The weakest intermolecular force
What is London dispersion force?
What effect does H-bonding have on the properties of the substance?
Hydrogen bonding leads to substantial increases in the expected boiling point, viscosity, etc.
Draw out Se2 Lewis Dot Structure
What is the VSEPR Shape for Se2
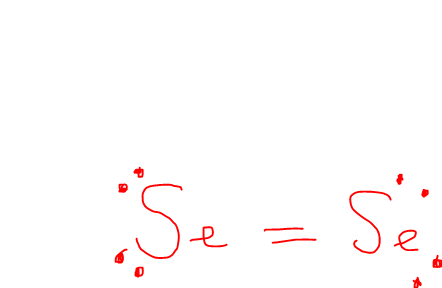 The VSEPR shape is Linear
The VSEPR shape is Linear
When do dipole-dipole forces occur?
Between polar molecules.
This type of molecule is like a couple that always argues over the remote, creating a bit of tension and is always taking opposite sides on any debate
What are polar molecules
A force used to describe when one side of a molecule has a slightly positive charge and the other side has a slightly negative charge.
What are dipole-dipole forces?
The boiling point of CH4 is much lower than that of H2S. This is because:
of dipole-dipole in H2S
Draw out the Lewis Dot Structure of Si2O
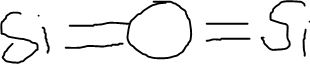
What does VSEPR stand for?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
This is the bond angle in a molecule with a tetrahedral shape, like methane (CH₄).
What is 109.5 degree
This intermolecular force is most like a friendship, where molecules hang out but don't get too close.
What is london dispersion forces
What is 1
Which would have a higher boiling point, HCl or Cl2?
HCl, because it has dipole-dipole interactions, while Cl2 only has London dispersion forces.
The amount of electron domain on HNO
What is 3
Is H2O2 polar or not?
Polar
Will HF mix with CO2?
No
In this molecule, the central atom is surrounded by six friends, making it feel like a party with no room for drama.
What is octahedral
The intermolecular forces exhibit in glycerin
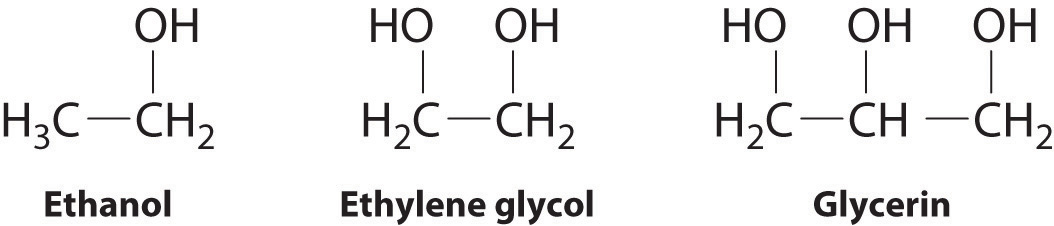
What is hydrogen bonding and dispersion
Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling point: CH4, C2H6, C3H8.
CH4, C2H6, C3H8 (boiling point increases with increasing molecular size and stronger London dispersion forces).
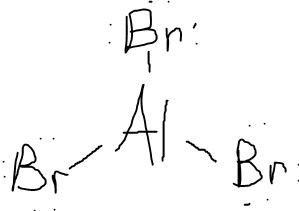
Draw out the Lewis Structure of AlBr3
Draw out and determine the Shape of SiBr4
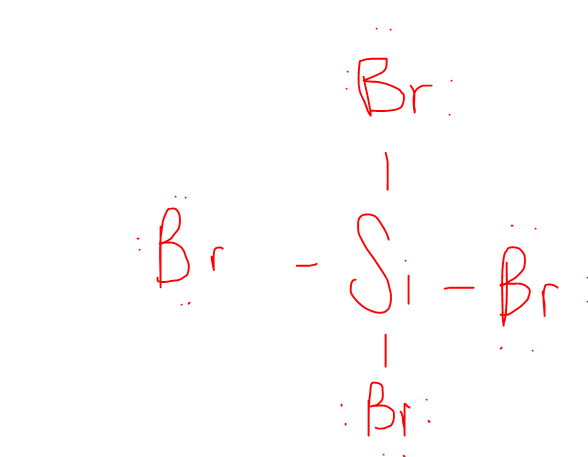 The VSEPR Shape is Tetrahedral / Non-Polar
The VSEPR Shape is Tetrahedral / Non-Polar
Is liquid water more dense than solid ice?
Yes!In ice, water molecules are arranged in a lattice structure due to hydrogen bonding, which takes up more space and makes ice less dense than liquid water.
In a molecular party, this type of guest takes up more space and causes everyone to feel a little squished...double bond, single bond or lone pairs
What happens to state (liquid,solid, gas) molecules as the intermolecular forces increase?
The stronger the intermolecular forces, the more likely to be in liquid and solid states.
Between SiO2 and SO2, which would have stronger intermolecular forces and why?
SO2, because it is polar and exhibits dipole-dipole interactions, whereas SiO2 is nonpolar and only has London dispersion forces.
The lewis structure of CH3CH2NCH3CH3
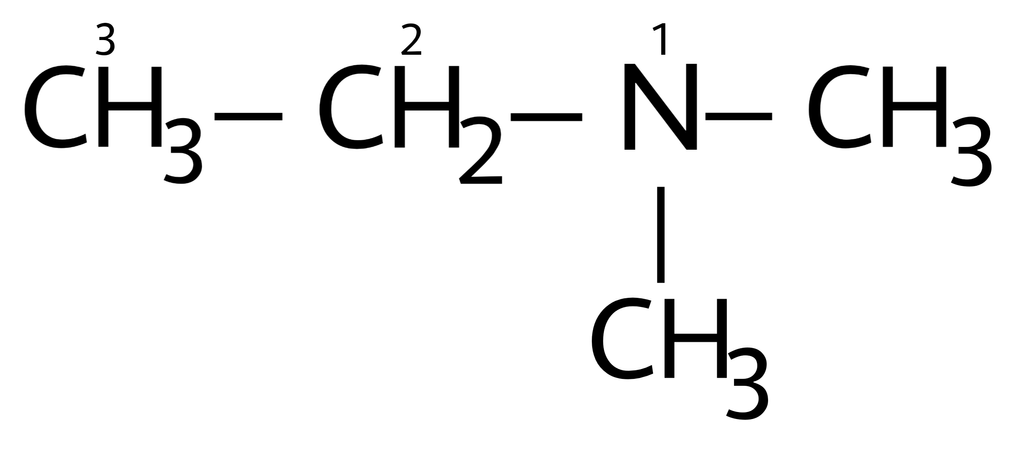
What is the VSEPR Shape of SCl2?
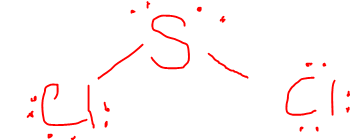 The VSEPR Shape is Angular/Bent / Polar
The VSEPR Shape is Angular/Bent / Polar
Arrange these molecules in order from largest to smallest bond angle: H₂O, CH₄, NH₃.
What is CH₄ (109.5°), NH₃ (107°), and H₂O (104.5°)?
In scenario of chocolate chips in a cookie and a glass of milk. What is the intermolecular force and what is the intramolecular force?
Intermolecular force: cookie and milk
Intramolecular force: chocolate chips in a cookie