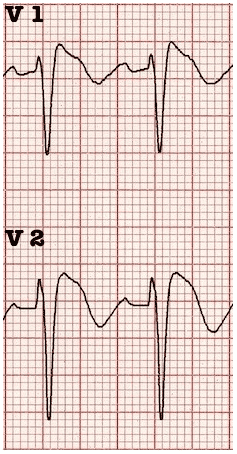 Type 1: Coved ST segment elevation > 2mm in > 1 of V1-V3 followed by negative twave (only EKG that is
Type 1: Coved ST segment elevation > 2mm in > 1 of V1-V3 followed by negative twave (only EKG that is
TYpe 2: Type 2: > 2 mm of saddleback shaped ST elevation
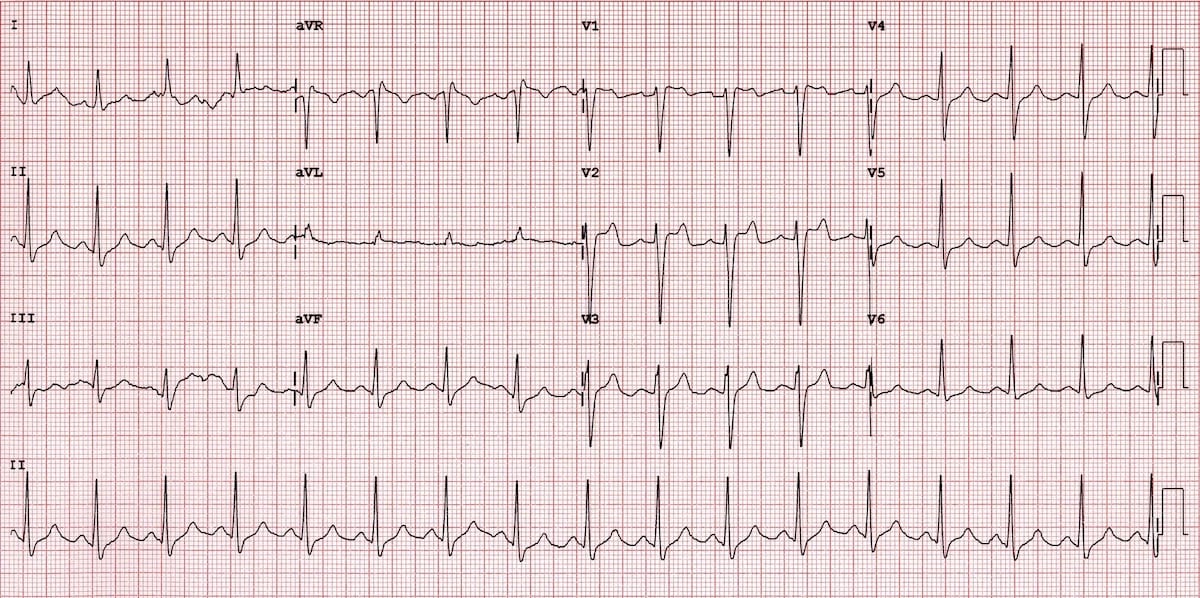
Type 3: Type 1 or Type 2 pattern but less than 2 mm
* Type 2 or 3 are nondiagnostic on their own and require further testing
PR prolongation can result from conduction delay in the AV node. In an EP Study, this interval is called the _____ interval
A-H interval
When heart block is transient or pending pacer placement, atropine or isoproterenol can be used in the short term. Isoproterenol should not be used in this clinical scenario:
acute myocardial infarction
This therapy is recommended if there is a dominant PVC morphology that can be targeted and antiarrythmic therapy is ineffective
catheter ablation
Therapy is rarely necessary in AIVR but may be needed if loss of AV synchrony and acceleration of heart rate produces symptoms or a fall in blood pressure. Options for intervention include: _____ or _____
accelerating the atrial rate through atropine or atrial pacing
During VT catheter ablation the tissue containing the VT substrate is recognized as a region of
____ without needing to induce VT.
Low voltage and abnormal electrograms
In patients with cardiac sarcoid VT is the presenting complaint in 1/3 of patients. An ICD is a class I indication for patients with sarcoid in the setting of _______
sustained VT or survivors of SCA or LVEF 35% or less if meaningful survival > 1 year. 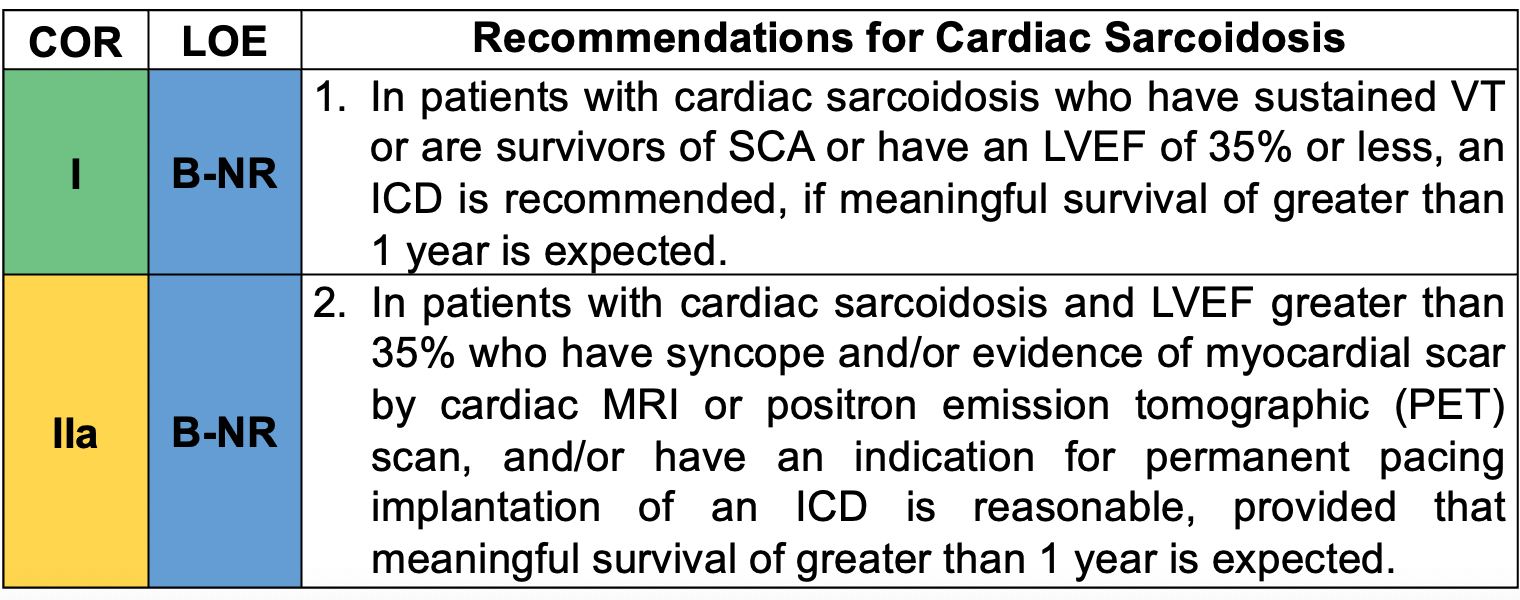
- granulomas heal leaving areas of fibrosis that can be substrate for scar-related reentrant sustained monomorphic VT
- Immunosuppressant therapy may prevent/slow active disease progression and improve AV blocks, but is unlikely to resolve VT once fibrosis has formed
What treatment is recommended for patients with asymptomatic short QT syndrome?
Nothing, observation alone. 
mutation found in 25-30% of patients with Brugada syndrome
SCN5A
Conduction delay in the His-Purkinje system causes prolongation in the _____ interval (think EP study)
HV interval
Both sinus bradyarrythmias and AV block can be caused by this phenomenon without any underlying conduction system disease.
Autonomic/neurally mediated bradycardia
increases in parasympathetic (vagal) tone can be triggered by a variety of events (hypersensitive carotid sinus syndrome, cough, syncope)
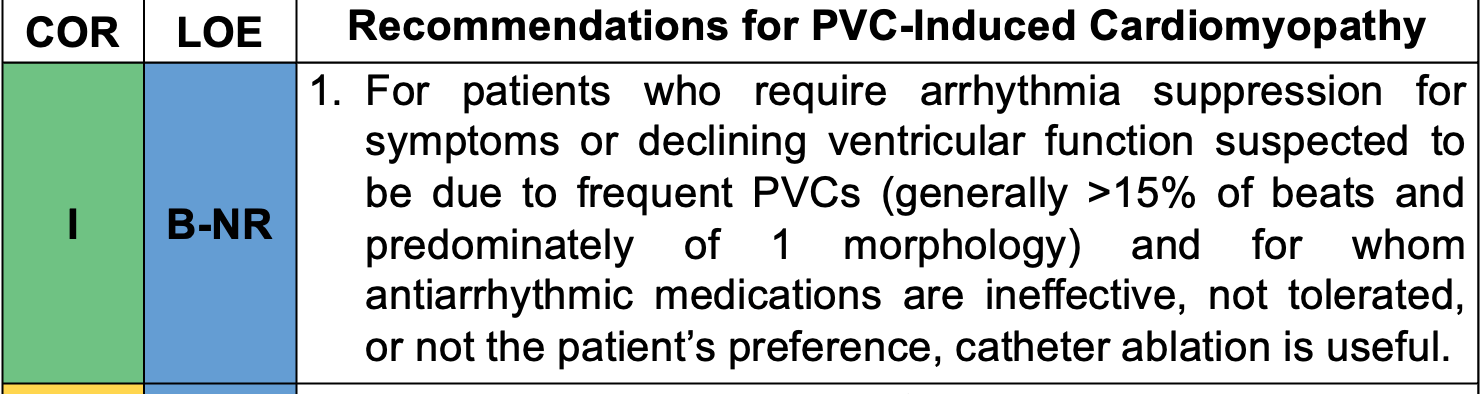
This disorder describes patients who requires arrythmia suppression for symptoms or declining ventricular function suspected to be due to frequent PVCS (generally > ___ % of beats and predominately of 1 morphology)
What is PVC cardiomyopathy? What is 15%?
This ventricular tachycardia can resemble SVT with aberrancy and it is well treated with ablation
Bundle branch reentry VT
VT catheter ablation mortality is of about _____% in patients with significant ventricular dysfunction.
1-3 %
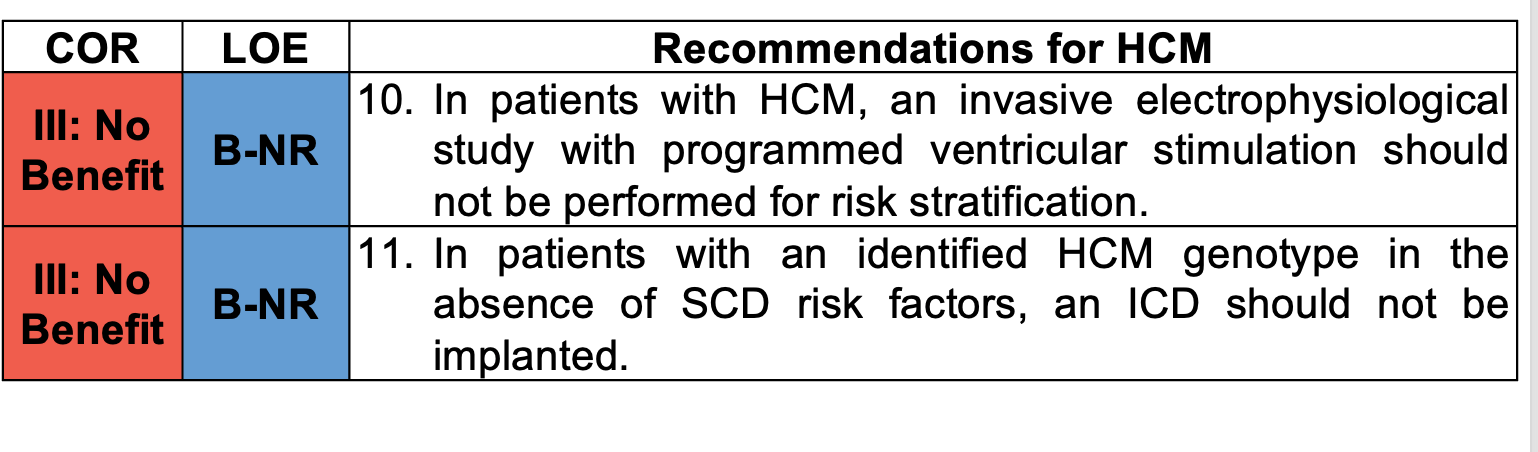
Name two class III indications for management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
EPS in patients with HCM or ICD implantation in patient with HCM genotype without risk factors for SCD
Prior to the development of Torsade de Pointes, the QTc interval is typically greater than ____ sec?
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is caused by a mutation in the cardaic ryanodine receptor and can cause bidirectional VT - triggered by stress or exertion. In this condition, ICD's should be ____, and ____ given as treatment.
avoided if possible. shocks from device can cause sympatheic activation and VT storms
Beta blockers (first line) + flecanide, left ventricular symptathetic denervation
If the QRS complex on the EKG is norma in contour and duration, the AV delay almost always resides in the
AV node
This is the treatment for symptomatic prolonged autonomic/neurally mediated bradycardia when the block is likely to be evanescent but still requires treatment or until adequate pacing therapy can be established _____ (*anticholinergic - inhibit the muscarinic receptors)
Atropine (1mg bolus, repeat every 3-5 min maximum of 3 mg)
A 45 year old woman has a PVC burden of 15%. Her EF is 60% and she is asymptomatic. Treatment of her PVCs with medications or ablation will improve her clinical outcomes. TRUE OR FALSE
FALSE. In the absence of evidence that PVCS are depressing ventricular function, suppression of PVCS with antiarrythmic medications has not generally been shown to improve outcomes.
- These patients require frequent follow-up
- Many of their PVCs will spontaneously resolve
Name four features that help distinguish VT from SVT with aberrancy
AV dissociation
precordial lead concordance (when all precordial leads on an electrocardiogram are either positive (positive concordance) or negative (negative concordance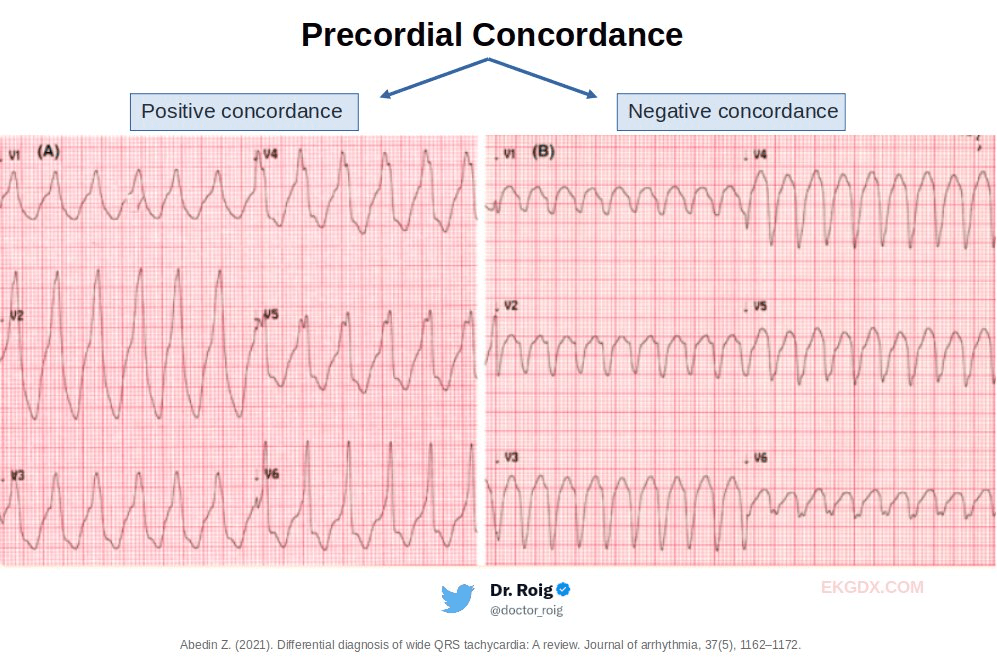
AVR with monophasic R wave or notched Q wave
atypical LBBB or RBBB
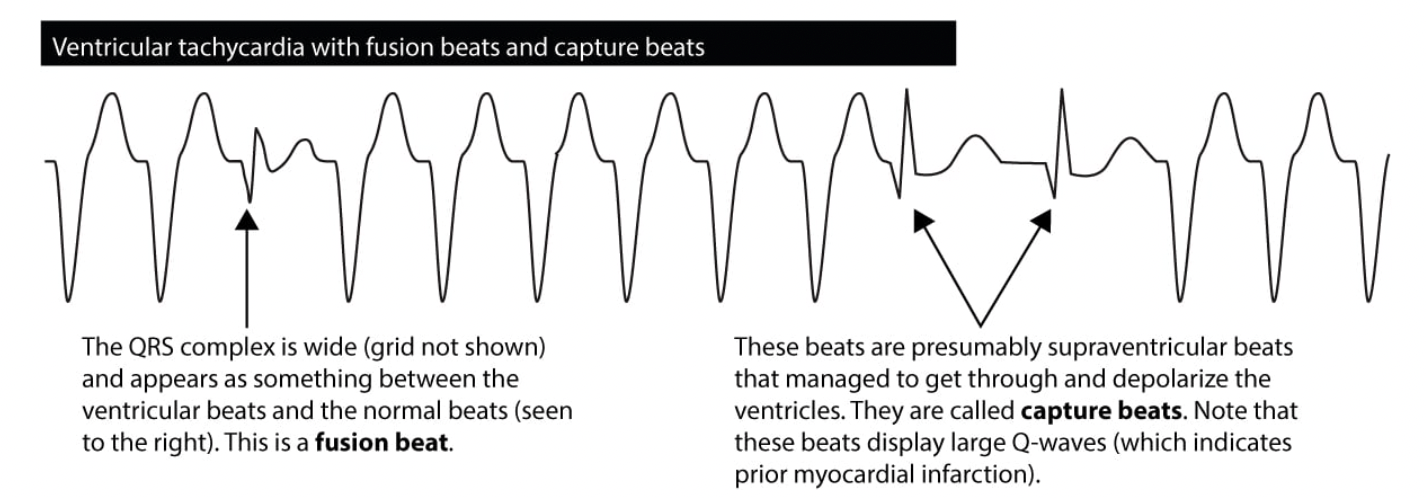
 capture beats/fushion beats
capture beats/fushion beats
In NICM percutaneous pericardial approach is often necessary to perform catheter ablation
because the location of the VT substrate is _________
Epicardial and intramural
ICD is reasonable (class IIa) in patients with the following conditions:
spontaneous NSVT or abnormal blood pressure response to exercise who have additional SCD risk modifiers or high risk features 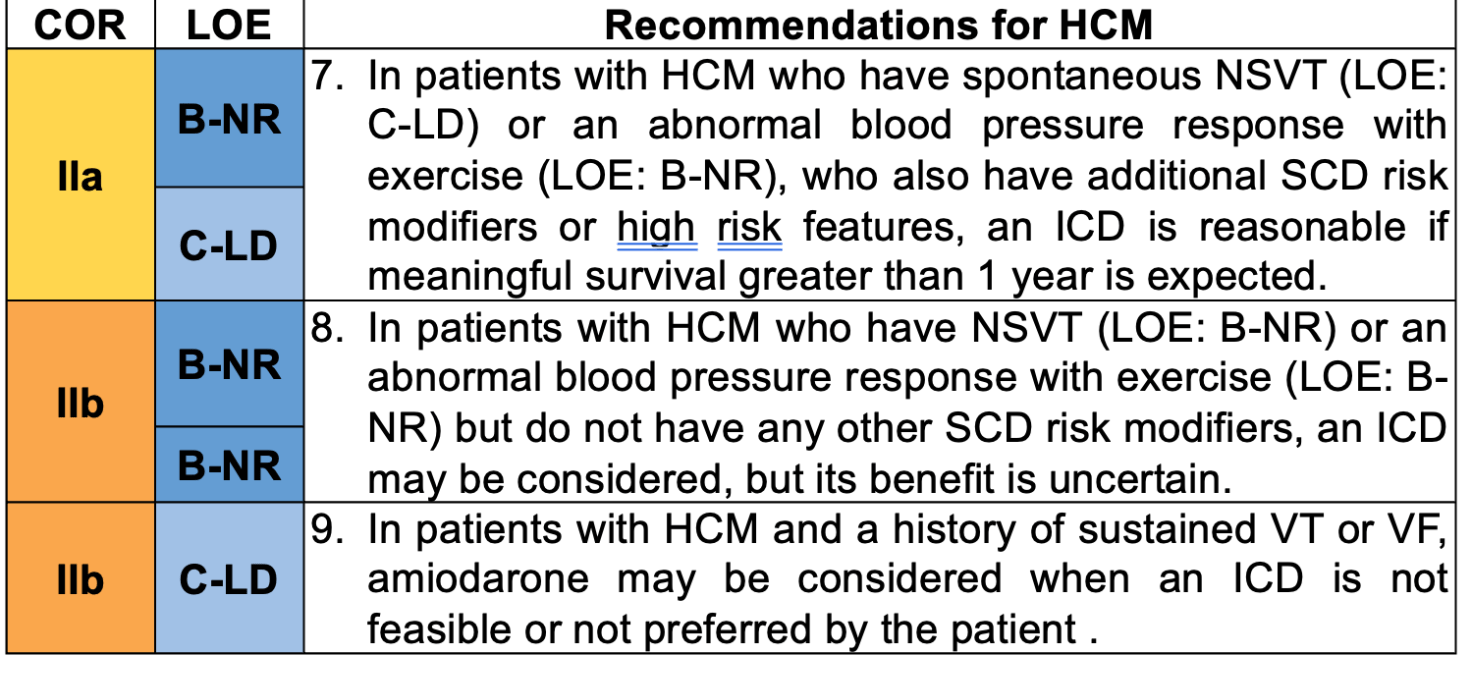
What are the ion channels that are affected in LQTS types 1, 2, and 3?
Answer: Type 1 and type 2 are potassium channels, and type 3 are sodium channels (SCN5A)
In patients with Brugada syndrome who have recurrent ICD shocks or recurrent VT who have declined ICD, _____ or ______ are recommended therapies.
Conduction disturbance of the type 1 second degree AV block [improves/worsens] with exercise
improves
A gradually diminishing intensity of S1, widening of the a to c interval, terminated by a pause and an a wave not followed by a v wave can been on physical exam in this AV block
Type I second degree AV block
Stroke volumes of PVCs are often insufficient to produce a palpable pulse, though PVCs are frequently audible. On pulse oximetry, frequent PVCs can cause _____
bradycardia
This is the preferred pharmacological agent to terminate sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia in hemodynamically stable patients
procainamide (contraindicated in ESRD due to risk of accumulation of its metabolities which can lead to QT prolongation and polymorphic VT)
PROCAMIO Study
The most common ECG abnormality in individuals with ARVC is __________
Twave inversions in V1-V3 or beyond
The two most common location of idiopathic ventricular tachycardia (VT in patients without structural heart disease) are ______ and _______. BONUS: other locations include ______, ______, ______>
Most common: right and left ventricular outflow regions
Other areas:
- papillary muscle arrythmias: EX. LV papillary muscle -> RBBB with S wave V4-V6 (posteromedial papillary muscle) or inferior rightward axis (anterolateral papillary muscle origin)
- Annular arrhythmias (mitral or tricuspid)
- Left fascicular reentrant tachycardia
What is the class I indication for all patients who have a causative mutation identified for long and short QT syndromes?
Genetic testing
_____ characterized by J point elevation > 1 mm in at least 2 continguous inferior or lateral leads of the 12 lead EKG and a QRS duration < 120 ms in leads without J wave. It is particularly common among athletes, young men and african americans. 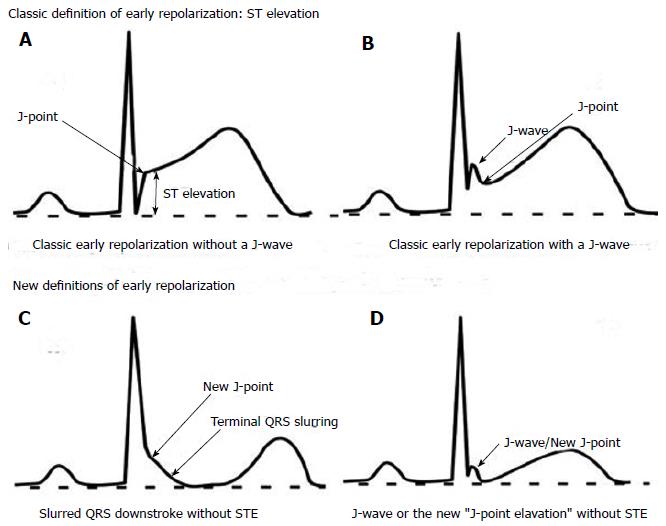
Early repolorization syndrome
classic EKG + VF or VT or syncope related to VT
TX: ICD
Vagal maneuvers improve conduction disturbance in type ____ second degree AV block
Type 2
This rhythm abnormality is shown in the intracardiac electrocardiogram
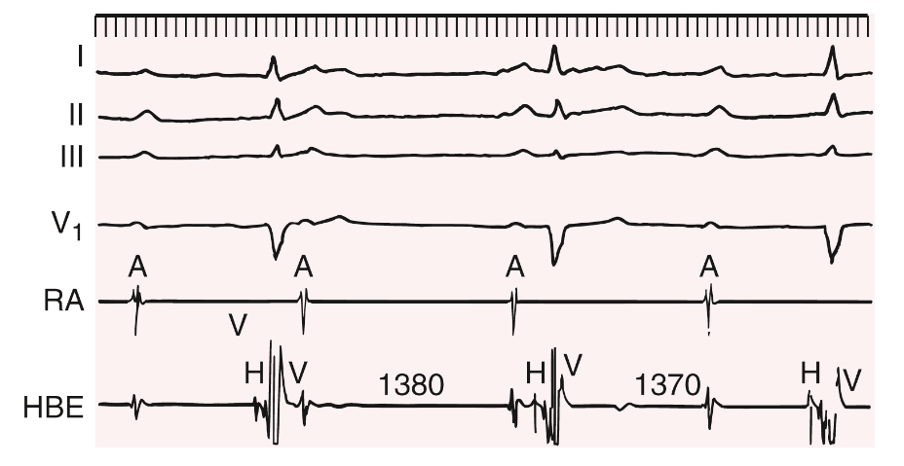
No P wave (A) is followed by a His bundle potential, whereas each ventricular depolarization is proceeded by a HIS bundle potential.