An ocean wave caused by an earthquake is called what?
Tsunami.
Before lava reaches the surface, the molten material is called?
magma.
What is this?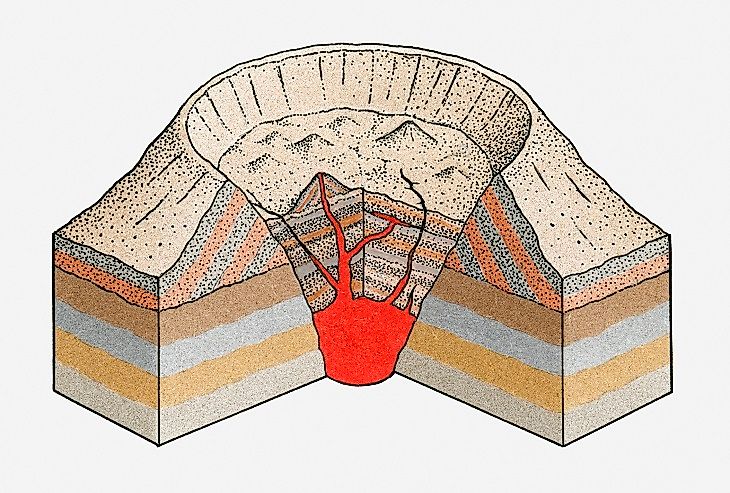
caldera volcano
S waves are also known as what?
Secondary
What are the three different types of stress that occur in the Earth's crust
Tension, Compression, Shearing
What causes earthquakes?
An earthquake is caused by a slip on a fault.
A what is a large tube in the ground that connects the magma chamber to the Earth's surface.
Pipe.
shield volcano
What kind of waves arrive at the surface first?
P waves.
Squeezes rock until it folds or breaks
Compression
What is stress that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called what?
Shearing
The huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mount is called a
Caldera.
What are the level areas on a volcano that has been built up over time because of the lave being dried up?
Lava Plateau
Which type of wave travels slower?
P waves or S waves
S waves.
Pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions.
shearing
An instrument that detects earth waves is a what?
Seismometer.
The volcano's along converging oceanic plate boundaries may form a what?
Island Arc.
What is a tall, cone shaped mountains in which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash?
Composite Volcano.
Which waves can travel through both liquids and solids?
P waves.
Pulls on the crust, stretching rock so it becomes thinner in the middle
Tension.
To tell how far an earthquake's epicenter from a seismograph, scientists need to measure the difference between the what?
Arrival of the P waves and S waves.
What provides that force that causes magma to erupt to the surface?
Dissolved gases trapped in the magma causing pressure to rise.
When lava has a high viscosity, it produces ash which all build up around the vent in a steep, coned shaped hill or small mountain.
Cinder Cone volcano.
What is the correct order from first to last, in different types of seismic waves to arrive at a seismograph.
P waves, S waves, Surface Waves.
What is ONE kind of land forms created by compression
Mountain ranges, ocean trenches, and volcanic arcs.